Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
 B5638 ACHPSummary: IκB kinase inhibitor
B5638 ACHPSummary: IκB kinase inhibitor -
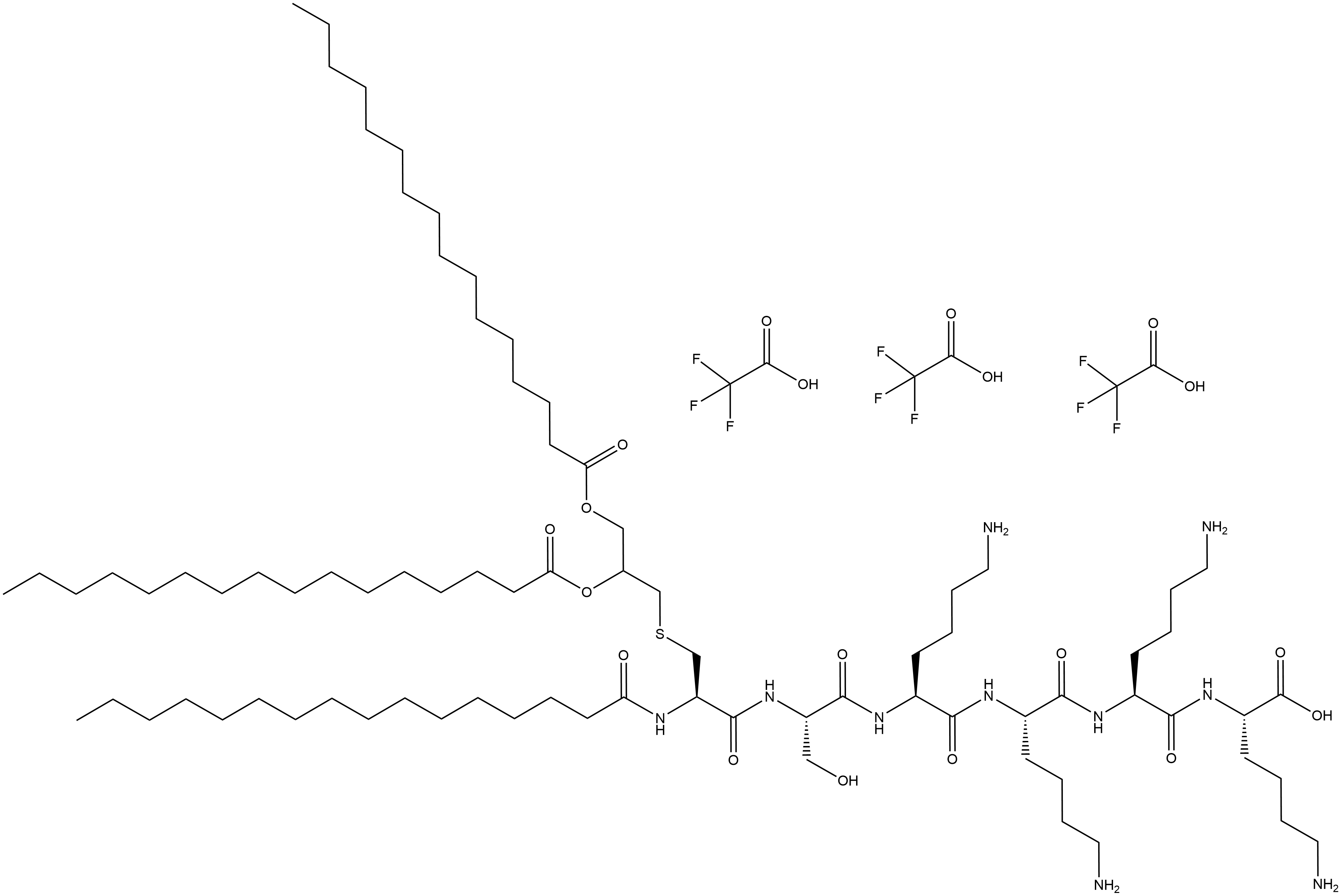 B5662 Pam3CSK4 TFASummary: A toll-like receptor 1/2 (TLR1/2) agonist
B5662 Pam3CSK4 TFASummary: A toll-like receptor 1/2 (TLR1/2) agonist -
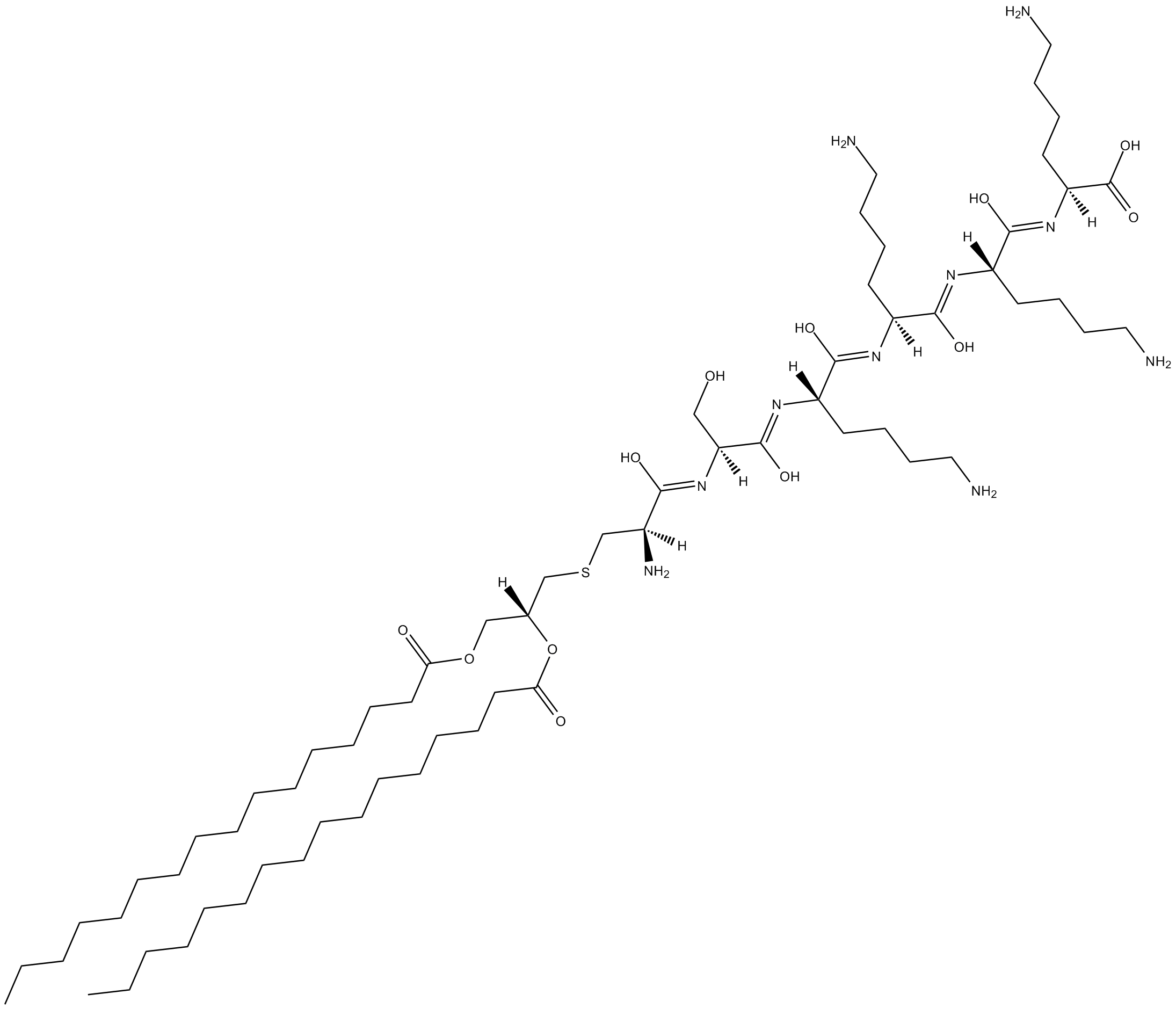 B5665 Pam2CSK4Summary: toll-like receptor 2/6 (TLR2/6) agonist
B5665 Pam2CSK4Summary: toll-like receptor 2/6 (TLR2/6) agonist -
 B5721 TAT 14Summary: Nrf2 activator
B5721 TAT 14Summary: Nrf2 activator -
 B1046 HPGDS inhibitor 1Summary: HPGDS inhibitor
B1046 HPGDS inhibitor 1Summary: HPGDS inhibitor -
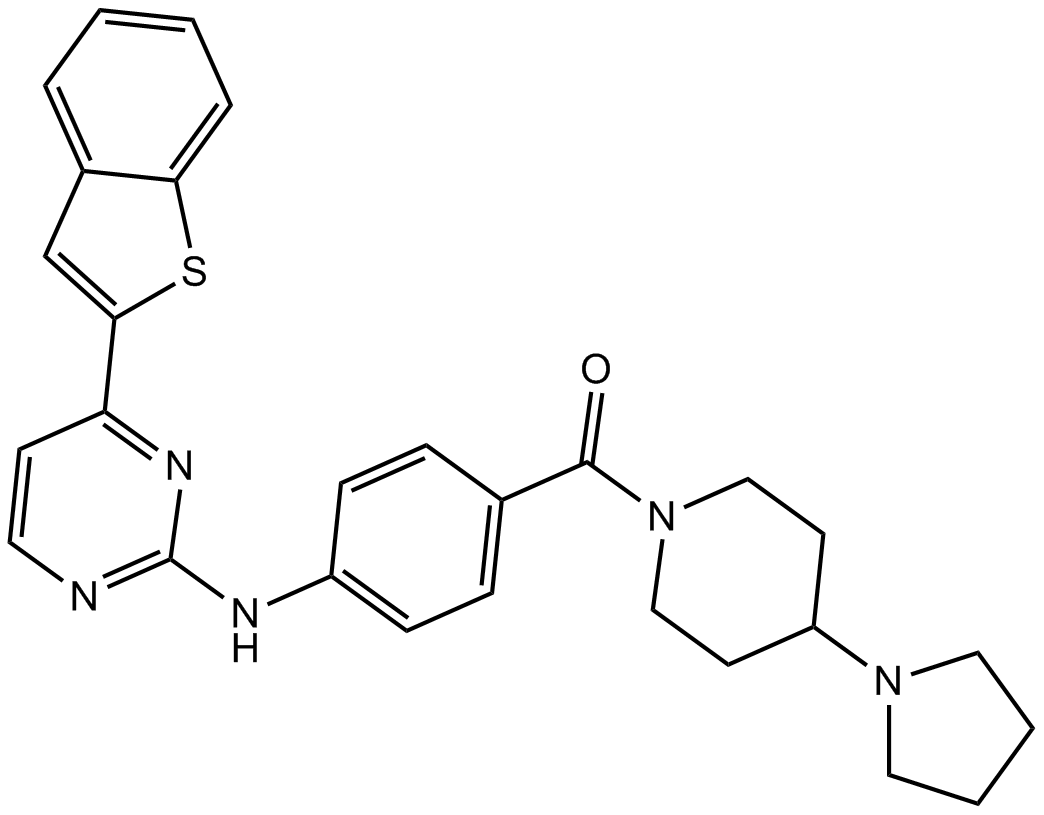 B1586 IKK-16 (IKK Inhibitor VII)1 CitationSummary: Selective IκB kinase inhibitor
B1586 IKK-16 (IKK Inhibitor VII)1 CitationSummary: Selective IκB kinase inhibitor -
![egg white lysozyme (19-36) [Gallus gallus]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1065.png) A1065 egg white lysozyme (19-36) [Gallus gallus]Summary: Dissolution of cell wall
A1065 egg white lysozyme (19-36) [Gallus gallus]Summary: Dissolution of cell wall -
![ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1069.png) A1069 ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]Summary: Ferritin heavy chain fragment
A1069 ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]Summary: Ferritin heavy chain fragment -
![IgG light chain variable region [Homo sapiens]/IgM/kappa antibody [Mus musculus]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1070.png) A1070 IgG light chain variable region [Homo sapiens]/IgM/kappa antibody [Mus musculus]Summary: IgG light chain region
A1070 IgG light chain variable region [Homo sapiens]/IgM/kappa antibody [Mus musculus]Summary: IgG light chain region -
![immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1071.png) A1071 immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Immunoglobulin light chain fragment
A1071 immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Immunoglobulin light chain fragment


