Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
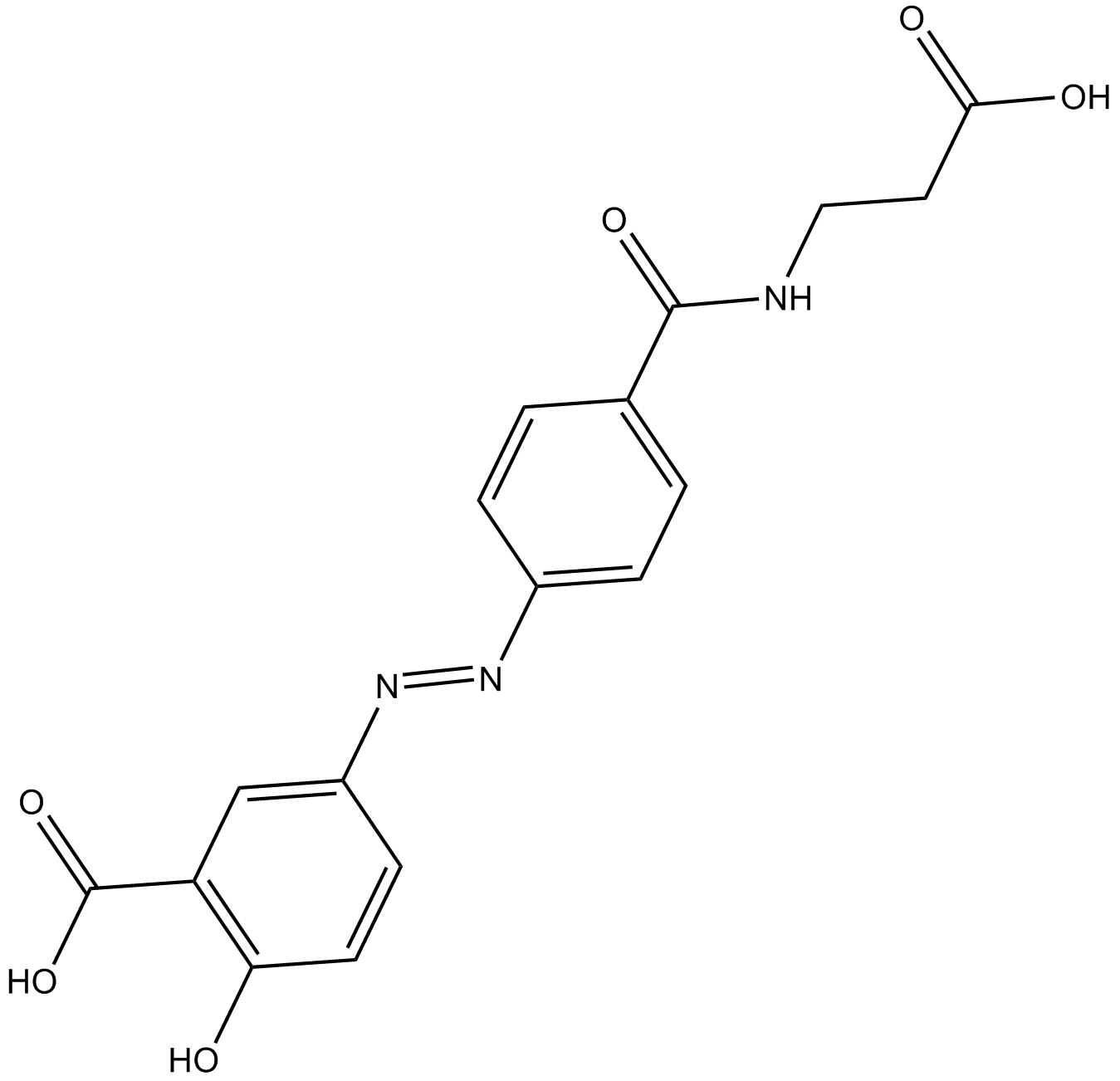 B3460 BalsalazideSummary: anti-inflammatory drug
B3460 BalsalazideSummary: anti-inflammatory drug -
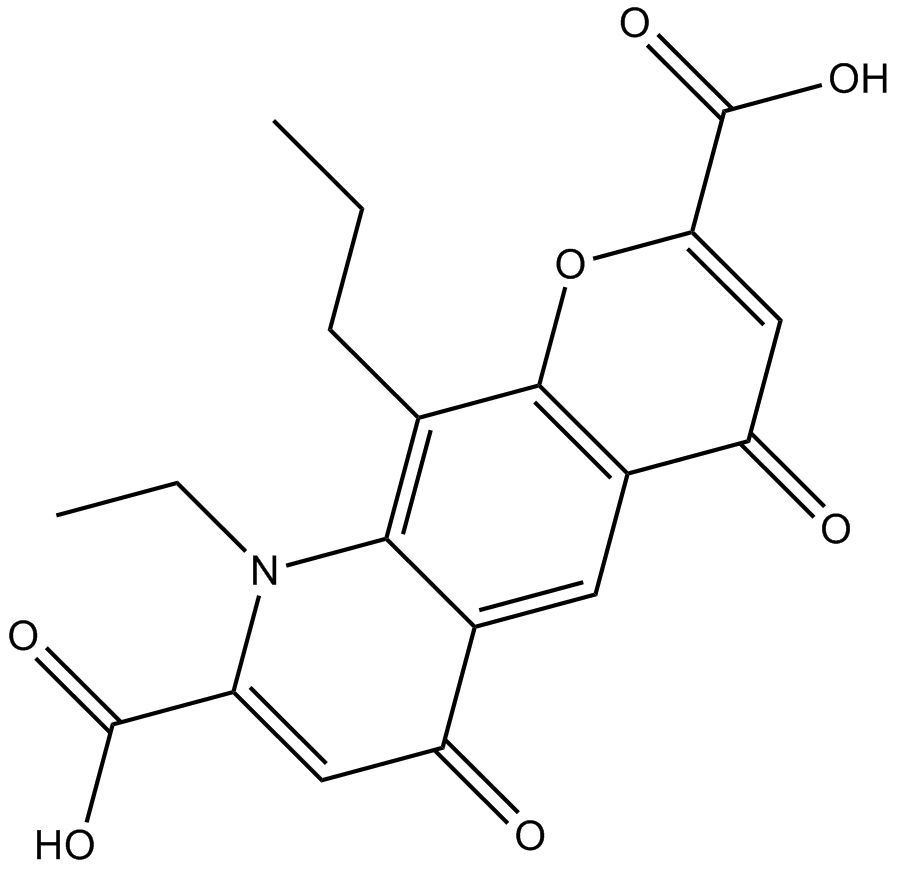 B3578 NedocromilSummary: anti-inflammatory agent
B3578 NedocromilSummary: anti-inflammatory agent -
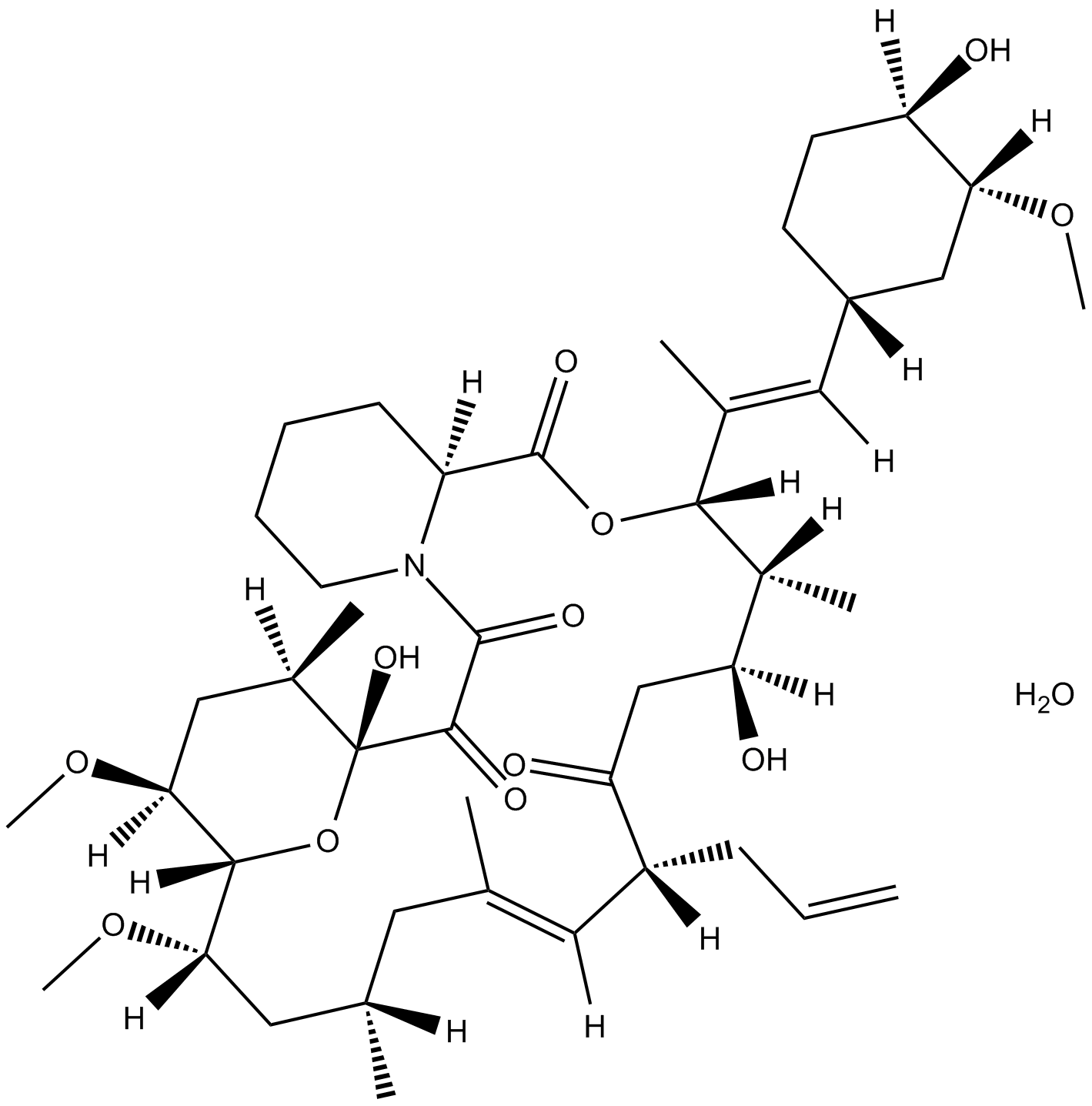 B3579 Tacrolimus monohydrateSummary: immunosuppressive drug
B3579 Tacrolimus monohydrateSummary: immunosuppressive drug -
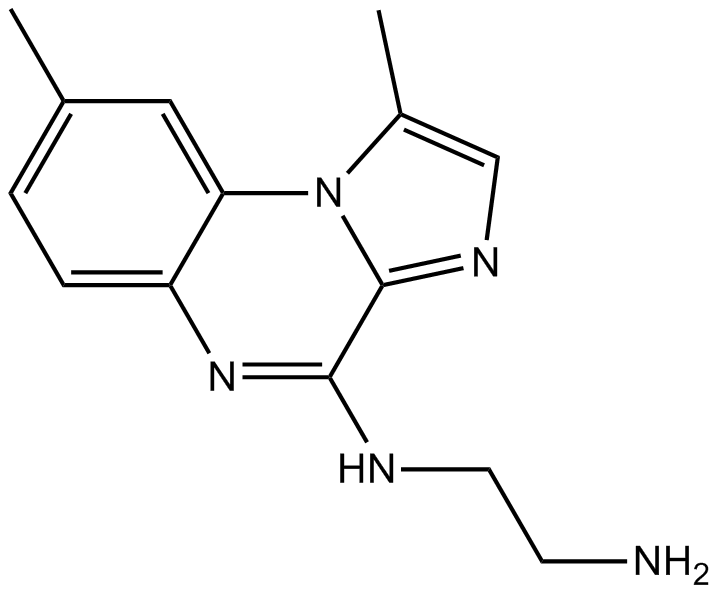 B4655 BMS-345541(free base)Summary: IKK-1/IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective
B4655 BMS-345541(free base)Summary: IKK-1/IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
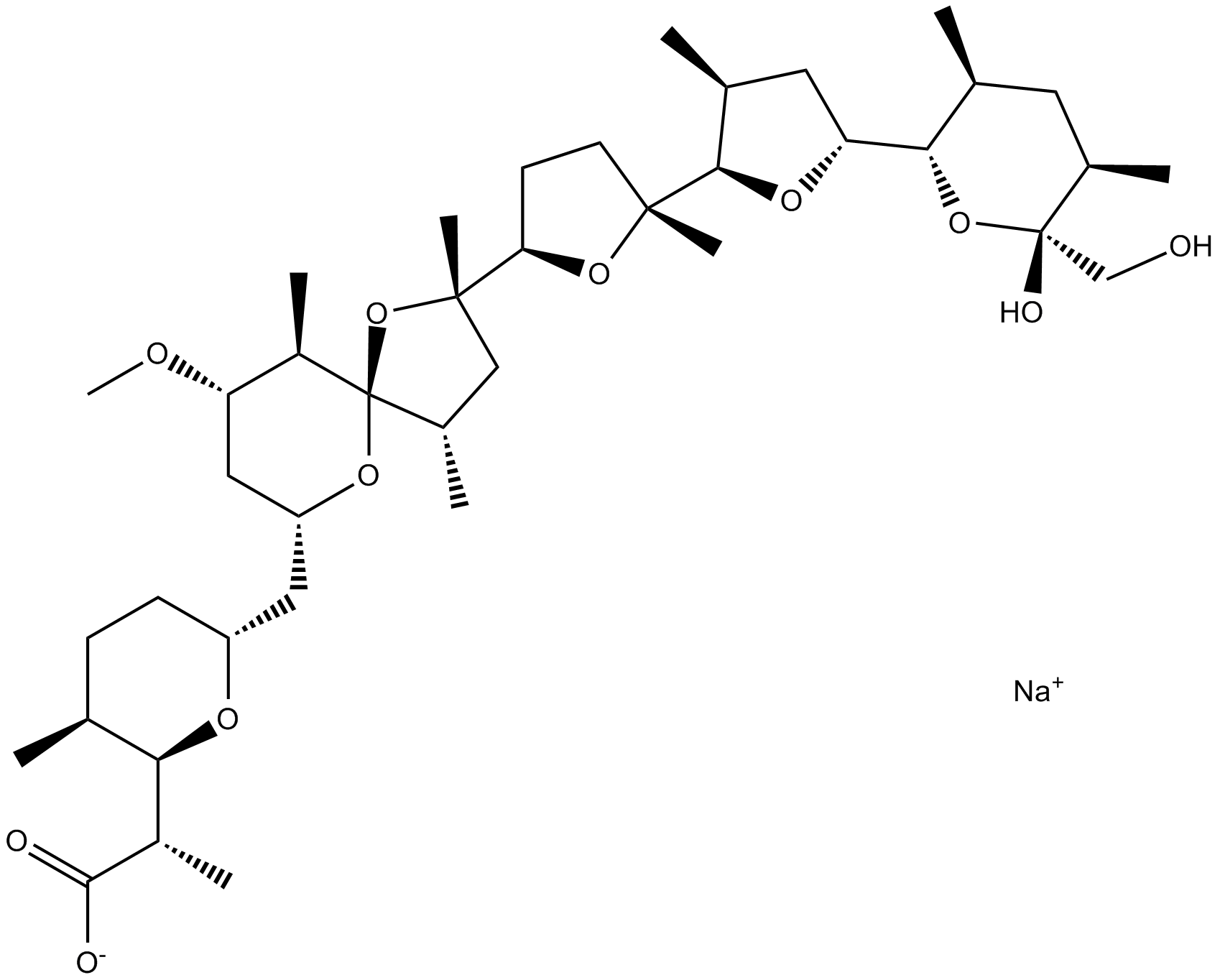 B7644 Nigericin sodium salt8 CitationSummary: ionophore that exchanges K+ for H+ across biological membranes
B7644 Nigericin sodium salt8 CitationSummary: ionophore that exchanges K+ for H+ across biological membranes -
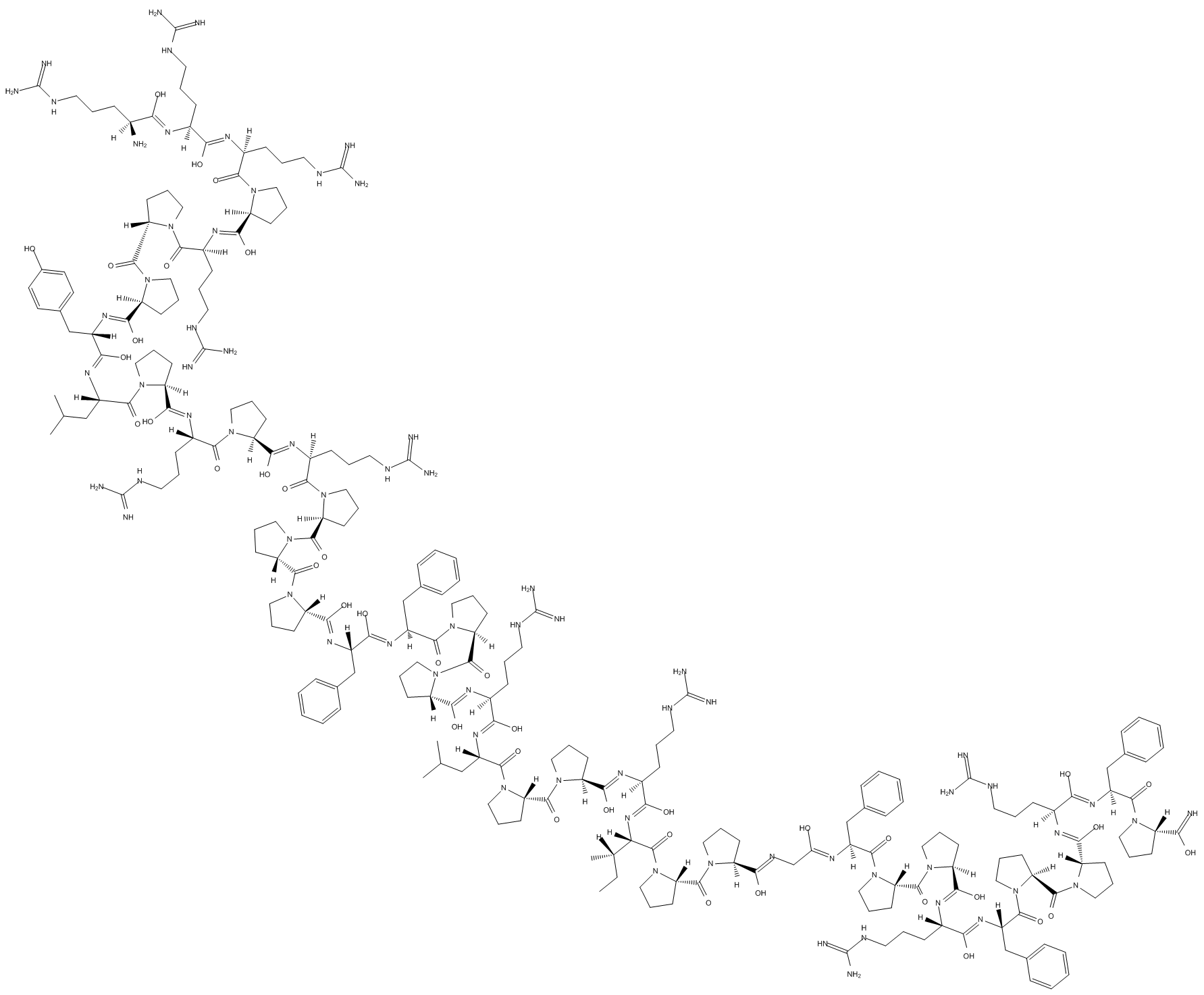 B5241 PR 39 (porcine)Summary: Antibacterial peptide
B5241 PR 39 (porcine)Summary: Antibacterial peptide -
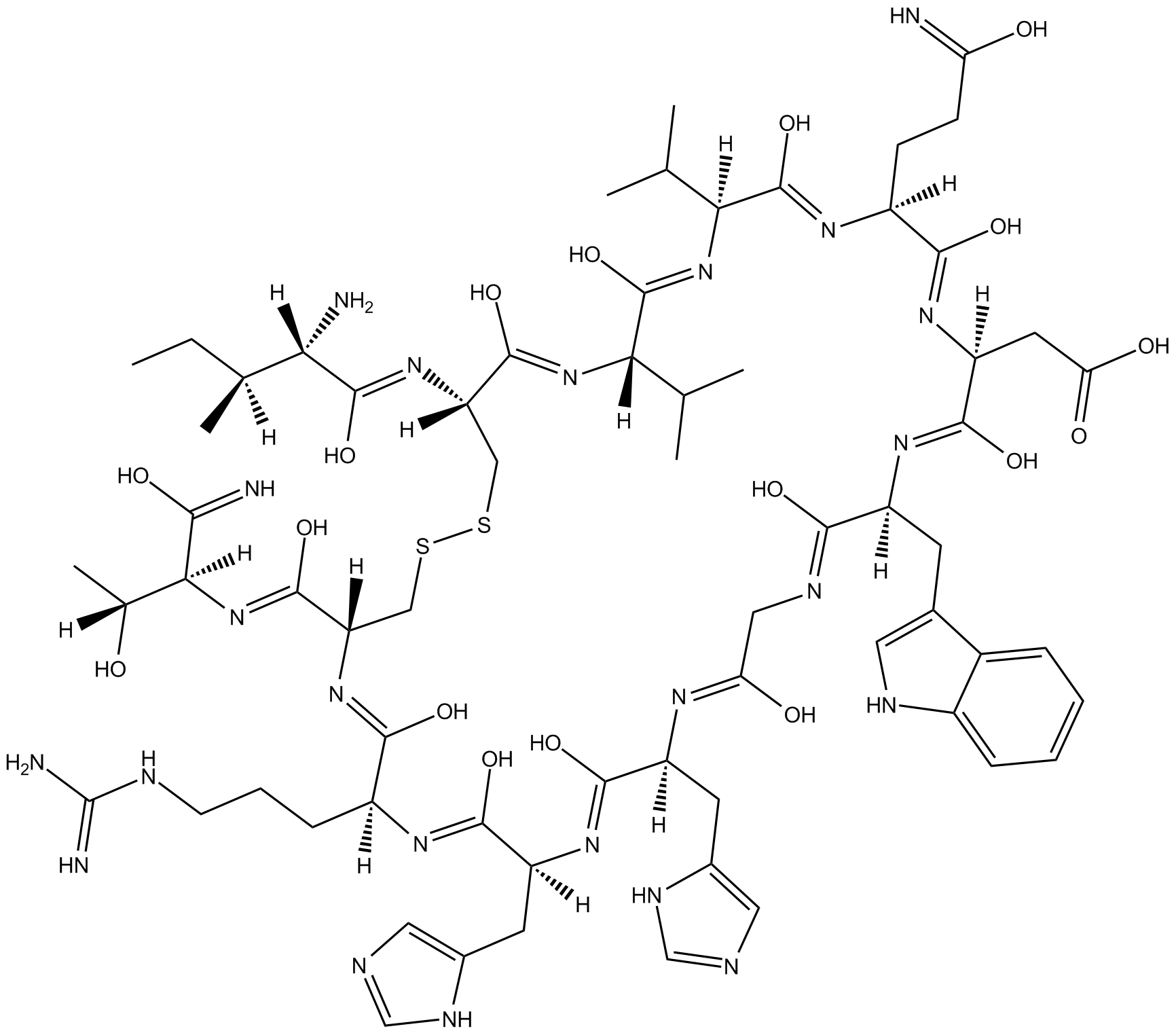 B5319 CompstatinSummary: Complement inhibitor
B5319 CompstatinSummary: Complement inhibitor -
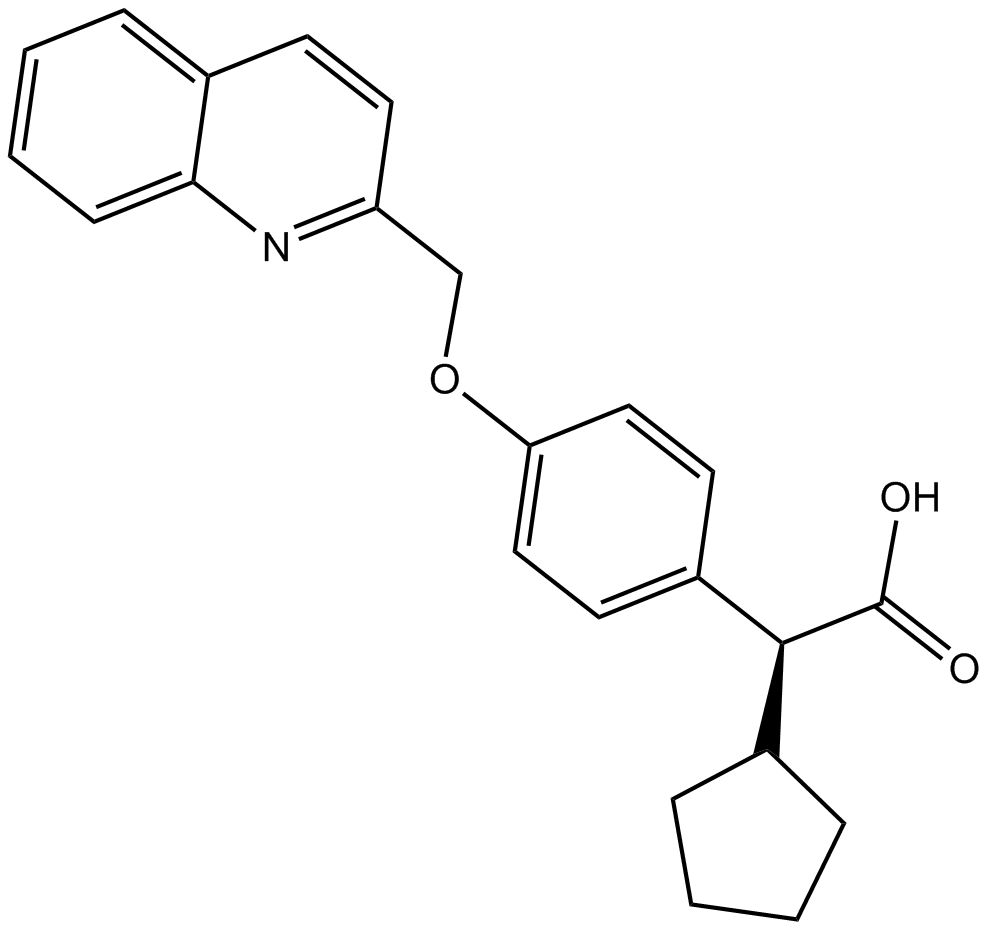 B5447 BAY-X 1005Summary: Potent FLAP inhibitor
B5447 BAY-X 1005Summary: Potent FLAP inhibitor -
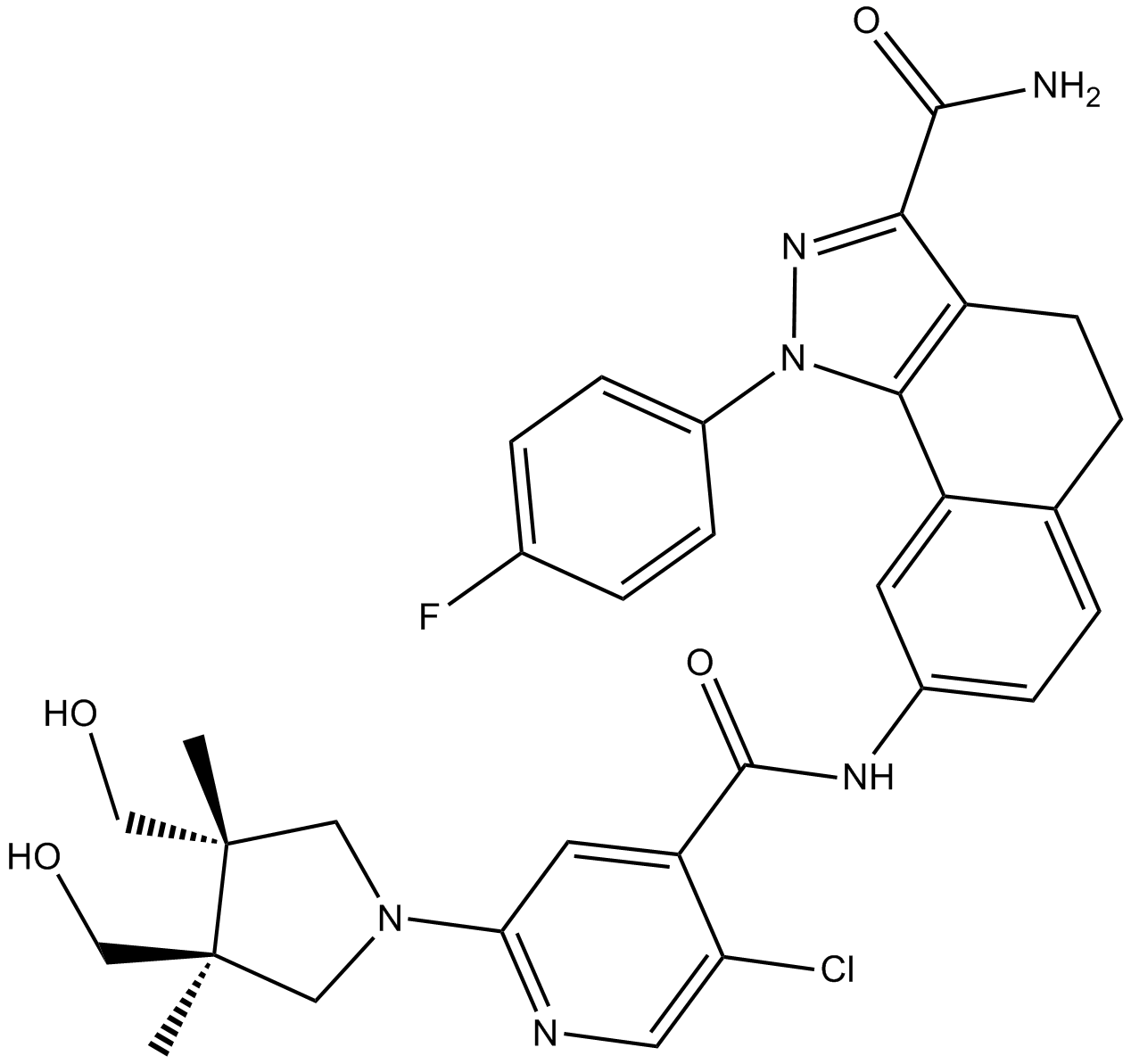 B5543 PF 184Summary: IKKβ inhibitor
B5543 PF 184Summary: IKKβ inhibitor -
 B5576 (±)-CPSI 1306Summary: macrophage inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor
B5576 (±)-CPSI 1306Summary: macrophage inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor


