Endocrinology and Hormones
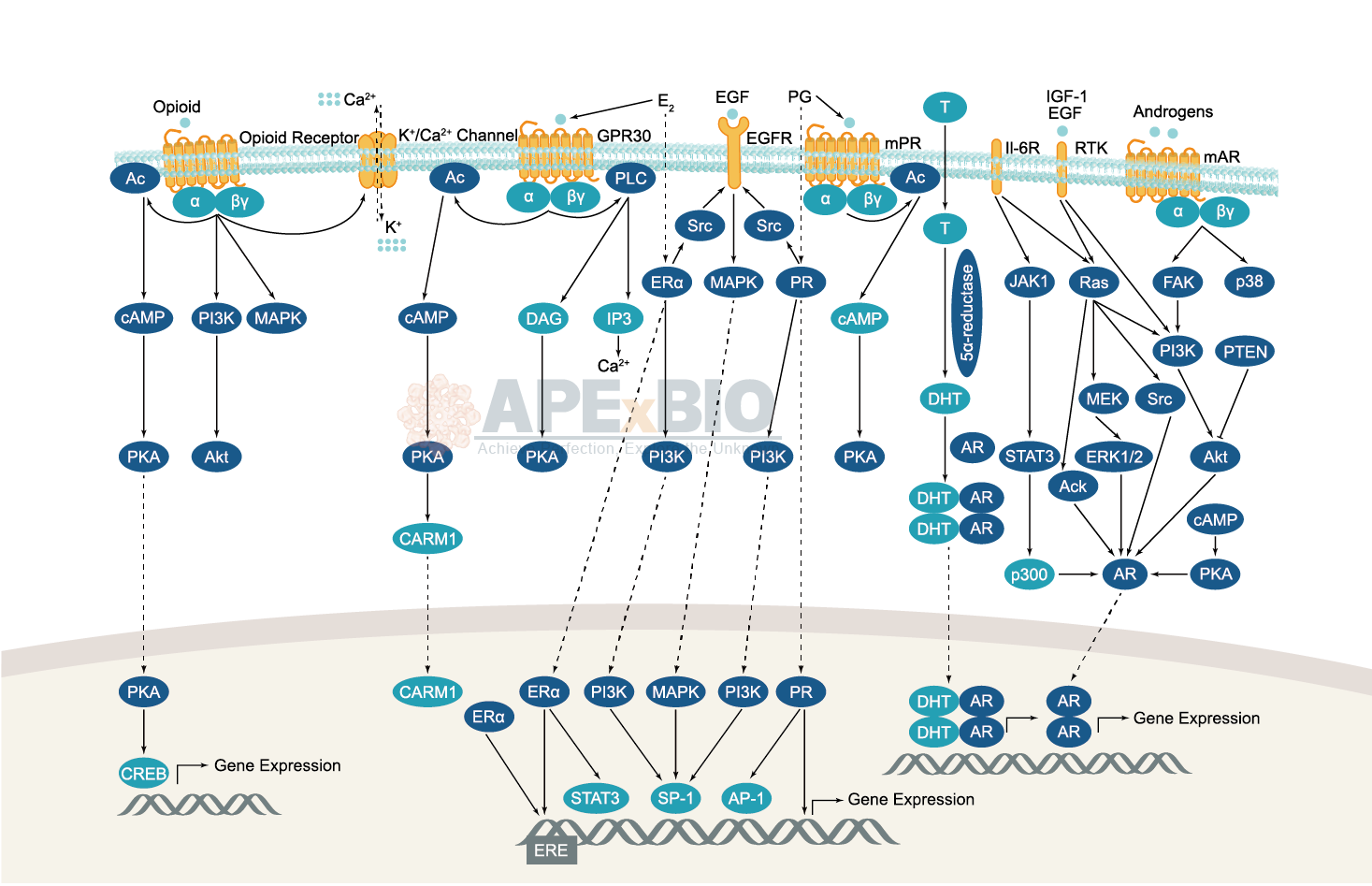

Endocrinology is the study of hormones, their receptors and intracellular signaling pathways, as well as the related diseases. The endocrine system functions can be broadly classified into several categories, including reproduction and sexual differentiation, development and growth, maintenance of the internal environment, and regulation of metabolism/nutrient supply.
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
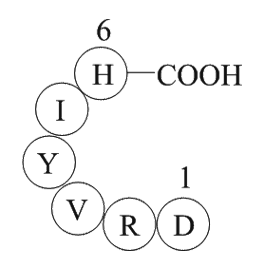 A1048 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1048 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
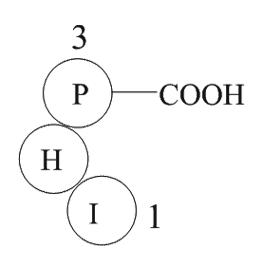 A1049 Angiotensin 1/2 (5-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1049 Angiotensin 1/2 (5-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
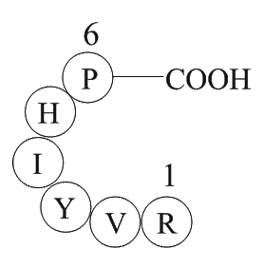 A1050 Angiotensin 1/2 (2-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1050 Angiotensin 1/2 (2-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
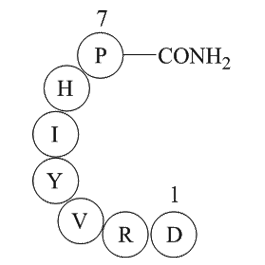 A1054 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-7) amideSummary: Vasoconstrictor
A1054 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-7) amideSummary: Vasoconstrictor -
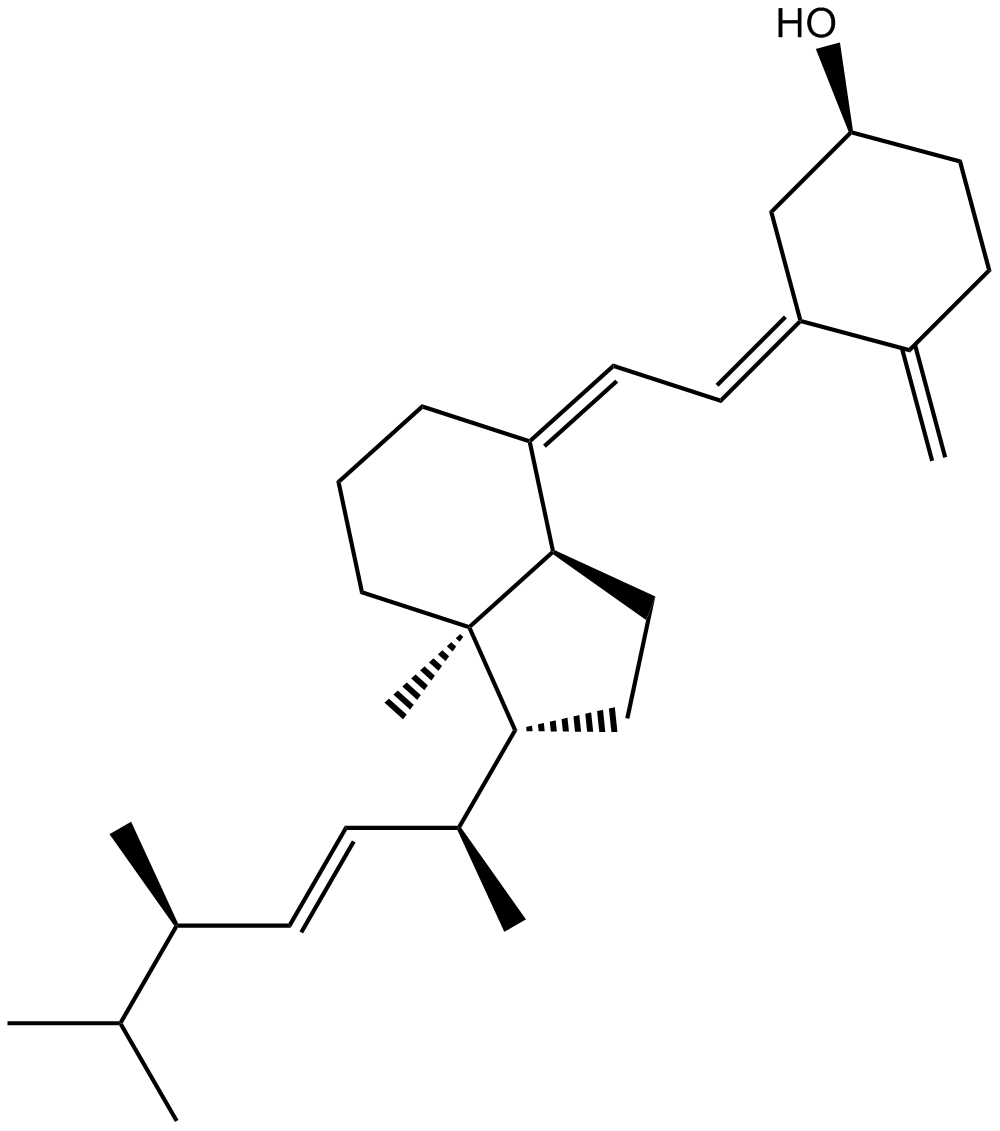 A8543 Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol)Summary: DNA Polymerase inhibitor
A8543 Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol)Summary: DNA Polymerase inhibitor -
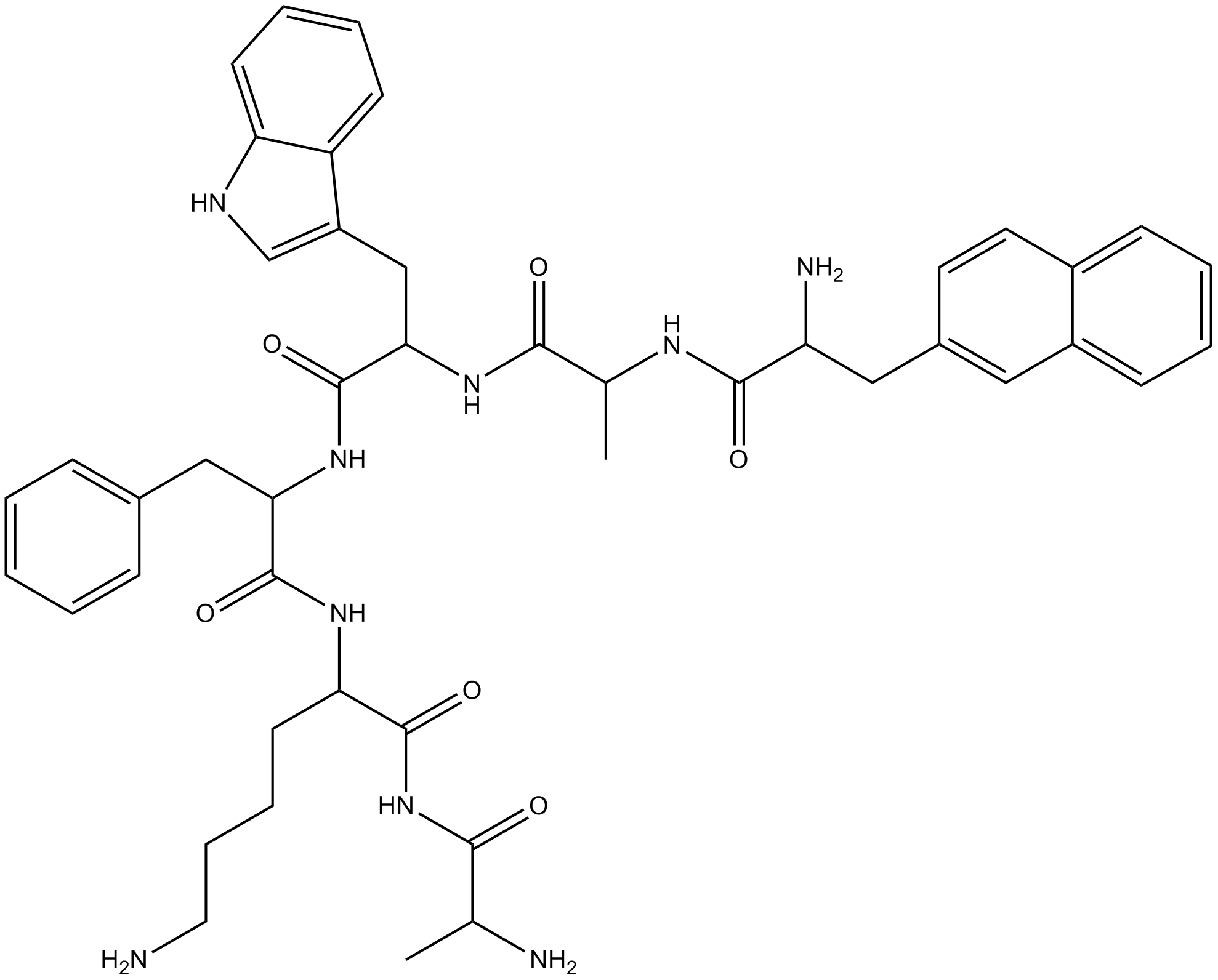 C6443 GHRP-2
C6443 GHRP-2 -
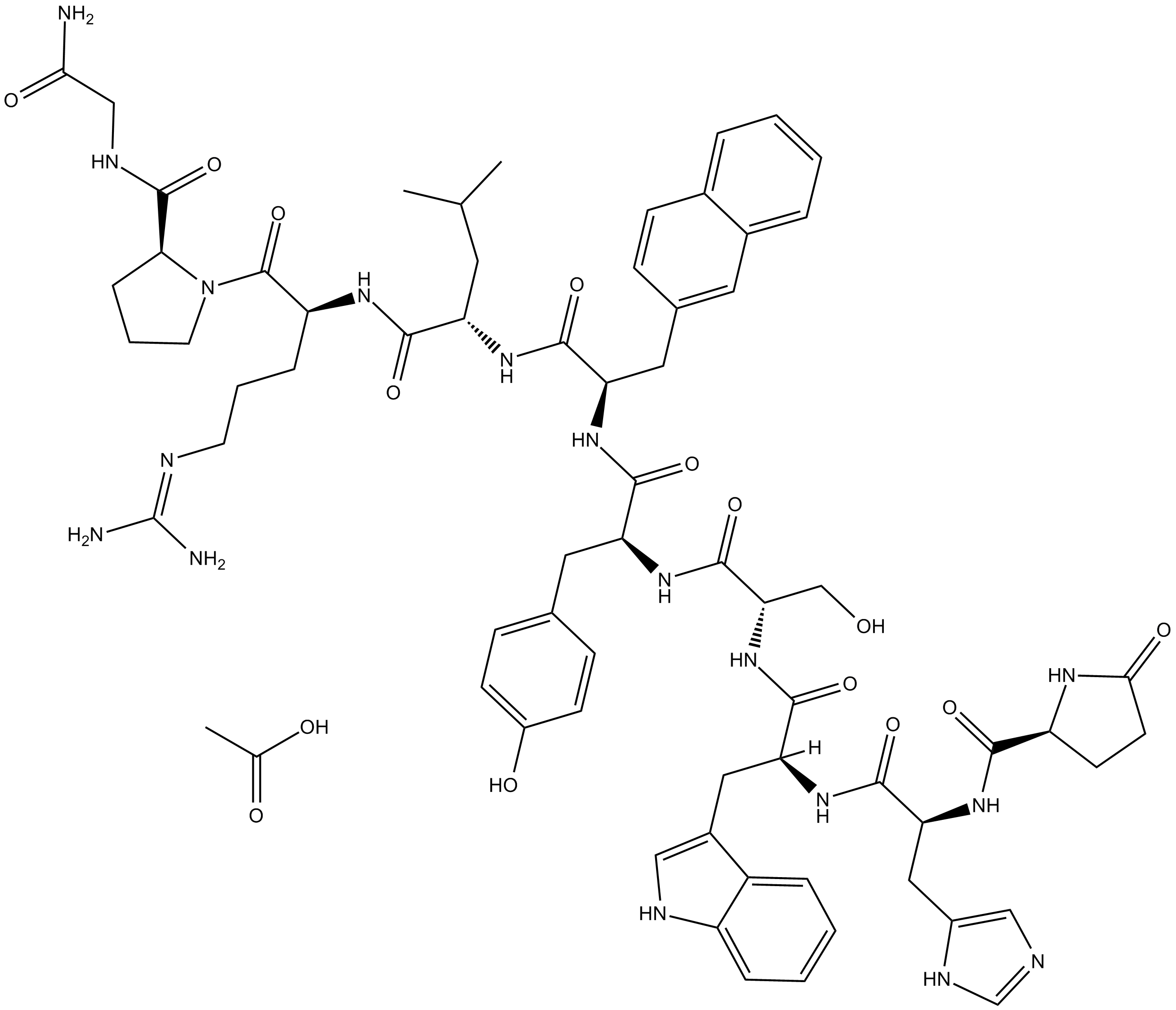 C6444 Nafarelin Acetate
C6444 Nafarelin Acetate -
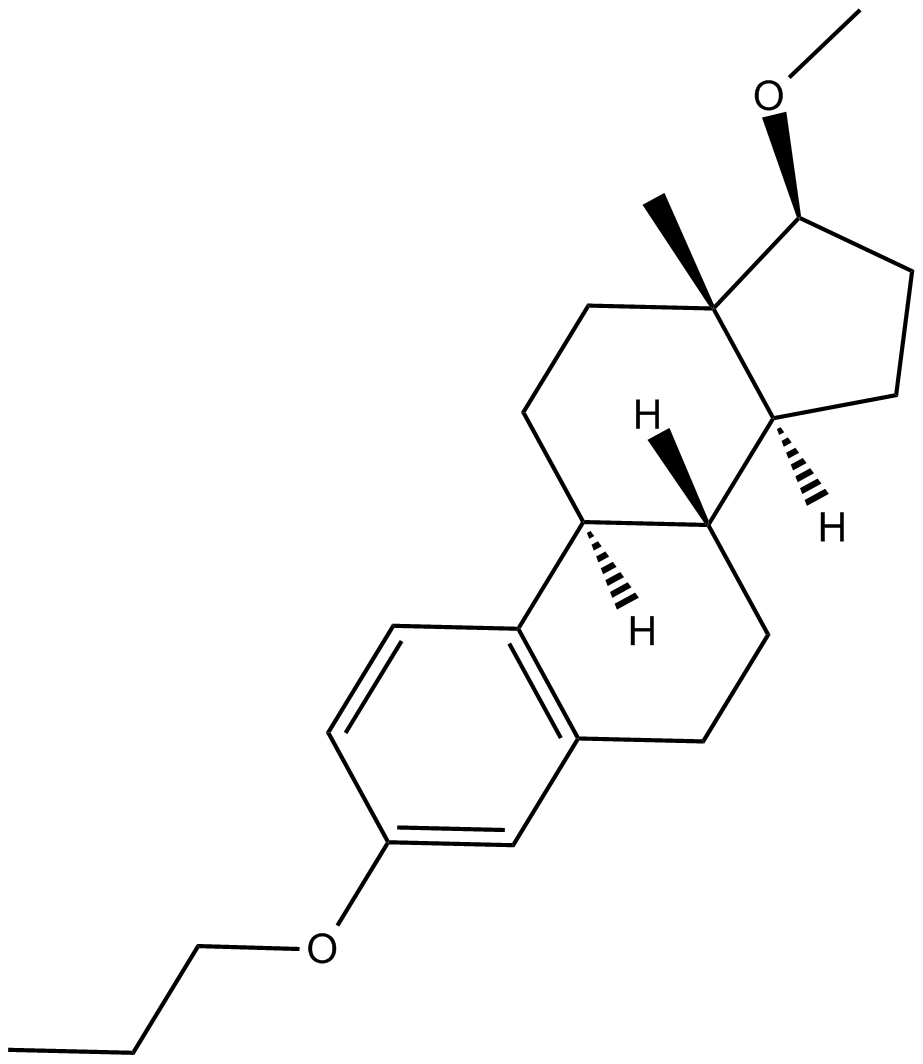 C6450 Promestriene
C6450 Promestriene -
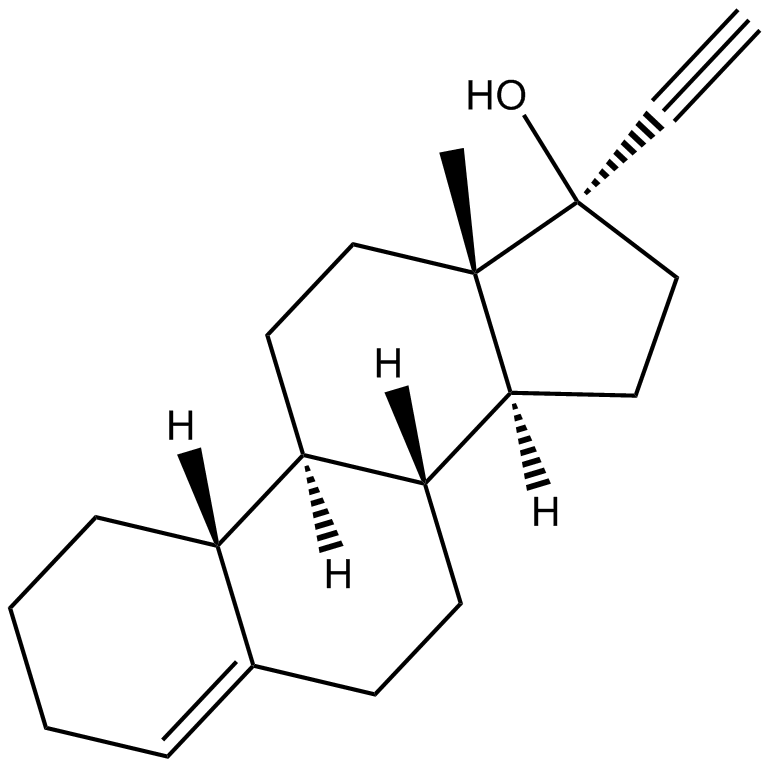 C6488 Lynestrenol
C6488 Lynestrenol -
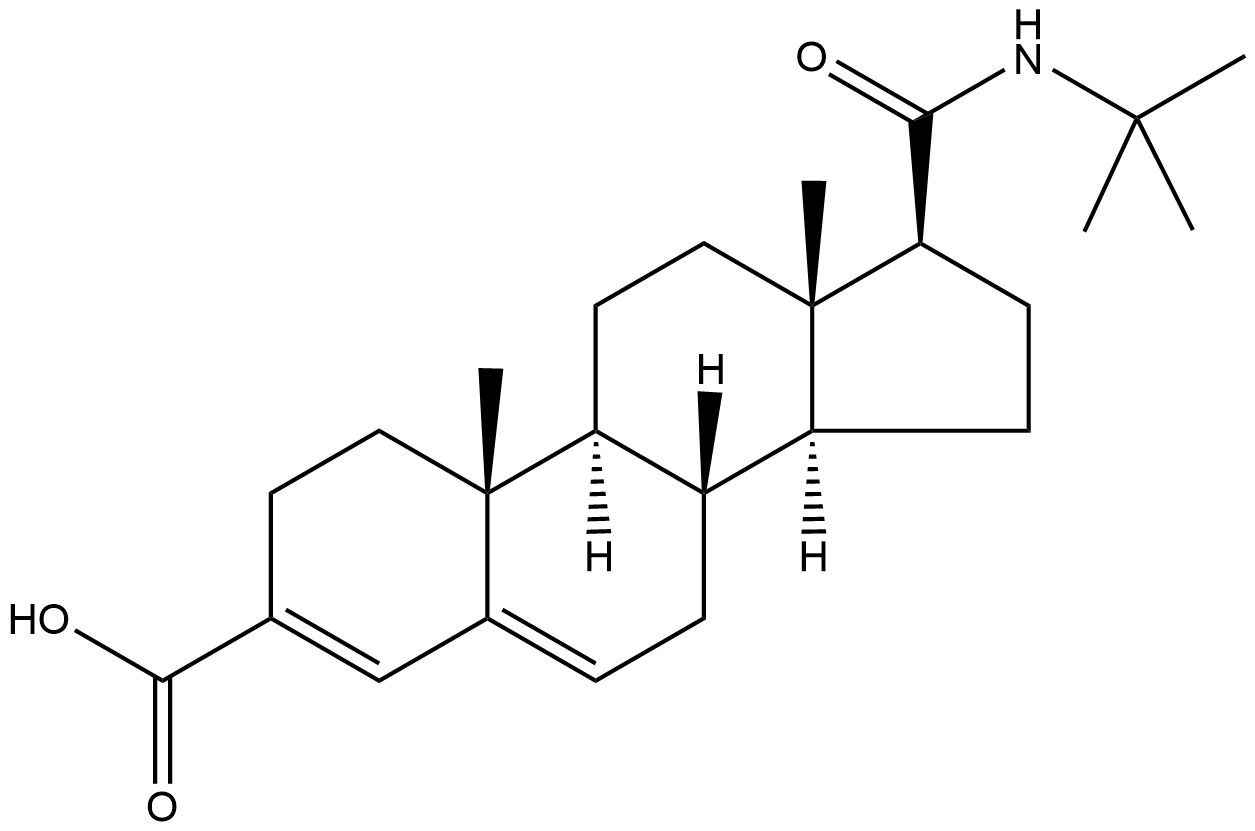 A9049 Epristeride
A9049 Epristeride


