Cell Cycle/Checkpoint
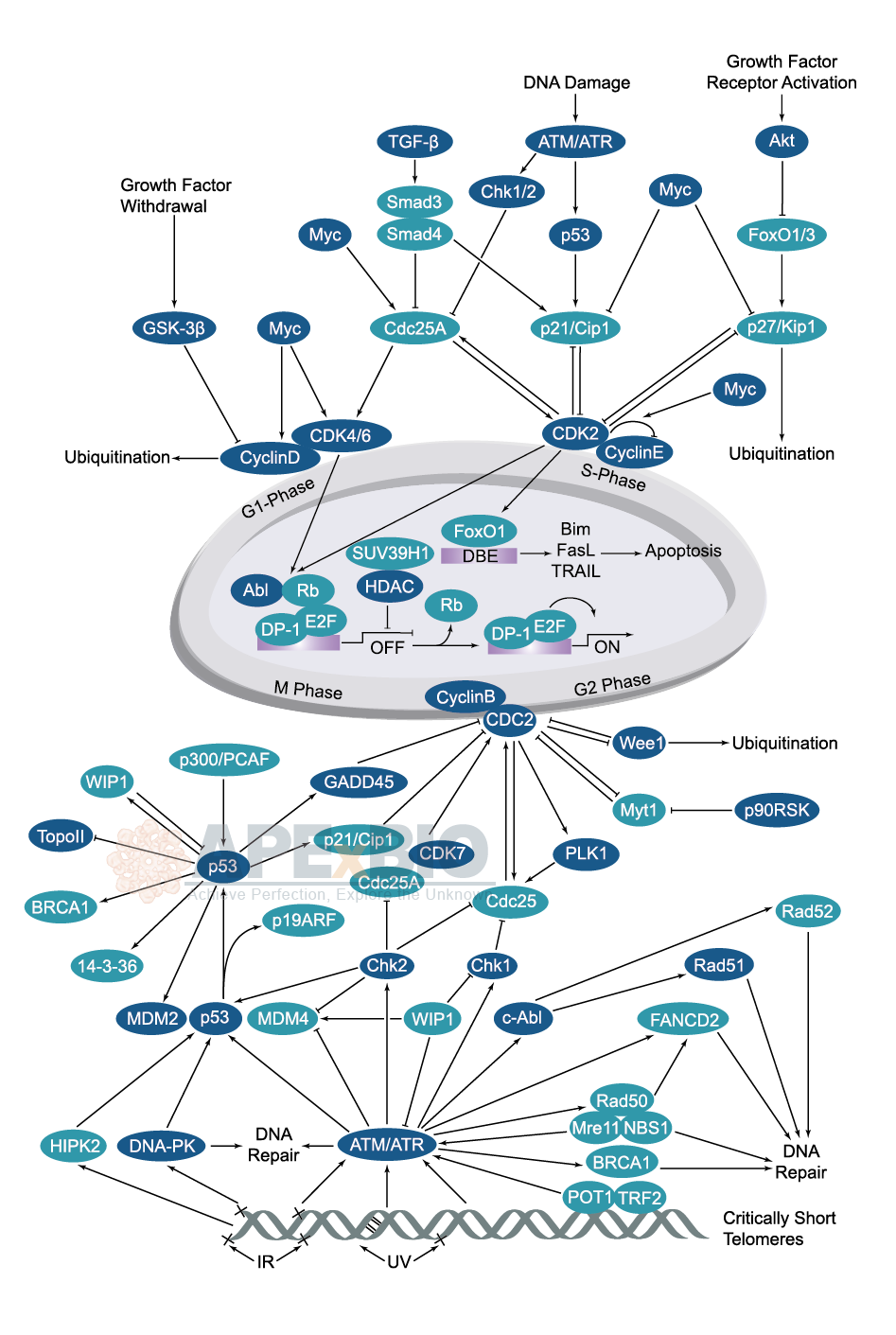

The cell cycle is consisted of 4 main phases: Gap 1 (G1), DNA replication (S), Gap 2 (G2), and mitosis (M). There are “checkpoints” mechanism regulates the transition between these phases, at the G1/S boundary, in the S-phase and during G2/M phases. Cell can only pass through these checkpoints when signaling factors are activated and free of DNA damage. Important proteins that control cell cycle events and checkpoints are cullins, cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), p53 and their inhibitors etc. Cdks family (Cdk2, Cdk3, Cdk4 and Cdk6) are Ser/Thr kinases that regulate cell cycle progression in association with cyclin binding partners (cyclin D, cyclin E and cyclin A) during all four phases. p53 halts the cell cycle if the DNA is damaged and allowing time for DNA repair to progress; it can also initiate apoptosis if DNA damage is too severe to be repaired.
-
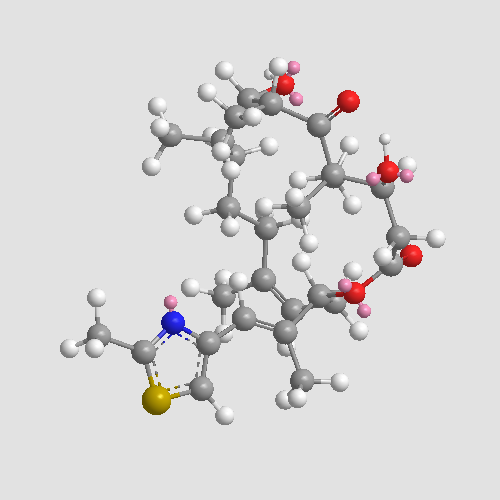 A3394 Epothilone DTarget: Microtubule/TubulinSummary: Natural polyketide compound
A3394 Epothilone DTarget: Microtubule/TubulinSummary: Natural polyketide compound -
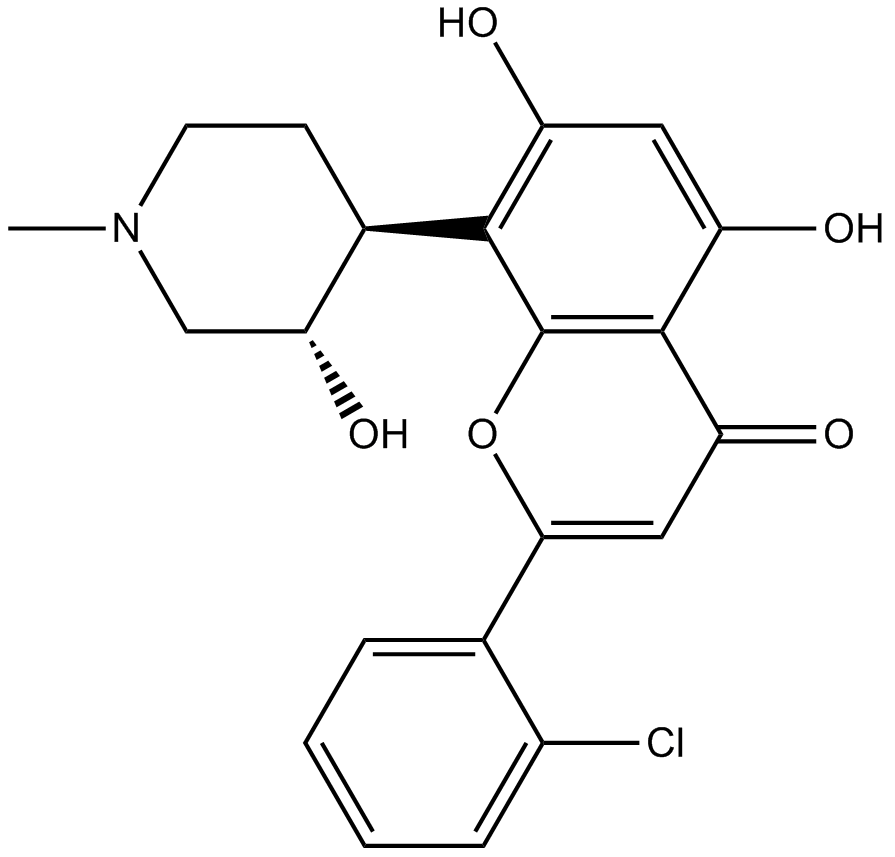 A3417 FlavopiridolTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: Pan-cdk inhibitor
A3417 FlavopiridolTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: Pan-cdk inhibitor -
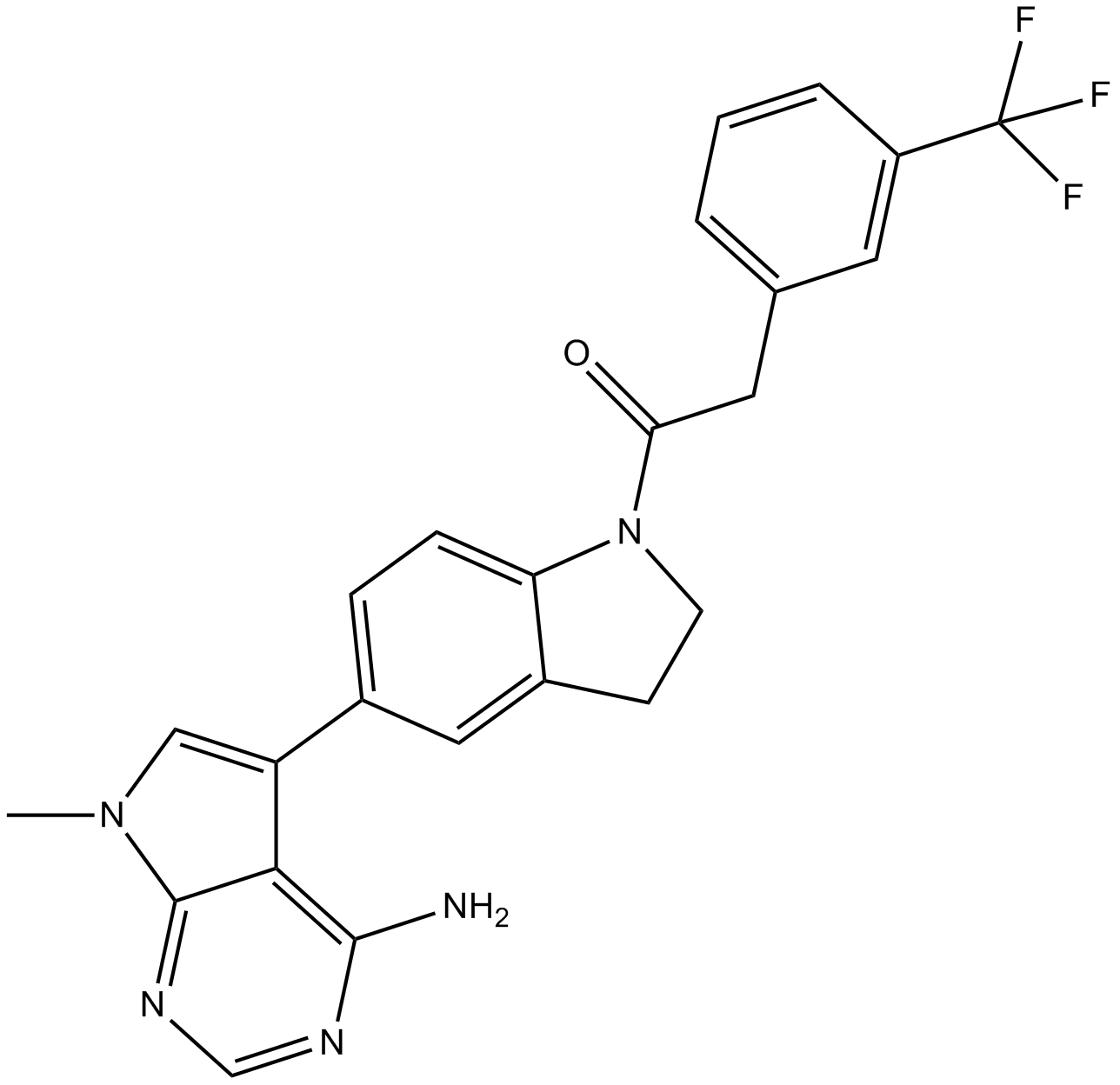 A3448 GSK260641413 CitationSummary: PERK inhibitor,potent and selective
A3448 GSK260641413 CitationSummary: PERK inhibitor,potent and selective -
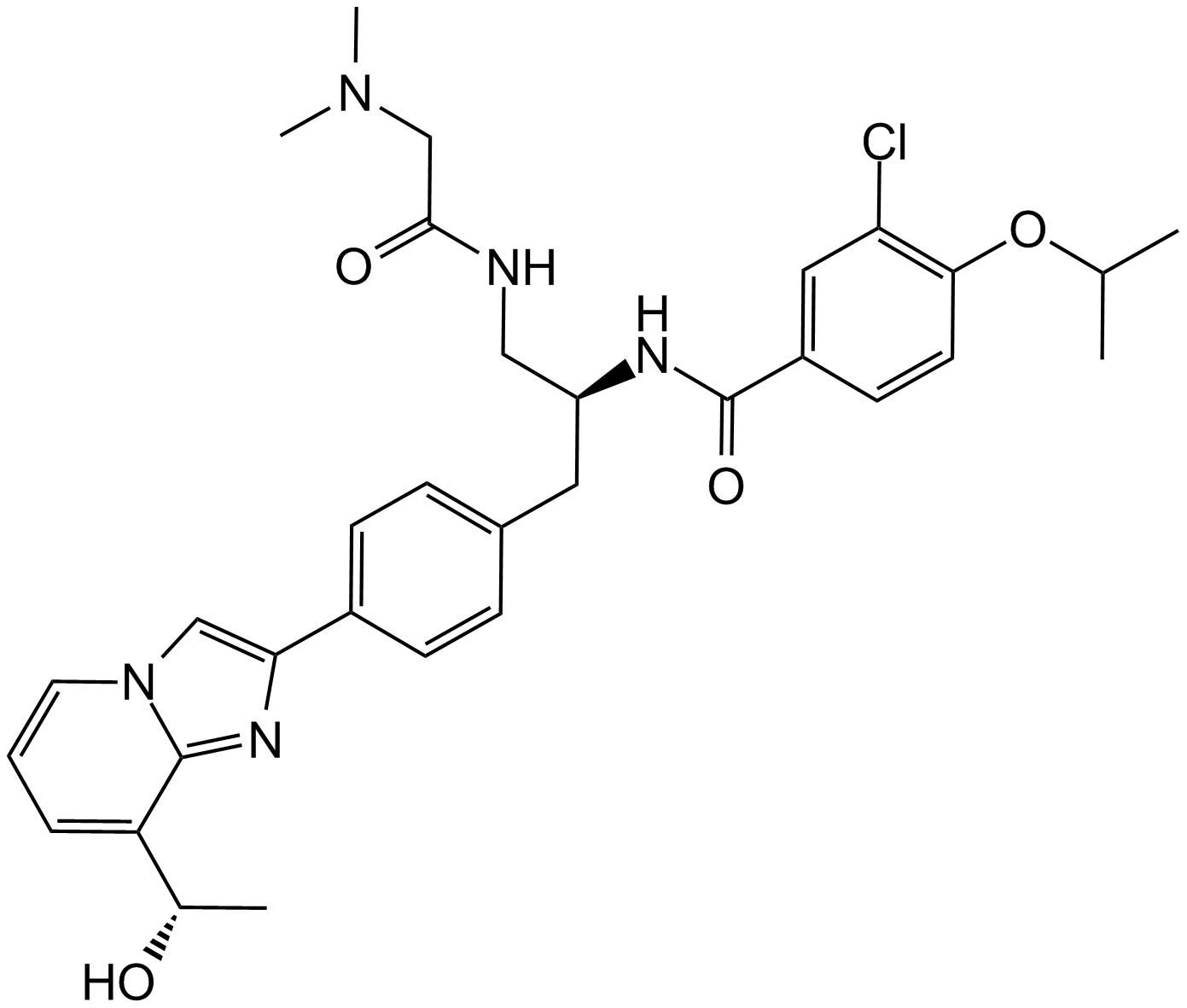 A3450 GSK-9232953 CitationSummary: CENP-E inhibitor,small-molecule
A3450 GSK-9232953 CitationSummary: CENP-E inhibitor,small-molecule -
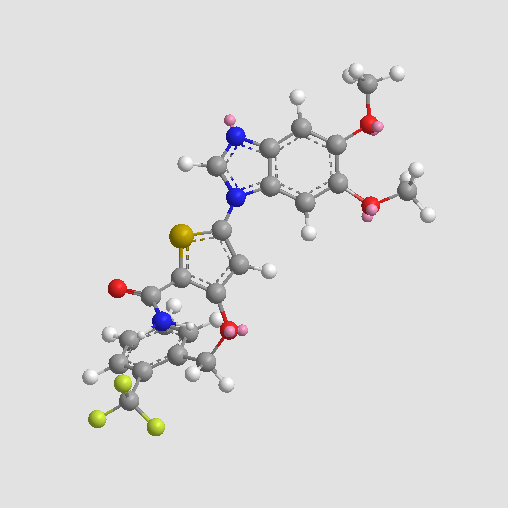 A3456 GW843682XSummary: PLK1/PLK3 inhibitor,potent and selective
A3456 GW843682XSummary: PLK1/PLK3 inhibitor,potent and selective -
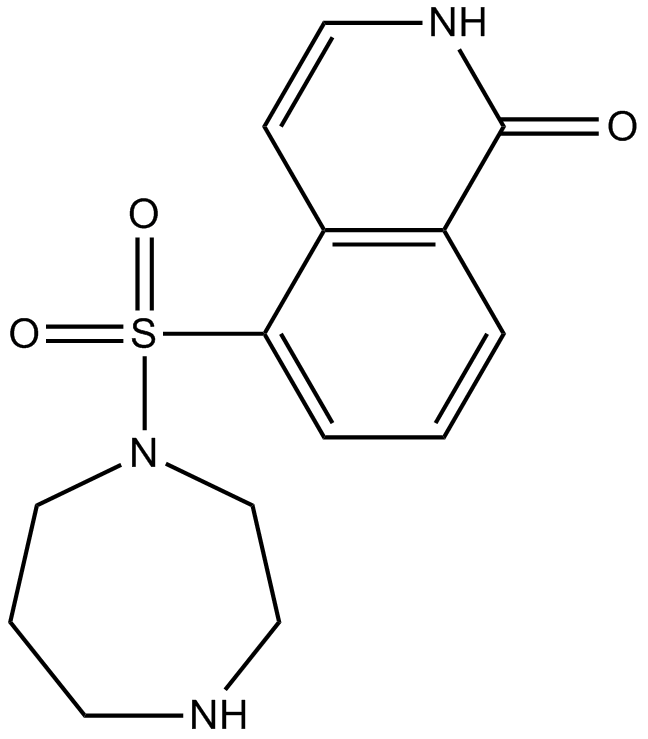 A3478 HydroxyfasudilTarget: ROCK|Rho-kinaseSummary: Rho-kinase inhibitor and vasodilator
A3478 HydroxyfasudilTarget: ROCK|Rho-kinaseSummary: Rho-kinase inhibitor and vasodilator -
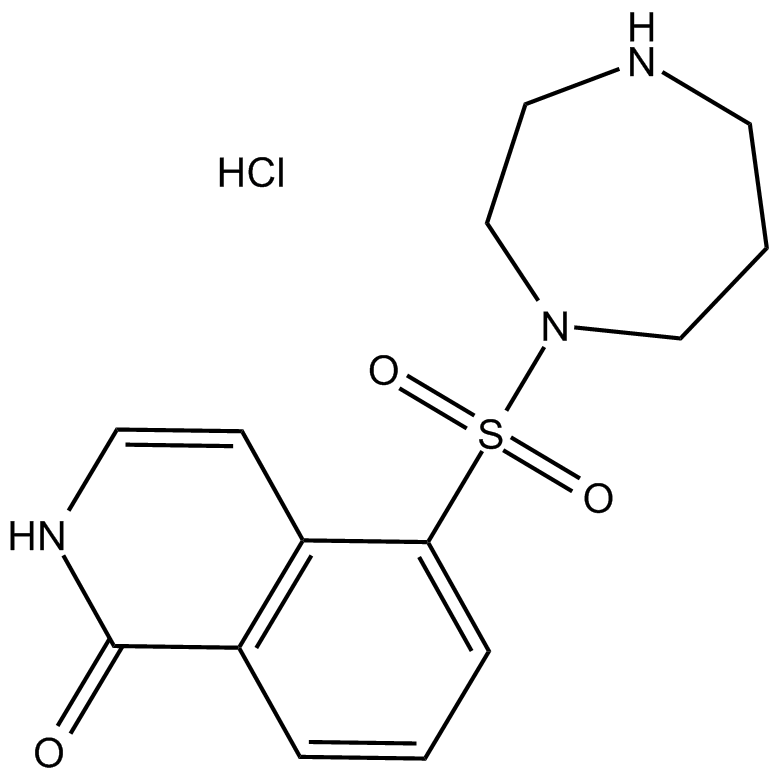 A3479 Hydroxyfasudil hydrochlorideSummary: Rho-kinase inhibitor and vasodilator
A3479 Hydroxyfasudil hydrochlorideSummary: Rho-kinase inhibitor and vasodilator -
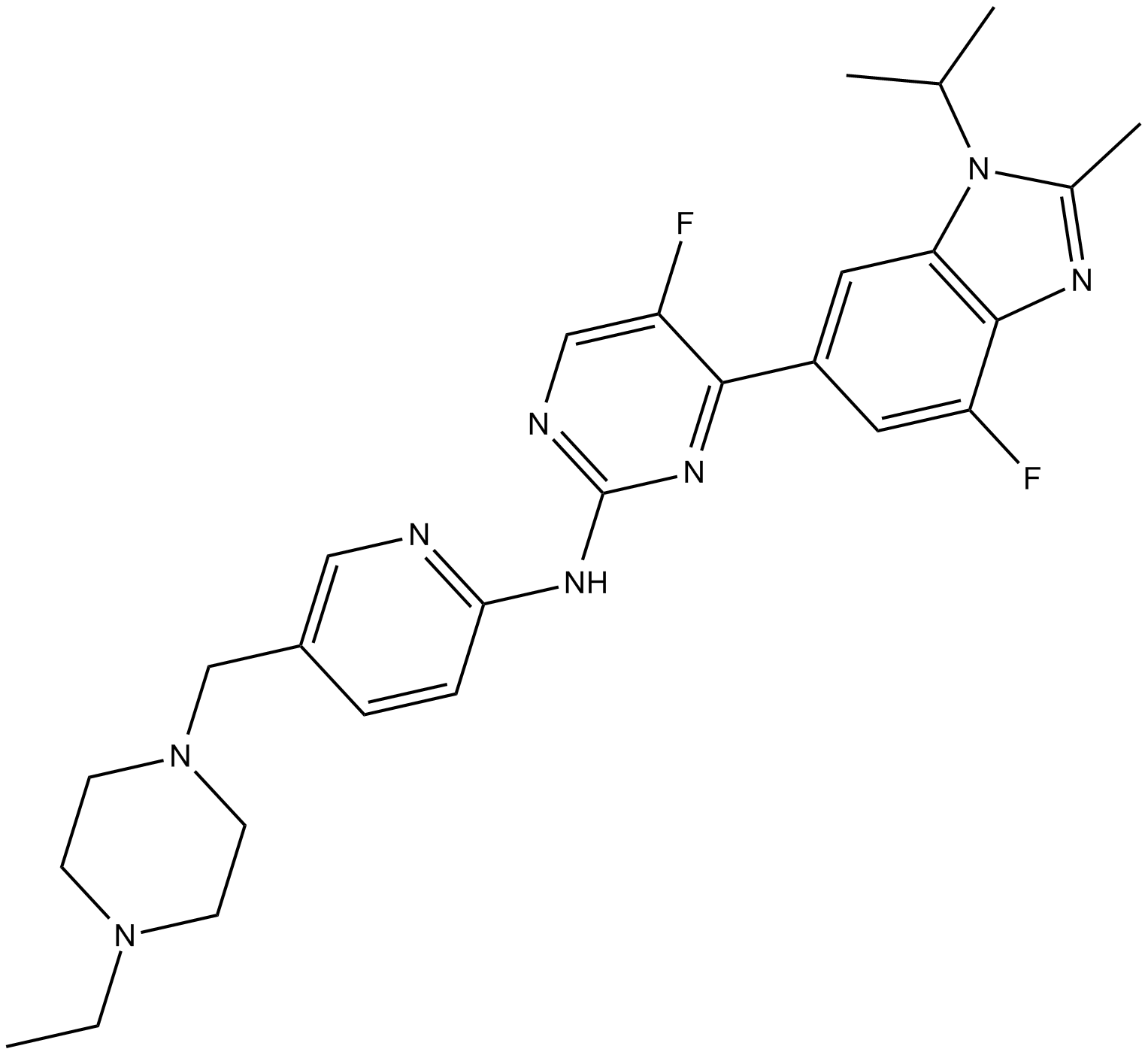 A3575 LY2835219 free baseSummary: CDK inhibitor
A3575 LY2835219 free baseSummary: CDK inhibitor -
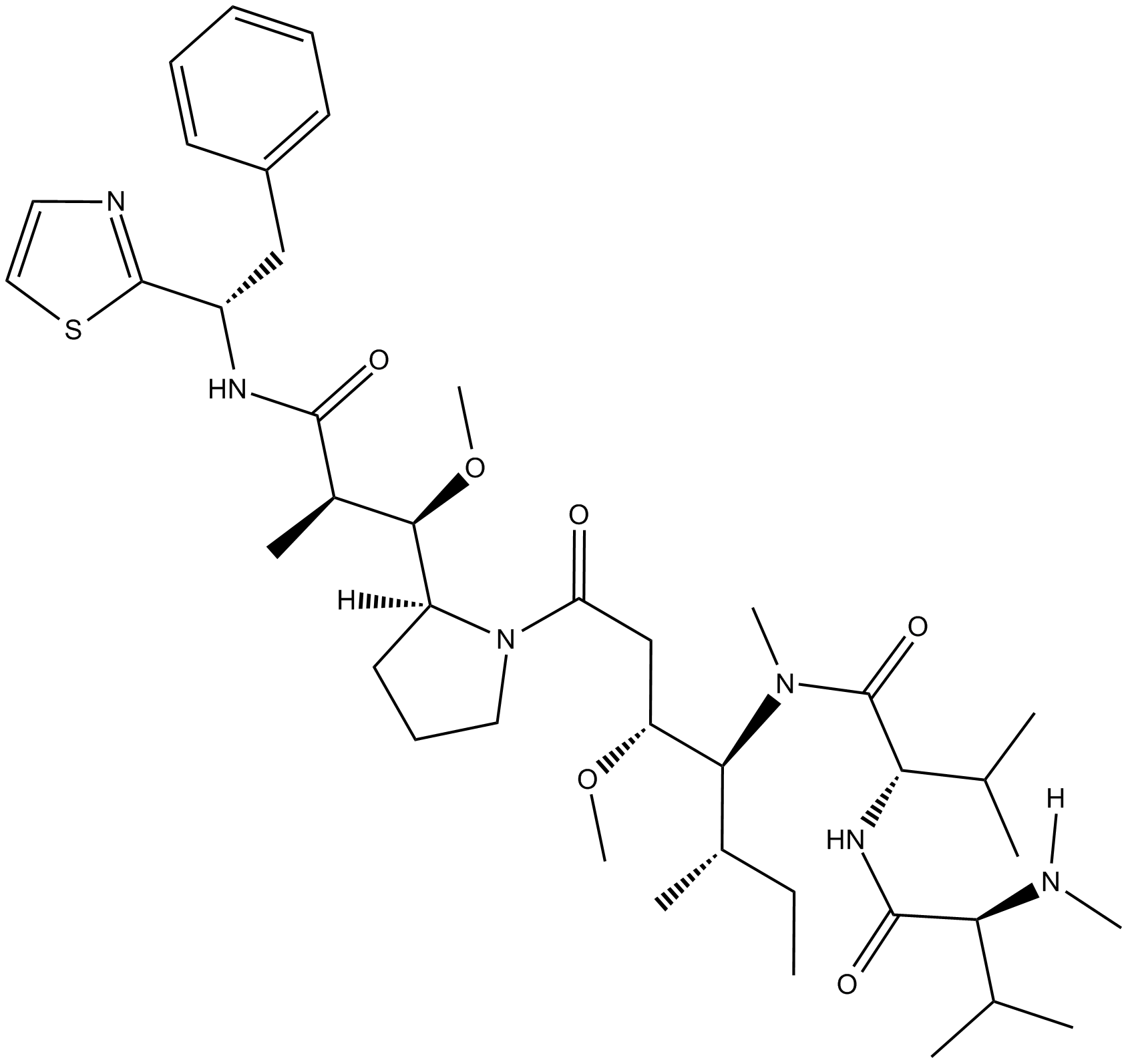 A3630 MMADSummary: Tubulin inhibitor,highly potent
A3630 MMADSummary: Tubulin inhibitor,highly potent -
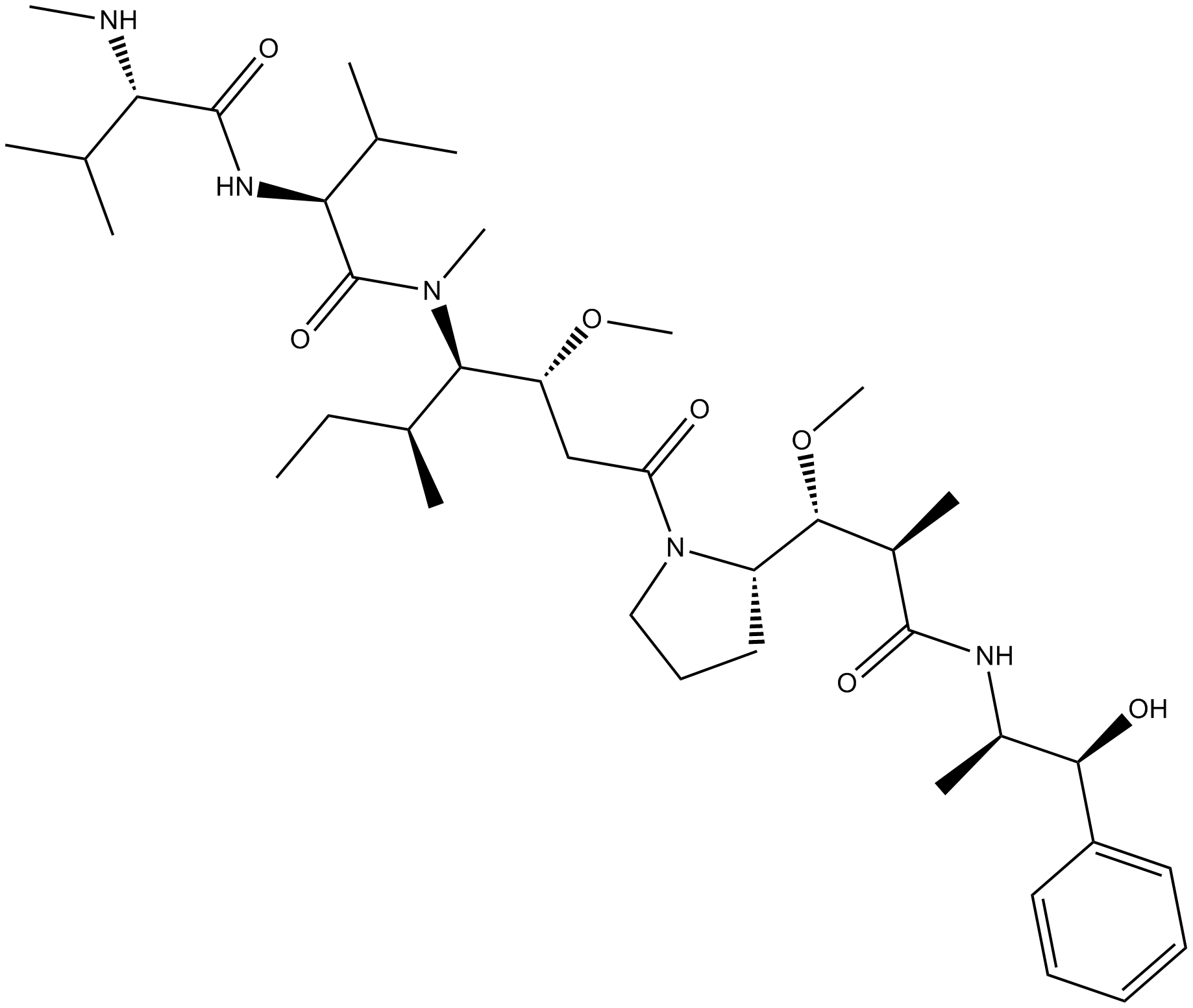 A3631 Monomethyl auristatin ESummary: A type of antimitotic agent that can also be widely used as a cytotoxic component for the preparation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer research.
A3631 Monomethyl auristatin ESummary: A type of antimitotic agent that can also be widely used as a cytotoxic component for the preparation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer research.


