Yonkenafil
Yonkenafil (CAS 804518-63-6) is a highly selective phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, with an IC₅₀ value of 2.01 nM for PDE5 and superior selectivity over other PDE isoforms. It exhibits broad and pronounced biological activities: in a streptozotocin (STZ, Cat. No. A4457)-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease rat model, continuous administration at 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg for 3 weeks improves cognitive deficits, suppresses excessive activation of microglia and astrocytes, reduces the levels of pro‑inflammatory cytokines such as TNF‑α and IL‑1β, and attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation. In LPS‑stimulated N9 microglial cells, Yonkenafil at 3–30 μM inhibits the production of NO, iNOS, and pro‑inflammatory mediators in a concentration‑dependent manner. In an acute middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) stroke model, intravenous or intraperitoneal administration at 8–32 mg/kg reduces infarct volume and cerebral edema; it remains effective even when dosing is delayed up to 4 h after stroke onset, and it preserves synaptic structure and improves neurological deficits with effects lasting up to 7 days.
The core mechanism of Yonkenafil involves inhibition of PDE5‑mediated cGMP hydrolysis, leading to elevated intracellular cGMP levels and subsequent activation of cGMP/PKA/PKG signaling pathways. On the one hand, this regulates NF‑κB transcriptional activity, thereby suppressing microglial activation and inflammatory cytokine release, while downregulating JNK phosphorylation and upregulating GSK3β (Ser9) phosphorylation to mitigate tau hyperphosphorylation. On the other hand, it reduces neuronal apoptosis through a cGMP‑dependent Nogo‑R/RhoA/PI3K/Akt pathway, and upregulates BDNF/TrkB and NGF/TrkA signaling to preserve synaptic function, ultimately conferring neuroprotective, anti‑inflammatory, and cognition‑enhancing effects.
References:
[1] Chen X, Wang N, Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhang T, Zhu L, Wang Y, Wu C, Yang J. Yonkenafil: a novel phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor induces neuronal network potentiation by a cGMP-dependent Nogo-R axis in acute experimental stroke. Exp Neurol. 2014 Nov;261:267-77. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Jul 23. PMID: 25064698.
[2] Zhao S, Yang J, Wang L, Peng S, Yin J, Jia L, Yang X, Yuan Z, Wu C. NF-κB Upregulates Type 5 Phosphodiesterase in N9 Microglial Cells: Inhibition by Sildenafil and Yonkenafil. Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2647-58. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9293-0. Epub 2015 Jun 25. PMID: 26108184.
[3] Zhu L, Zhang Z, Hou XJ, Wang YF, Yang JY, Wu CF. Inhibition of PDE5 attenuates streptozotocin-induced neuroinflammation and tau hyperphosphorylation in a streptozotocin-treated rat model. Brain Res. 2019 Nov 1;1722:146344. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146344. Epub 2019 Jul 22. PMID: 31344367.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | 4°C, protect from light |
| M.Wt | 487.61 |
| Cas No. | 804518-63-6 |
| Formula | C24H33N5O4S |
| Synonyms | Tunodafil |
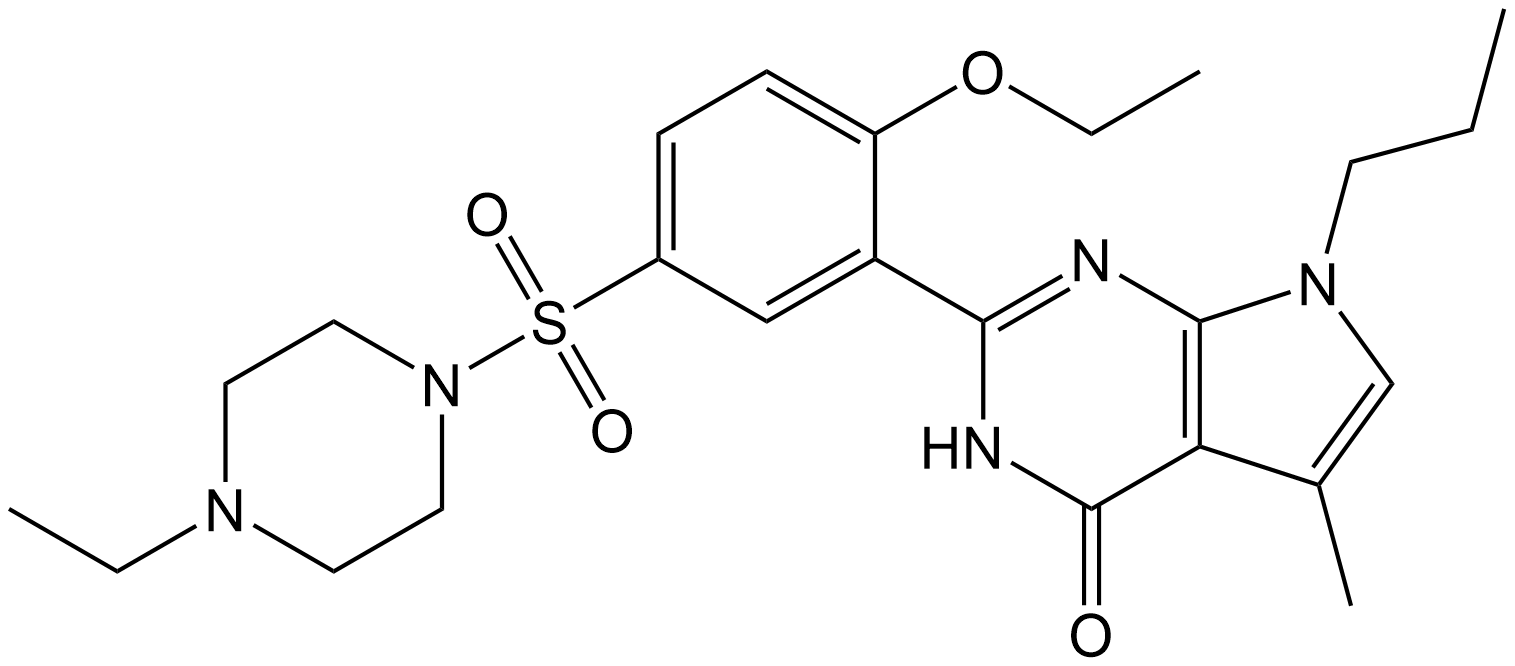
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-ethoxy-5-((4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-5-methyl-7-propyl-3,7-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCOC1=CC=C(S(N2CCN(CC)CC2)(=O)=O)C=C1C(N3)=NC4=C(C(C)=CN4CCC)C3=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |