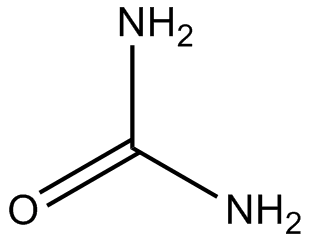
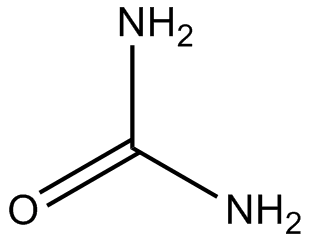
Urea
Urea is an organic compound generated by the urea cycle enzymes, which is then eliminated through fluids, especially urine. Blood urea nitrogen has been utilized to evaluate renal function for decades. In addition, urea has been used clinically for a variety of dermatological diseases over a century. Urea is a potent emollient and keratolytic agent, making it an effective topical monotherapy for conditions such as dry and scaly skin. Due to its high solubility in aqueous solution, urea further extends its applications in laboratory, serving as a powerful protein denaturant for assessing protein stability, the effects of mutations on stability, and protein unfolding.
References:
1. Wang H, Ran J, Jiang T. Urea. Subcellular Biochemistry, 2014, 73: 7-29.
2. Pan M, Heinecke G, Bernardo S, et al. Urea: a comprehensive review of the clinical literature. Dermatology Online Journal, 2013, 19(11): 20392.
3. Bennion BJ, Daggett V. The molecular basis for the chemical denaturation of proteins by urea. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(9): 5142-5147.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at RT |
| M.Wt | 60.06 |
| Cas No. | 57-13-6 |
| Formula | CH4N2O |
| Solubility | ≥19.27 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥55.7 mg/mL in H2O; ≥6 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | urea |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NC(N)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure