Topotecan
Topotecan (CAS No. 123948-87-8) is a semi-synthetic camptothecin derivative. Its core target is topoisomerase I (Topo I). By forming a stable, cleavable DNA/Topo I/drug complex, it blocks DNA replication and repair and induces cell apoptosis. Its activity is characterized by cytostatic effects and clinical efficacy.
The concentration commonly used in experiments is 0.1–10 μM (for in vitro tumor cell assays). In combination therapy experiments, the dosage can be adjusted to 0.75–1.5 mg/m² (in vitro equivalent concentration based on clinical conversion). The clinically effective therapeutic concentration corresponds to multiple administration regimens: the conventional intravenous dose is 1.5 mg/m² per day (administered consecutively for 5 days, with a 21-day cycle). For the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer, it can be combined with drugs such as cisplatin (CAS No. 15663-27-1, Catalog No.: A8321). For first-line treatment of small cell lung cancer (SCLC), it can be used in combination with paclitaxel (CAS No. 33069-62-4, Catalog No.: A4393), etoposide (CAS No. 33419-42-0, Catalog No.: A1971), and other agents. The oral formulation has a bioavailability of 30%–40%, with a commonly used dose of 2.3 mg/m² per day (administered consecutively for 5 days).
Its biological activity is reflected in broad-spectrum antitumor effects, with definite efficacy against ovarian cancer, SCLC, and other malignancies. It can cross the blood-brain barrier and has no cross-resistance with cisplatin, paclitaxel, and similar drugs. Its main toxicity is reversible neutropenia, with mild non-hematological toxicities. It is indicated for the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer, SCLC, and certain solid tumors.
References:
[1] Kollmannsberger C, Mross K, Jakob A, Kanz L, Bokemeyer C. Topotecan - A novel topoisomerase I inhibitor: pharmacology and clinical experience. Oncology. 1999;56(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000011923. PMID: 9885371.
[2] Ardizzoni A. Topotecan in the treatment of recurrent small cell lung cancer: an update. Oncologist. 2004;9 Suppl 6:4-13. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.9-90006-4. PMID: 15616145.
[3] Stewart DJ. Topotecan in the first-line treatment of small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 2004;9 Suppl 6:33-42. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.9-90006-33. PMID: 15616148.
[4] Lihua P, Chen XY, Wu TX. Topotecan for ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Apr 16;2008(2):CD005589. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005589.pub2. PMID: 18425923; PMCID: PMC6905487.
- 1. Ivan Rivera, Sabah Shammari, et al. "Dna2 Responds to Endogenous and Exogenous Replication Stress in Drosophila melanogaster." Genes (Basel). 2025 Sep 25;16(10):1133. PMID: 41153349
- 2. Lambo S, Gröbner SN, et al. "The molecular landscape of ETMR at diagnosis and relapse." Nature. 2019 Dec;576(7786):274-280 PMID: 31802000
- 3. Manasi Ratnaparkhe, John Wong, et al. "Defective DNA damage repair leads to frequent catastrophic genomic events in murine and human tumors." bioRxiv. 2018 May 4
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 421.45 |
| Cas No. | 123948-87-8 |
| Formula | C23H23N3O5 |
| Synonyms | SKF 104864A; NSC 609669; Hycamtin |
| Solubility | ≥21.1 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
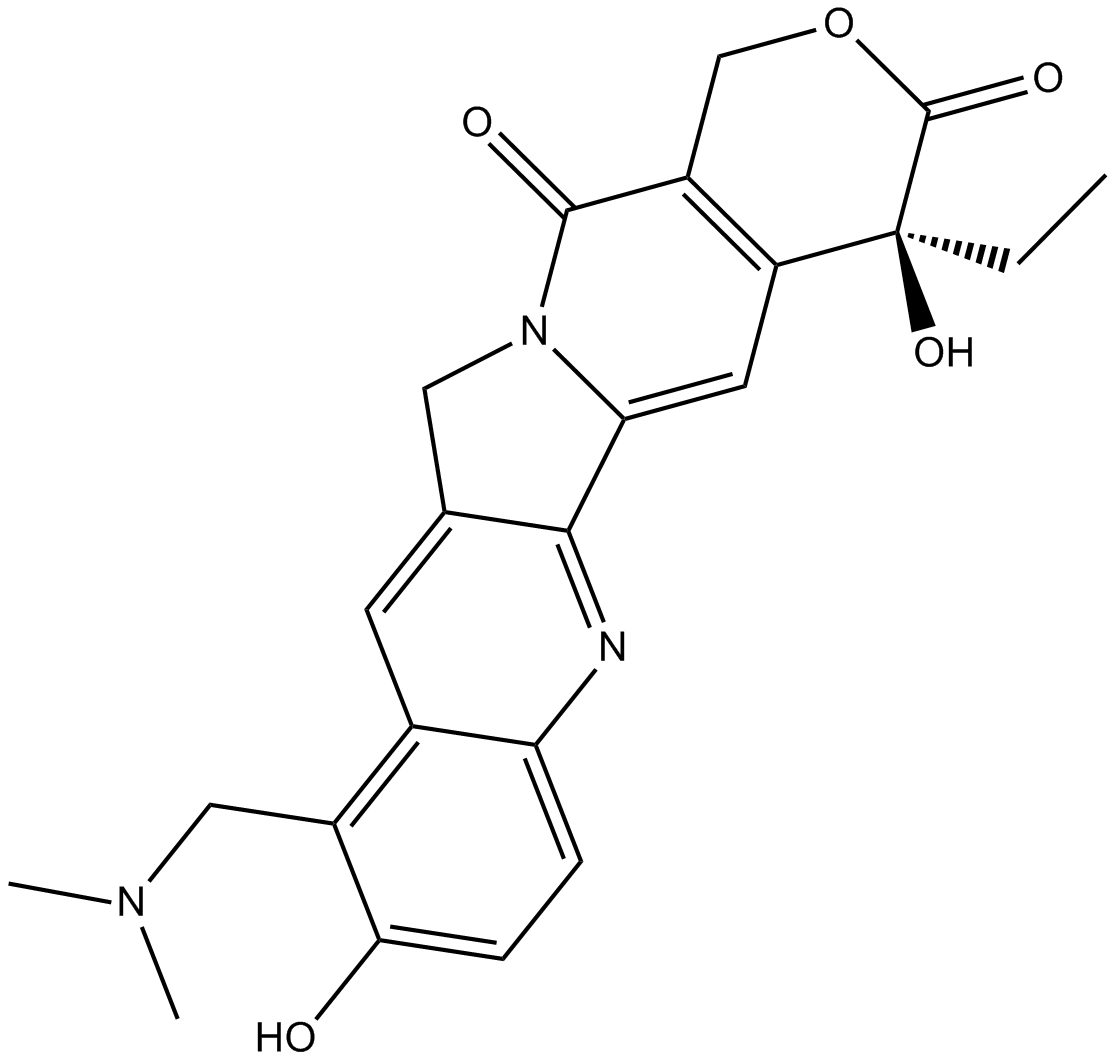
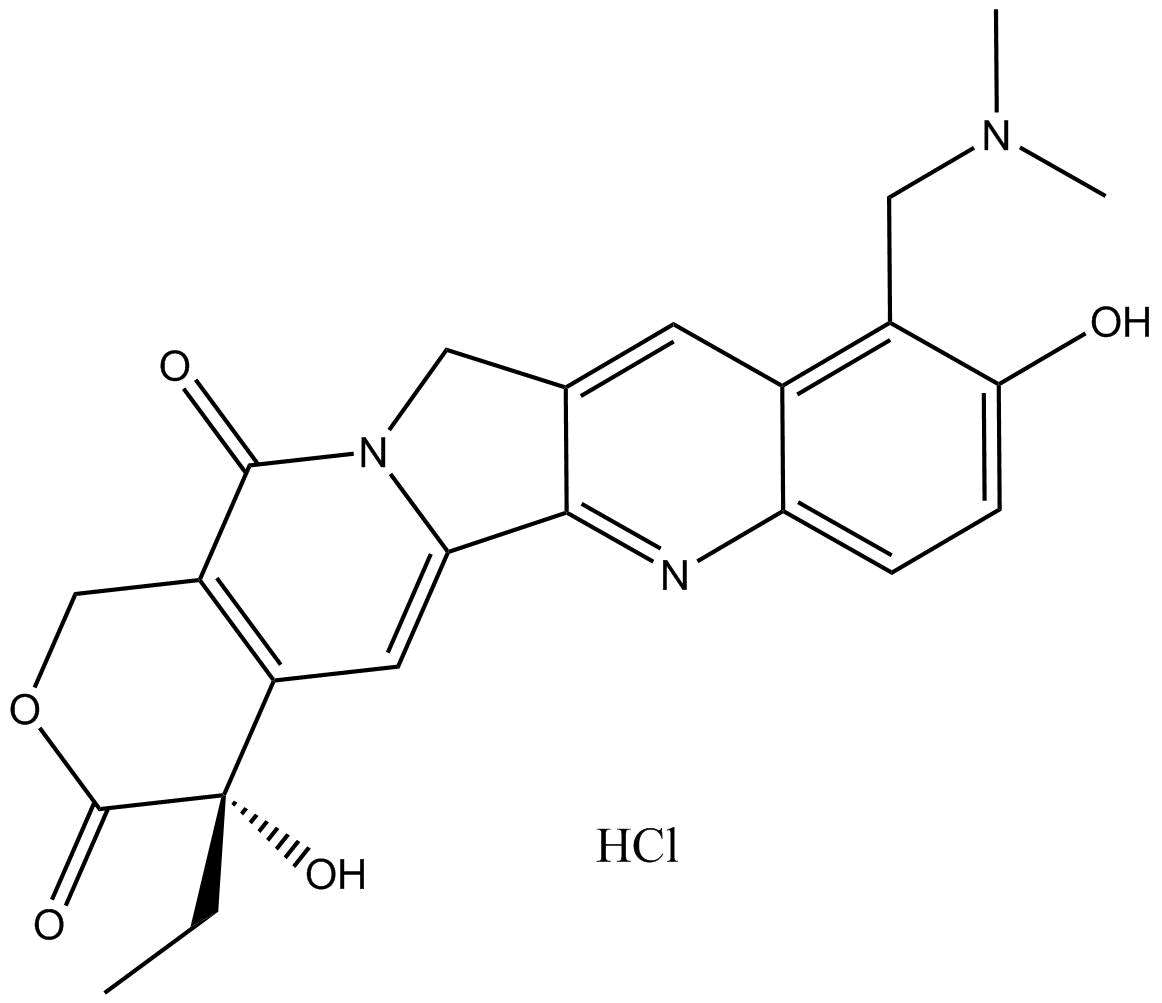
| Chemical Name | (S)-10-((dimethylamino)methyl)-4-ethyl-4,9-dihydroxy-1H-pyrano[3',4':6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinoline-3,14(4H,12H)-dione |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC[C@](C(C=C1N2Cc3cc(c(CN(C)C)c(cc4)O)c4nc13)=C(CO1)C2=O)(C1=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Human glioma cell lines U251, U87, GSCs-U251 and GSCs-U87 |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0.02, 0.2, 2, 20 or 40 μmol/L topotecan for 12, 24 or 48 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Topotecan obviously inhibited proliferation of not only human glioma cells but also glioma stem cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. In addition, topotecan (3 μmol/L, 24 h) induced cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 and S phases and promoted apoptosis. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Mouse models of aggressive pediatric solid tumor |
|
Dosage form |
1 mg/kg Once daily by oral gavage |
|
Applications |
Metronomic administration of topotecan and pazopanib showed a statistically significant antitumor activity compared with respective single agents in pediatric tumor mouse models, representing a valid option as a maintenance therapy in aggressive pediatric solid tumors. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Zhang FL, Wang P, Liu YH, et al. Topoisomerase I inhibitors, shikonin and topotecan, inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of glioma cells and glioma stem cells. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e81815. 2. Kumar S, Mokhtari RB, Sheikh R, et al. Metronomic oral topotecan with pazopanib is an active antiangiogenic regimen in mouse models of aggressive pediatric solid tumor. Clinical Cancer Research, 2011, 17(17): 5656-5667. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure

Related Biological Data
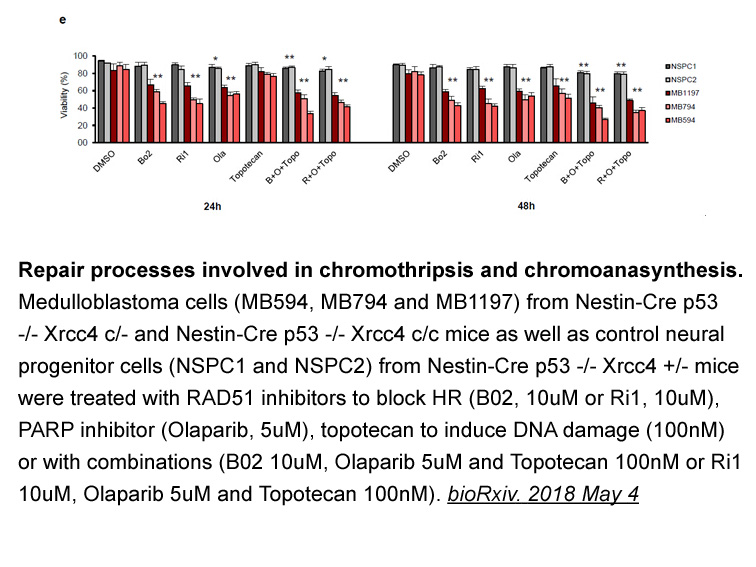
Related Biological Data