thymine
Thymine is one of the four important bases in DNA and belongs to the pyrimidine class of bases. It pairs with adenine (A) through two hydrogen bonds to form the double helix structure of DNA. In organisms, the metabolism of Thymine is mainly catalyzed by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). Studies have shown that DPD in the liver of rats has a high affinity for Thymine, with a Km value of approximately 2.2 μM, indicating that DPD has a strong affinity for Thymine and a high catalytic efficiency. Abnormal DPD activity may lead to metabolic disorders of Thymine, thereby affecting the DNA synthesis and repair processes. The structural stability and metabolic pathways of Thymine are crucial for maintaining genomic stability, and related studies are of great significance for understanding genetic diseases and drug metabolism.
| Physical Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 126.11 |
| Cas No. | 65-71-4 |
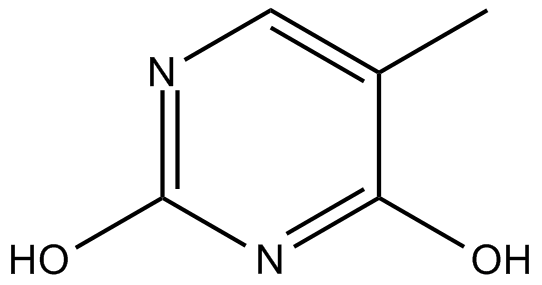
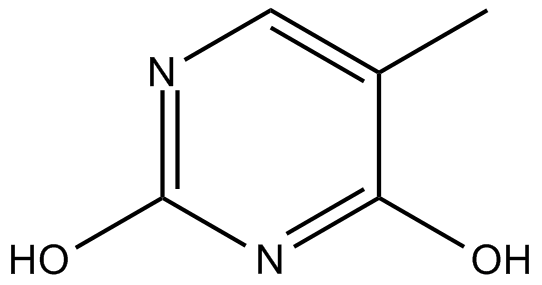
| Formula | C5H6N2O2 |
| Synonyms | Thymine |
| Solubility | ≥0.83 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥1.21 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic; ≥23.4 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-diol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC1=CN=C(O)N=C1O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure