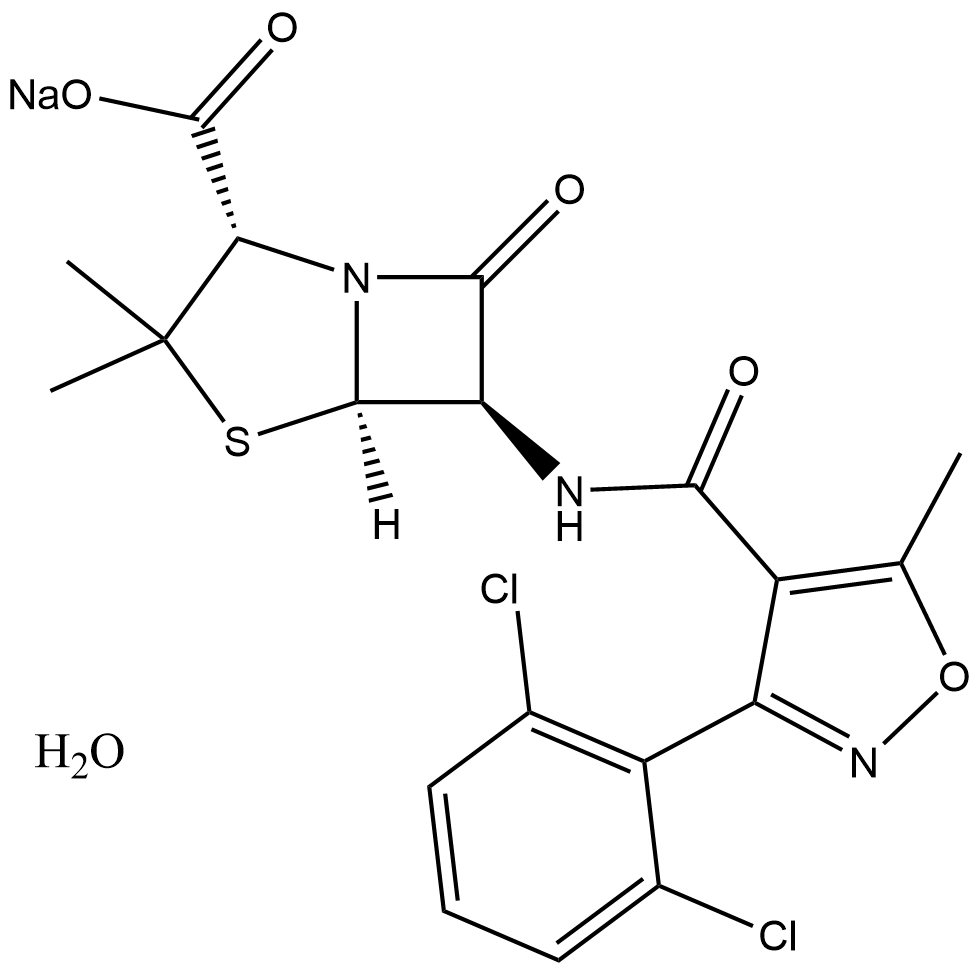
Sodium dicloxacillin monohydrate
Sodium dicloxacillin monohydrate (CAS No. 13412-64-1) is the monohydrate form of dicloxacillin sodium (CAS No. 343-55-5, Cat. No. B1930). As a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the penicillin class, dicloxacillin exerts its core biological activity by inhibiting the growth of Gram-positive bacteria, such as methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). Its mechanism of action targets bacterial penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), thereby blocking bacterial cell wall synthesis to achieve bactericidal effects.
Notably, the half-maximal effective concentration (EC₅₀) of dicloxacillin is strain- and environment-dependent. In vitro assays (pH 7.4) demonstrated that the extracellular EC₅₀ against the MSSA ATCC 25923 strain was 0.06 mg/L, with an intracellular EC₅₀ of 0.04 mg/L; in contrast, the extracellular and intracellular EC₅₀ values against the clinical MSSA strain E19977 were 0.50 mg/L and 0.31 mg/L, respectively. For the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), at pH 7.4, the MIC values for ATCC 25923 and E19977 strains were 0.125 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L, respectively, while a 4-fold reduction in MIC was observed when the pH was adjusted to 5.4.
Regarding the application concentrations: in in vitro cellular experiments using the THP-1 macrophage model, a gradient concentration range of 0.1×MIC to 100×MIC (corresponding to 0.0125–12.5 mg/L) was typically employed. In animal experiments based on the mouse peritonitis model, a single subcutaneous injection dose of 0.25–340 mg/kg was administered, and the cumulative dose for multi-dose regimens ranged from 240 to 1200 mg/24 kg·h. For clinical applications, the effective therapeutic concentration is achieved via the recommended oral dosage for adults: 500 mg administered four times daily or 1 g administered three times daily, which results in a steady-state peak plasma concentration of approximately 20 mg/L and a trough concentration of approximately 0.7 mg/L. To ensure optimal therapeutic efficacy, it is critical to maintain the free drug concentration above the MIC (fT_MIC) for ≥100% of the dosing interval. This antibiotic is indicated for the treatment of MSSA infections involving the skin, soft tissues, bones, and other related sites. Additionally, it should be noted that dicloxacillin can induce the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4, which may potentially trigger clinically relevant drug-drug interactions.
References:
[1] Salem H, Saleh GA. Selective spectrophotometric determination of phenolic beta-lactam antibiotics. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002 Jun 15;28(6):1205-13. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(02)00027-4. PMID: 12049985.
[2] Sandberg A, Jensen KS, Baudoux P, Van Bambeke F, Tulkens PM, Frimodt-Møller N. Intra- and extracellular activities of dicloxacillin against Staphylococcus aureus in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jun;54(6):2391-400. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01400-09. Epub 2010 Mar 22. PMID: 20308386; PMCID: PMC2876366.
[3] Stage TB, Graff M, Wong S, Rasmussen LL, Nielsen F, Pottegård A, Brøsen K, Kroetz DL, Khojasteh SC, Damkier P. Dicloxacillin induces CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in vivo and in vitro. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;84(3):510-519. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13467. Epub 2018 Jan 10. PMID: 29105855; PMCID: PMC5809358.
| Storage | Store at 4℃ sealed and dried. |
| M.Wt | 510.32 |
| Cas No. | 13412-64-1 |
| Formula | C19H18Cl2N3NaO6S |
| Synonyms | Dicloxacillin sodium salt monohydrate |
| Chemical Name | sodium (2S,5R,6R)-6-(3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate hydrate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1[C@@H](NC(C2=C(C)ON=C2C3=C(Cl)C=CC=C3Cl)=O)[C@]4([H])N1[C@@H](C(O[Na])=O)C(C)(C)S4.O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |