Sodium butyrate
Sodium butyrate (CAS 156-54-7) is a small-molecule inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs), enzymes that regulate gene expression by deacetylating histone proteins. By inhibiting HDAC activity, sodium butyrate increases histone acetylation levels, modifying transcription factor functions and subsequently affecting gene transcription. In vitro, sodium butyrate promotes apoptosis in colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cell lines (RG/C2 and AA/CI, respectively), suggesting anticancer research applications. In vivo, sodium butyrate administration in transgenic mouse models of Huntington's disease improved survival, motor function, and mitigated neuropathological damage. Thus, sodium butyrate is valuable in biomedical research targeting epigenetic regulation and neurodegenerative diseases.
- 1. Ying Shi, Lin Xing, et al. "Butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced glomerulopathy through GPR43-Sirt3 pathway." Cambridge University Press: 22 November 2024
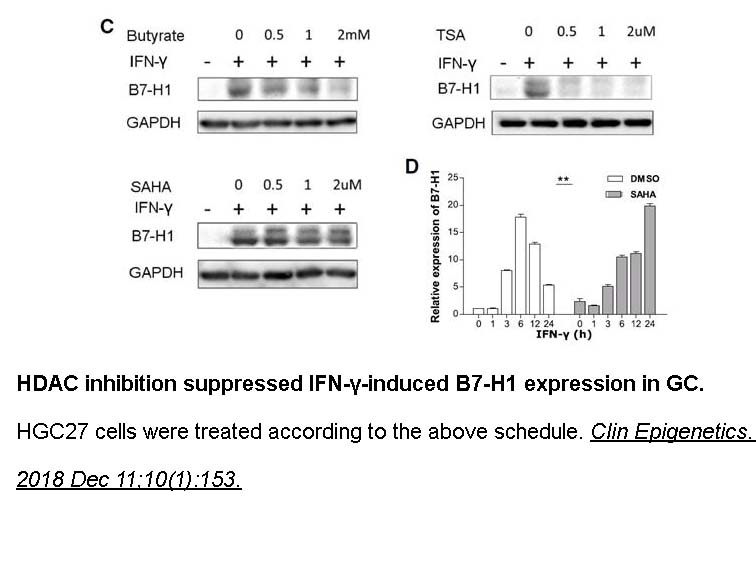
- 2. Deng R, Zhang P, et al. "HDAC is indispensable for IFN-γ-induced B7-H1 expression in gastric cancer." Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Dec 11;10(1):153. PMID:30537988
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 110.09 |
| Cas No. | 156-54-7 |
| Formula | C4H7NaO2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in DMSO; ≥4 mg/mL in H2O; ≥5.87 mg/mL in EtOH |
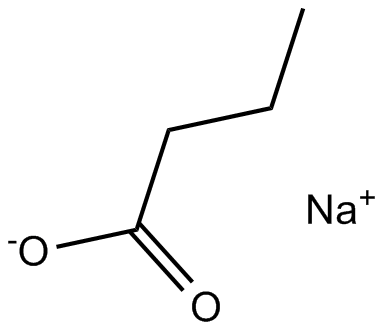
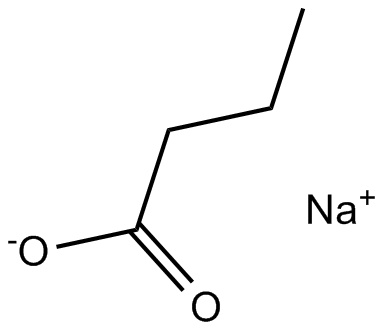
| Chemical Name | sodium;butanoate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCCC([O-])=O.[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
2 adenoma-derived cell lines (AA/Cl and RG/C2) |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is limited. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20 °C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
1 ~ 4 mM; 4 days |
|
Applications |
In RG/C2 cells, Sodium Butyrate at the concentrations of 2 mM and above reduced the attached-cell yield to approximately 50% of the control, and significantly increased the proportion of floating cells. It was demonstrated that the increase in the percentage of floating cells was attributed to the induction of apoptosis and not simply due to increased necrosis. Compared with RG/C2 cells, AA/Cl cells were more sensitive to Sodium Butyrate. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
An R6/2 transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease (HD) |
|
Dosage form |
100, 200, 400, 600, 1200, 5000 and 10,000 mg/kg; i.p.; q.d. |
|
Applications |
In an R6/2 transgenic mouse model of HD, Sodium Butyrate significantly extended survival in a dose-dependent manner, improved body weight and motor performance, as well as delayed the neuropathological sequelae. Moreover, Sodium Butyrate increased the level of histone and specificity protein-1 acetylation, and protected against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Hague A1, Manning AM, Hanlon KA, Huschtscha LI, Hart D, Paraskeva C. Sodium butyrate induces apoptosis in human colonic tumour cell lines in a p53-independent pathway: implications for the possible role of dietary fibre in the prevention of large-bowel cancer. Int J Cancer. 1993 Sep 30;55(3):498-505. [2]. Ferrante RJ1, Kubilus JK, Lee J, Ryu H, Beesen A, Zucker B, Smith K, Kowall NW, Ratan RR, Luthi-Carter R, Hersch SM. Histone deacetylase inhibition by sodium butyrate chemotherapy ameliorates the neurodegenerative phenotype in Huntington's disease mice. J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 15;23(28):9418-27. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data