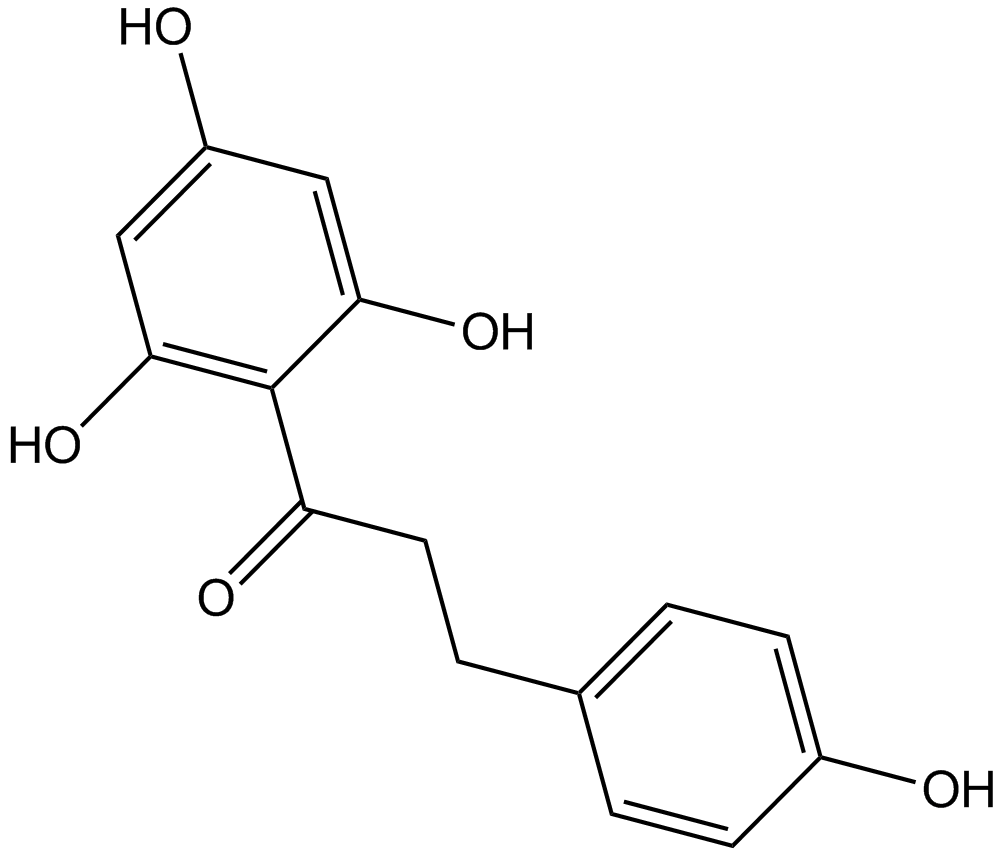
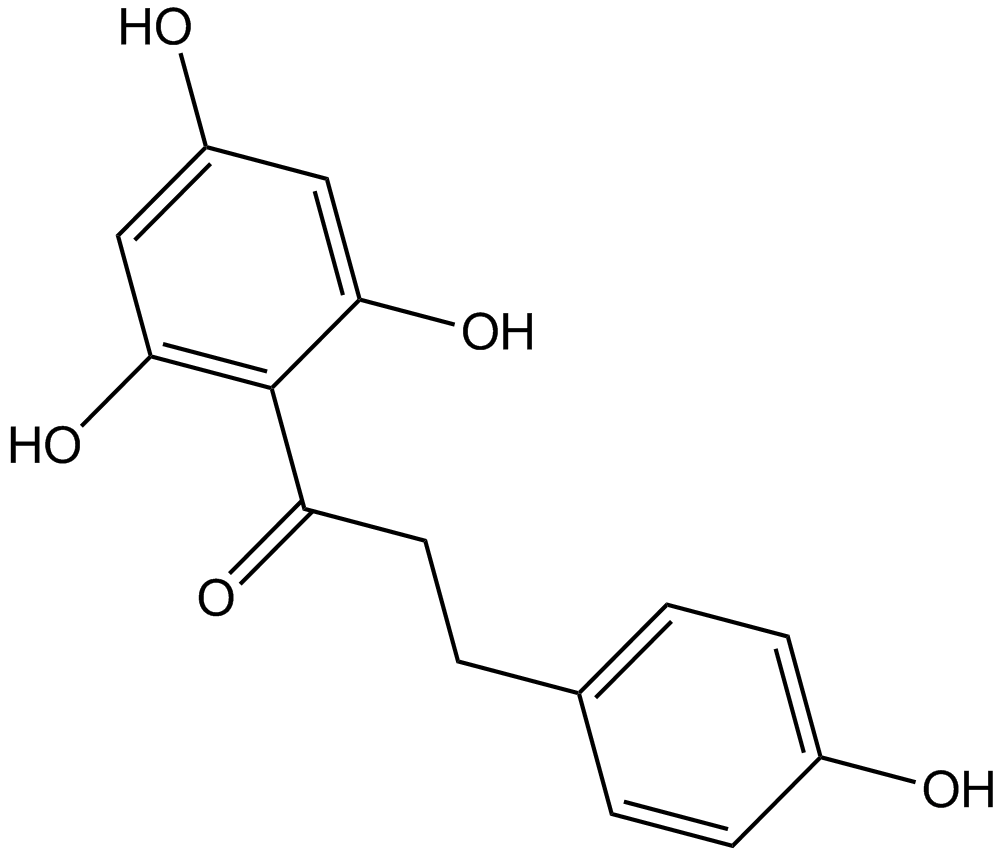
Phloretin
Phloretin (CAS 60-82-2) is a naturally occurring dihydrochalcone phenolic compound derived primarily from apple leaves and Manchurian apricot. It functions as an inhibitor of sodium-glucose linked transporters (SGLT1 and SGLT2), proteins involved in glucose uptake and reabsorption in intestinal and renal tissues. Phloretin inhibits glucose uptake via these transporters, exhibiting an IC50 of approximately 49 ± 12 μM. In cell-based studies, it enhances lipolysis, increases AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation, and suppresses adipogenic transcription factors and MAPK signaling. Animal research demonstrates that oral administration of Phloretin reduces blood glucose and improves lipid profiles in diabetic mouse models, highlighting its utility in metabolic research.
References:
[1] Huang W C et al. , Phloretin and phlorizin promote lipolysis and inhibit inflammation in mouse 3T3-L1 cells and in macrophage-adipocyte co-cultures. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013, 57: 1807-1817.
[2] Kasahara T, Kasahara M. Expression of the rat GLUT1 glucose transporter in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1996, 315 ( Pt 1):177-182.
[3] Najafian M, Jahromi M Z, Nowroznejhad M J, Phloridzin reduces blood glucose levels and improves lipids metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2012, 39(5): 5299-306.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 274.27 |
| Cas No. | 60-82-2 |
| Formula | C15H14O5 |
| Synonyms | NSC 407292;RJC 02792 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥105 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥87.6 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Oc1ccc(CCC(c(c(O)cc(O)c2)c2O)=O)cc1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
U87 and U251 cell lines |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >9.25mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0-300 μM; 12, 24, and 48 h; 37°C |
|
Applications |
In U87 and U251 cell lines, Phloretin inhibited colony formation in a concentration-dependent manner. Phloretin also inhibited cell growth in a concentration- and time-dependent way. In U87 cells, Phloretin induced cell cycle arrest at the G0-G1 phase and significantly induced apoptosis. Phloretin also triggered the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and generated reactive oxygen species (ROS). |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthmatic mice |
|
Dosage form |
5, 10, or 20 mg/kg; intraperitoneally injection |
|
Application |
In ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthmatic mice, Phloretin (PT) could significantly diminish airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR). Phloretin significantly reduced numbers of eosinophils and total cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BalF). Phloretin also decreased malondialdehyde levels in the lung and reduced Th2 cytokine production in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Huang WC1, Fang LW2, Liou CJ3, et al. Phloretin Attenuates Allergic Airway Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Asthmatic Mice. Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 13;8:134. [2] Najafian M, Jahromi M Z, Nowroznejhad M J, Phloridzin reduces blood glucose levels and improves lipids metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2012, 39(5): 5299-306. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure