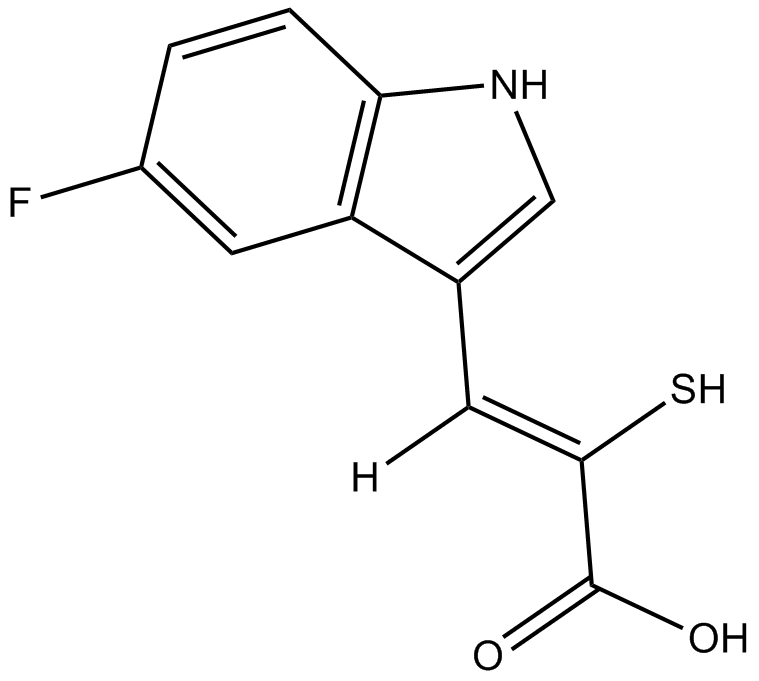
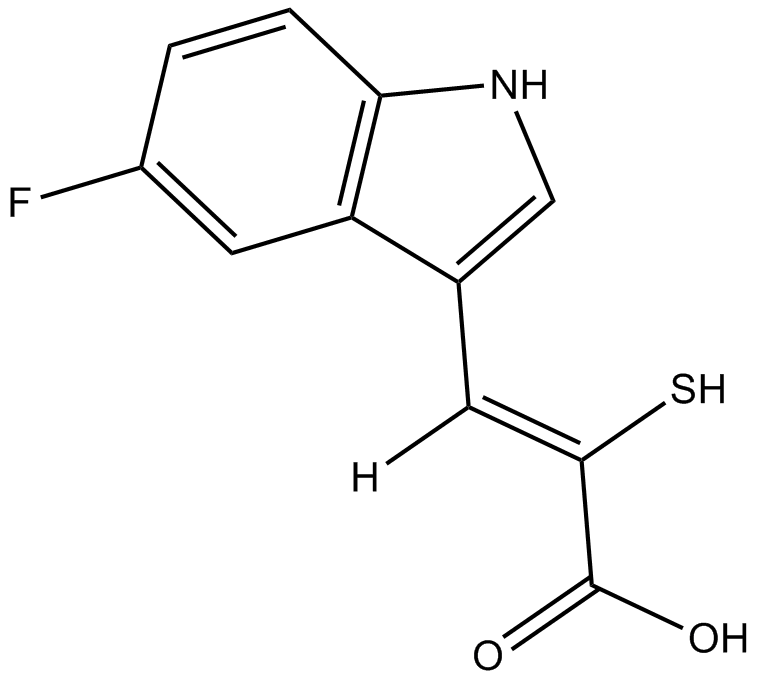
PD 151746
PD 151746 is a potent and selective inhibitor of calpain with Ki value of 0.26 μM for μ-Calpain.
Calpain is a calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine protease that expressed in mammals and many other organisms. Calpain plays an important role in cell mobility and cell cycle progression.
PD 151746 is a cell-permeable, potent and selective calpain inhibitor. PD151746 significantly inhibited NMDA-induced α-spectrin breakdown product (SBDP) of 145 kDa and completely inhibited the fragmentation of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-α (CaMPK-IIα) and nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which were cleaved by calpain [1]. In cerebellar granule cells, PD151746 inhibited serum/potassium (S/K) withdrawal induced apoptosis by 29% through inhibition of calpain. Also, PD151746 inhibited the increase of MEF2 phosphorylation and cdk5/p25 formation and inhibited caspase-3 activity [2]. In human hepatoma G2 cells, PD151746 significantly reduced insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis and increased the amount of protein tyrosine phosphatase-ε (PTPε), which suggested that calpain played an important role in regulation of insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis [3]. In HEK-293 cells expressing human formyl peptide receptor (hFPR) or hFPR-like 1 (hFPRL1), PD151746 increased cytoplasmic free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) [4].
References:
[1]. Hajimohammadreza I, Raser KJ, Nath R, et al. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIalpha undergo neurotoxin-induced proteolysis. J Neurochem, 1997, 69(3): 1006-1013.
[2]. Verdaguer E, Alvira D, Jiménez A, et al. Inhibition of the cdk5/MEF2 pathway is involved in the antiapoptotic properties of calpain inhibitors in cerebellar neurons. Br J Pharmacol, 2005, 145(8): 1103-1011.
[3]. Meier M, Klein HH, Kramer J, et al. Calpain inhibition impairs glycogen syntheses in HepG2 hepatoma cells without altering insulin signaling. J Endocrinol, 2007, 193(1): 45-51.
[4]. Fujita H, Kato T, Watanabe N, et al. Stimulation of human formyl peptide receptors by calpain inhibitors: homology modeling of receptors and ligand docking simulation. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2011, 516(2): 121-127.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 237.25 |
| Cas No. | 179461-52-0 |
| Formula | C11H8FNO2S |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥11.6 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥12.78 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | (Z)-3-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-mercaptoacrylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(/C(\S)=C/c1c[nH]c(cc2)c1cc2F)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Cerebellar granule cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is > 11.6 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20 °C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
20 or 40 μM; 24 hrs |
|
Applications |
In cerebellar granule cells, pre-treatment with 20 or 40 μM PD 151746 for 24 hrs inhibited calpain and thus, protected neurons against the effect of serum/potassium (S/K) withdrawal, restoring the number of cell survival. Moreover, PD 151746 at the dose of 40 μM inhibited the increase of MEF2 phosphorylation and cdk5/p25 formation, as well as inhibited caspase-3 activity. |
|
References: [1]. Verdaguer E, Alvira D, Jiménez A, et al. Inhibition of the cdk5/MEF2 pathway is involved in the antiapoptotic properties of calpain inhibitors in cerebellar neurons. Br J Pharmacol, 2005, 145(8): 1103-1011. | |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure