Novobiocin
Novobiocin (CAS No. 303-81-1) is an aminocoumarin compound whose core biological activities include antibacterial, antiparasitic, and antiviral effects. Its targets include bacterial DNA gyrase (subunit B, inhibiting ATPase activity) and heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90, C-terminal nucleotide-binding site). It can also inhibit bacterial DNA replication, cell membrane synthesis, and vacuole formation. IC??/EC?? values are well defined: anti-Theileria equi 165 μM, anti-Babesia caballi 84.85 μM; anti-Plasmodium falciparum (FCC1 strain 280 μM, VNS strain 210 μM); anti-Toxoplasma gondii 3.12 μg/ml (approximately 5.09 μM); anti-severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) EC?? 25.12 μM. MIC data for Gram-positive bacteria: for methicillin-susceptible staphylococci (MSS) from healthy dogs, the susceptibility rate is 95.4%, and for methicillin-resistant strains (MRS) 52.9%; for MSS from dogs with dermatophytosis, the susceptibility rate is 93.3%, and for MRS 80%. When combined with lactoferrin, the MIC against Escherichia coli ATCC25922 can be reduced to 1/64 × MIC (16 μg/ml). Common working concentrations: in vitro cell experiments 1–200 μM (antiparasitic/antiviral), 50 μg/ml (inhibition of Enterococcus faecalis protoplasts); in animal experiments, mice receive intraperitoneal injection at 5–100 mg/kg (NOAEL is 50 mg/kg). Effective therapeutic concentrations: oral administration in dogs for upper respiratory tract infections (often in combination with tetracycline); in humans, oral doses of 1–2 g/day have been used (blood concentration about 30.7 μM), and high doses of 3–9 g/day can reach 150 μM. In vitro reference concentrations for antiparasitic/antiviral activity are 5–200 μM. Combination with lactoferrin (bovine lactoferrin, CAS No. 936541-36-5, Cat. No.: BA1990) can reduce the effective antibacterial concentration.
References:
[1] Sanchez MS, Watts JL. Enhancement of the activity of novobiocin against Escherichia coli by lactoferrin. J Dairy Sci. 1999 Mar;82(3):494-9. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(99)75259-8. PMID: 10194666.
[2] Fulham KS, Lemarie SL, Hosgood G, Dick HL. In vitro susceptibility testing of meticillin-resistant and meticillin-susceptible staphylococci to mupirocin and novobiocin. Vet Dermatol. 2011 Feb;22(1):88-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2010.00921.x. Epub 2010 Oct 12. PMID: 21039985.
[3] Mbaba M, Mabhula AN, Boel N, Edkins AL, Isaacs M, Hoppe HC, Khanye SD. Ferrocenyl and organic novobiocin derivatives: Synthesis and their in vitro biological activity. J Inorg Biochem. 2017 Jul;172:88-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.04.014. Epub 2017 Apr 13. PMID: 28441548.
[4] Tsuchikado R, Kami S, Takahashi S, Nishida H. Novobiocin inhibits membrane synthesis and vacuole formation of Enterococcus faecalis protoplasts. Microb Cell. 2020 Aug 10;7(11):300-308. doi: 10.15698/mic2020.11.735. PMID: 33150162; PMCID: PMC7590531.
[5] Suthar A, Maji C, Gopalkrishnan A, Raval SH, Kumar R, Kumar S. Anti-piroplasmic activity of novobiocin as heat shock protein 90 inhibitor against in vitro cultured Theileria equi and Babesia caballi parasites. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021 Jul;12(4):101696. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101696. Epub 2021 Feb 27. PMID: 33677232.
[6] Emami S, Sadeghi M, Shahdin S, Daryani A, Khalilian A, Pirestani M, Hosseini SA, Montazeri M, Nejad ZH, Sarvi S. In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Parasitic Activities of Quinolone-Coumarin Hybrids Derived from Fluoroquinolones and Novobiocin Against Toxoplasma gondii. Acta Parasitol. 2024 Jun;69(2):1275-1283. doi: 10.1007/s11686-024-00852-9. Epub 2024 May 16. PMID: 38753101.
[7] Chen Q, Li J, Wang X, Huang C, Yan H, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen K. Drug Repurposing: In Vitro Evaluation of Simeprevir as a Novel Antiviral Drug Against Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J Med Virol. 2025 Oct;97(10):e70655. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70655. PMID: 41117261.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Tightly sealed and desiccated at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 612.62 |
| Cas No. | 303-81-1 |
| Formula | C31H36N2O11 |
| Synonyms | Albamycin;Cathomycin |
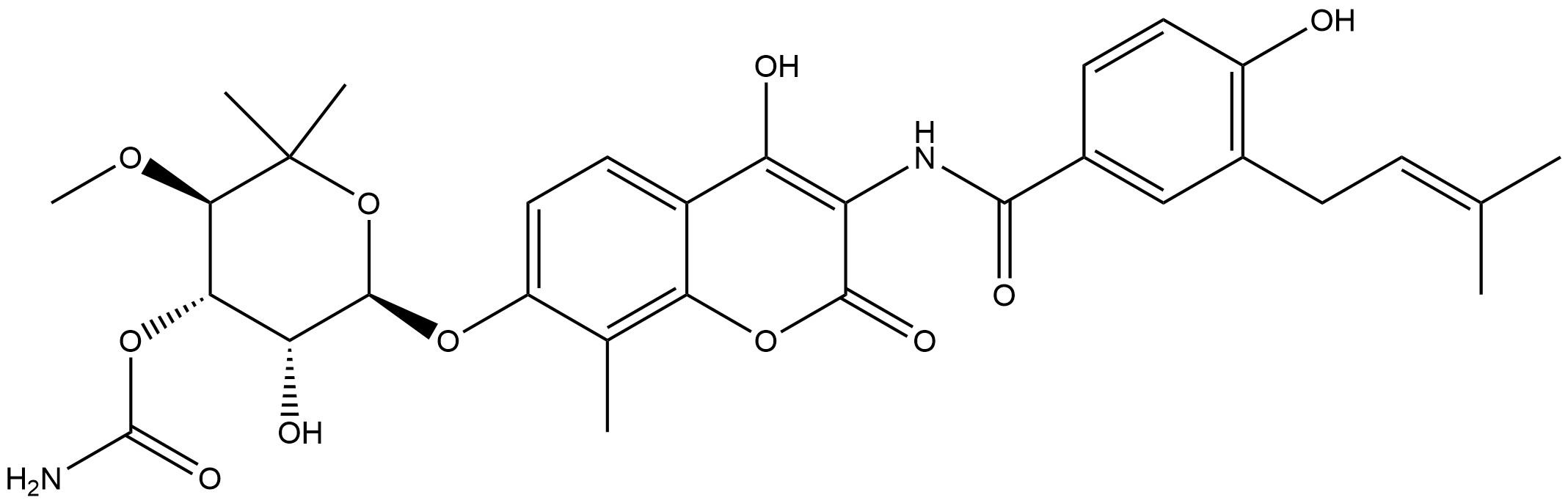
| Chemical Name | (3R,4S,5R,6R)-5-hydroxy-6-((4-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzamido)-8-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)oxy)-3-methoxy-2,2-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl carbamate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(N)O[C@H]([C@H]1OC)[C@H]([C@H](OC2=CC=C3C(OC(C(NC(C4=CC(C/C=C(C)/C)=C(O)C=C4)=O)=C3O)=O)=C2C)OC1(C)C)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |