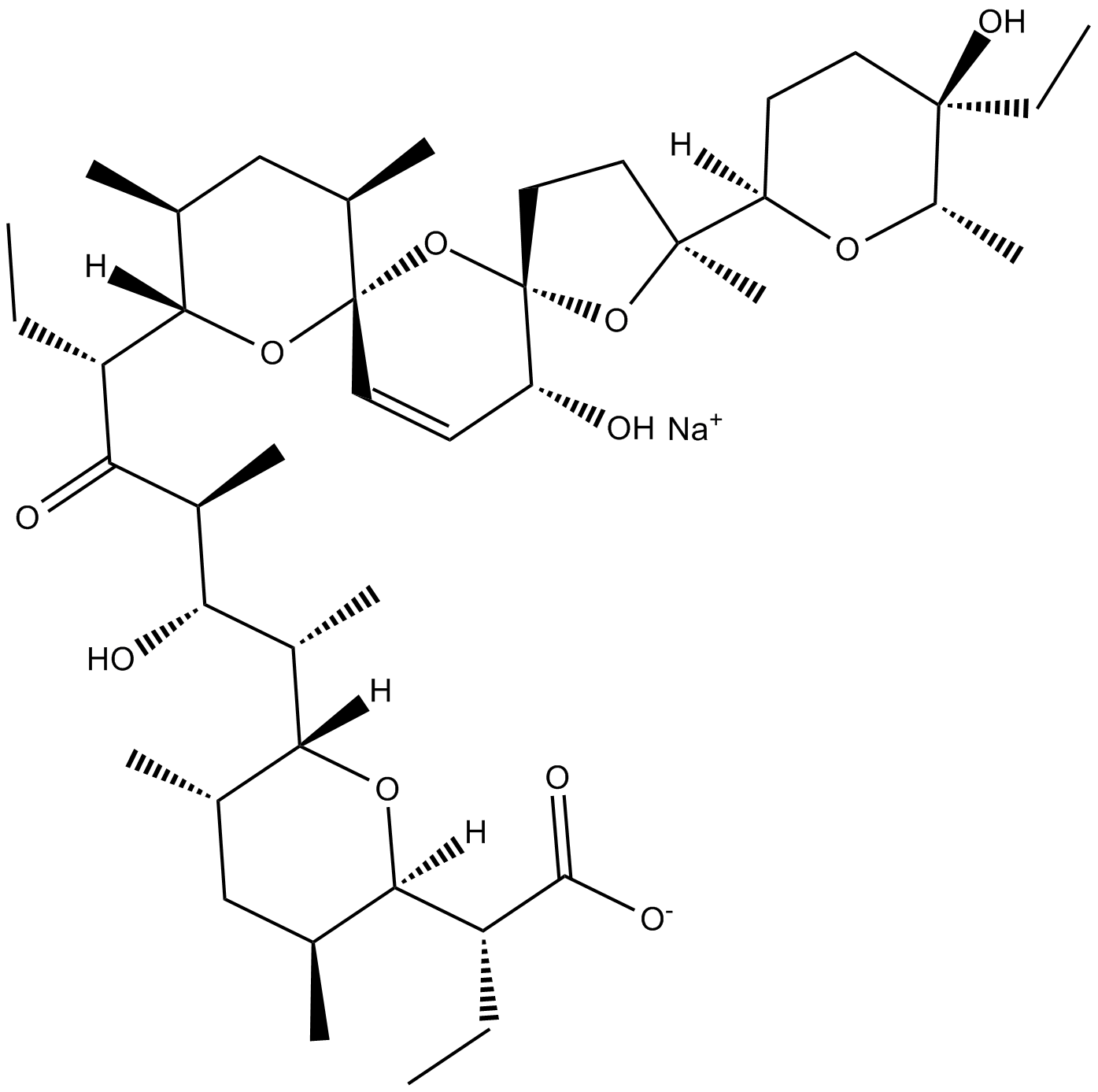
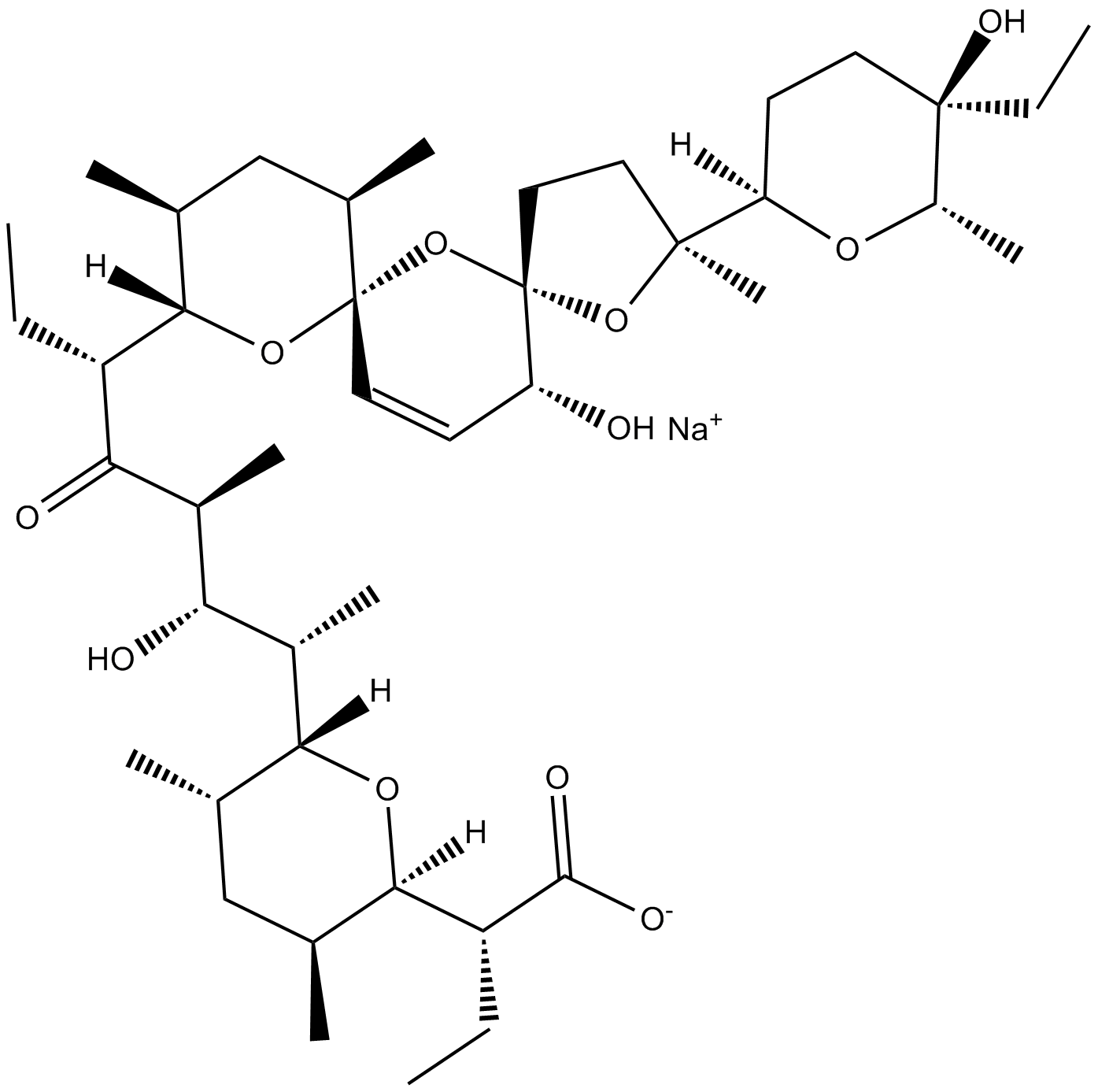
Narasin (sodium salt)
IC50: 3.2 μM: blocks NF-κB signaling via inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation
Narasin, isolated from certain Streptomyces sp. is an ionophore antibiotic. As a coccidiostat, it can be used in veterinary practice for gastrointestinal parasites. Narasin has been shown to induce tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis by ER stress in glioma cells and to dampen NF-κB signaling by suppressing the phosphorylation of IκBα. NF-κB, as a transcription factor, plays a vital role across many cellular processes which are involved in neuronal and embryonic development, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune responses to infection and inflammation.
In vitro: Narasin caused suicidal erythrocyte death or eryptosis. When human erythrocytes were exposed to narasin, it was shown that narasin resulted in the increase of annexin-V-binding indicating cell membrane scrambling with phosphatidylserine translocation to the erythrocyte surface and the decrease of forward scatter reflecting cell shrinkage, which indicated the death of erythrocyte [1]. Narasin blocked NF-κB signaling via inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation at a lower concentration [2].
In vivo: New Zealand White rabbits were given narasin 4-48 p. p. m, in pelleted feed. After 4 weeks, the experiments indicated that narasin protected rabbits from severe coccidiosis induced by E. flavescens, E. perforans E. magna, E. intestinalis, and E. stiedai. In addition, narasin reduced oocyst output in a highly effective fashion [3].
References:
[1]. Bouguerra, G., Bissinger, R., Abbes, S., & Lang, F. Stimulation of Eryptosis by Narasin. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2015; 37(5):1807-1816.
[2]. Miller, S., Huang, R., Sakamuru, S., Shukla, S., Attene-Ramos, M., & Shinn, P. et al. Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of NF-κB signaling and their mechanism of action. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2010; 79(9): 1272-1280.
[3]. Peeters, J., Geeroms, R., Antoine, O., Mammerickx, M., & Halen, P. Efficacy of narasin against hepatic and intestinal coccidiosis in rabbits. Parasitology. 1981; 83(02): 293-301.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 787 |
| Cas No. | 58331-17-2 |
| Formula | C43H71O11·Na |
| Synonyms | 4-Methylsalinomycin,Monteban,Narasin A |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 4S-methyl-salinomycin, monosodium salt |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C[C@@H]1[C@@]([C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)C([C@@H]([C@]2([H])[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)[C@]3(O[C@@]4(CC[C@]([C@@]5([H])CC[C@@](CC)(O)[C@H](C)O5)(C)O4)[C@H](O)C=C3)O2)CC)=O)([H])O[C@]([C@@H](CC)C([O-])=O)([H])[C@@H](C)C1.[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure