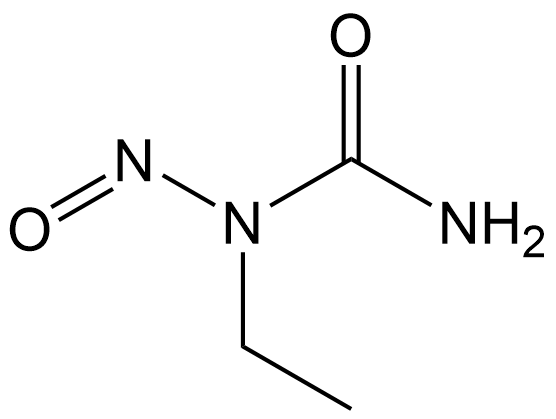
N-Ethyl-N-nitrosourea
N-Ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU, CAS No.: 759-73-9) is a potent DNA alkylating agent. It primarily alkylates DNA nucleotides, leading to base mismatches and strand breaks, thereby causing gene mutations. ENU can induce benign and malignant tumors in various animal models, including those in neural tissues, stomach, esophagus, pancreas, respiratory tract, intestines, lymphoreticular tissues, skin, and kidneys. In in vitro experiments, the activity level of ENU is usually in the low micromolar to nanomolar range, depending on the cell type and experimental conditions. In cell and animal models, ENU is often used to induce specific gene mutations to study gene function and disease mechanisms. The dose or concentration used in experiments typically depends on the experimental design and research objectives. In addition, ENU is also used to establish animal tumor models to investigate the mechanisms of tumor initiation and progression.
| Storage | -20°C, stored under nitrogen |
| M.Wt | 117.11 |
| Cas No. | 759-73-9 |
| Formula | C3H7N3O2 |
| Synonyms | N-Nitroso-N-ethylurea; ENU; NSC 45403 |
| Chemical Name | 1-ethyl-1-nitrosourea |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=NN(C(=O)N)CC |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |