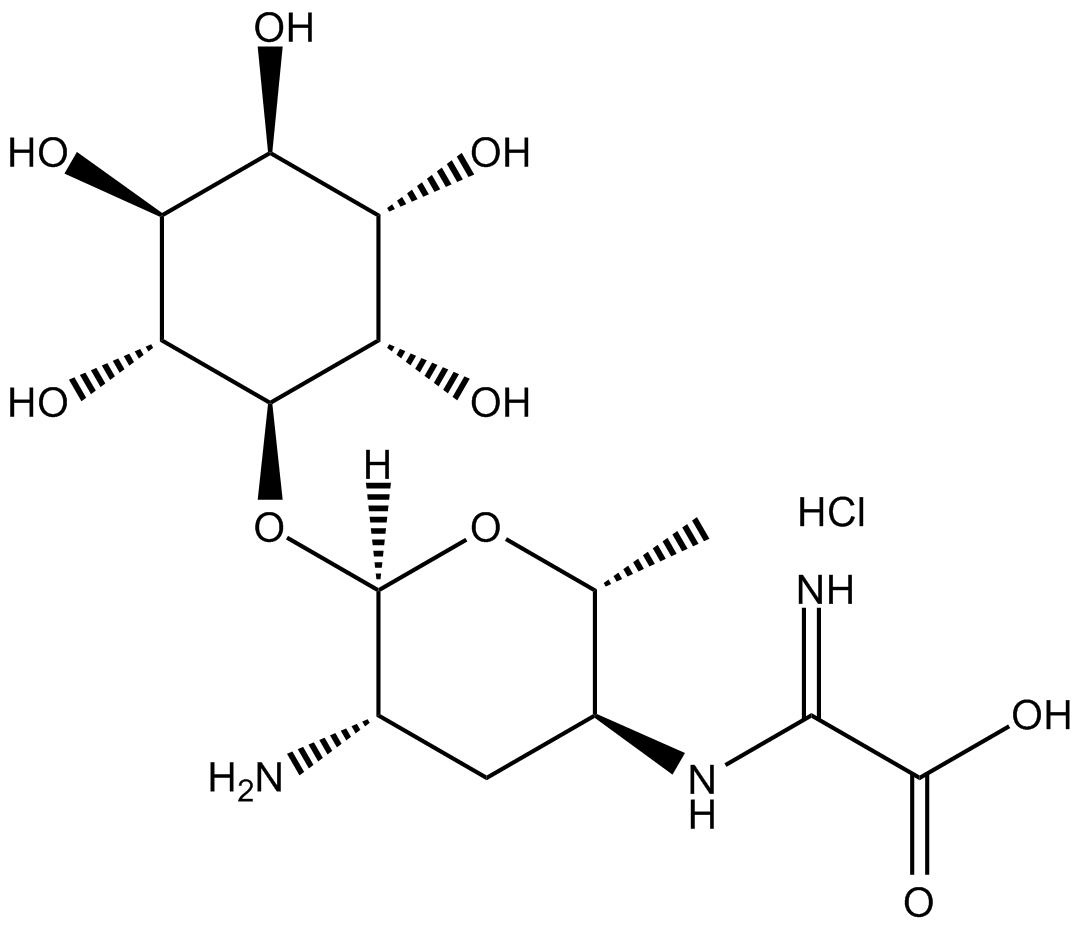
Kasugamycin (hydrochloride)
Kasugamycin is an aminoglycosidic antibiotic.
Aminoglycoside, a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial therapeutic agent, inhibits protein synthesis and contains as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside.
In vitro: Kasugamycin could inhibit protein synthesis by interacting with the 30S ribosomal subunit. The mechanism of inhibition of protein synthesis appeared to be different from that of other aminoglycosides, such as kanamycin, streptomycin, neomycin, gentamicin. The initiation complex formation on 30S ribosomes could be inhibited by kasugamycin but not by streptomycin, kanamycin or gentamicin, though the binding of fMet-tRNA to 70S ribosomes was inhibited by both streptomycin and by kasugamycin. [1].
In vivo: Five groups, each consisting of five guinea pigs, were infected with Shibaura strain; two groups were treated by injection with kasugamycin. All animals treated with 1 mcg/g were killed showing an average survival period of 7.4 days, which was close to the average survival period of 6.2 days in the control group; while all animals treated with 5 mcg/g survived. The other two groups were treated with kasugamycin from the icteric stage to the 10th day after infection. Two animals of the 5 mcg/g group survived, showing no leptospira in the kidney; the other three died in an average of 7.7 days. Three animals of the 10 mcg/g group survived; while the other two animals died in 6.5 days on an average . The total amounts of kasugamycin administered to the infected guinea pigs from the febrile stage were 10.8 mg (the 1 mcg/g group) and 54.0 mg (the 5 mcg/g group) [2].
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
References:
[1] Okuyama, A. ,Machiyama, N.,Kinoshita, T., et al. Inhibition by kasugamycin of initiation complex formation on 30S ribosomes. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 43(1), 196-199 (1971).
[2] Kitaoka M, Mori M, Arimitsu Y. In vitro and in vivo effects of kasugamycin on Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1975 Oct-Dec;28(5-6):285-90.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 415.8 |
| Cas No. | 19408-46-9 |
| Formula | C14H25N3O9·HCl |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in DMSO; ≥41.6 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming |
| Chemical Name | 3-O-[2-amino-4-[(carboxyiminomethyl)amino]-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-α-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl]-D-chiro-inositol, monohydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C[C@H]([C@H](C[C@@H]1N)NC(C(O)=O)=N)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O)O)O)[C@H]1O.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
L. icterohaemorrhagiae |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is < 4.16 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
50 μg/ml |
|
Applications |
When 50 μg/ml Kasugamycin was added to 5 tubes of Korthof medium inoculated with L. icterohaemorrhagiae, the growth of Leptospira was all inhibited. After 48 hours of incubation, 100 μg/ml Kasugamycin was added, although the subculture continued negative growth was shown, but not all cultures were inhibited. Similar results were obtained with other strains. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Guinea pigs |
|
Dosage form |
1 μg/g, 5μg/g, 10 μg/g |
|
Application |
All animals treated with 1 μg/g were killed and showed an average survival time of 7.4 days, which is similar to the average survival time of 6.2 days in the control group. All animals treated with 5 μg/g survived. From the icteric stage to the 10th day after infection, the other two groups were treated with kasugamycin. Two animals in the 5 μg/g group survived, and the kidneys did not have leptospira. The other three animals died on an average of 7.7 days. Three animals in the 10 μg/g group survived, while the other two animals died on an average of 6.5 days. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Kitaoka M, Mori M, Arimitsu Y. In vitro and in vivo effects of kasugamycin on Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1975 Oct-Dec;28(5-6):285-90. PubMed PMID: 1047116. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure