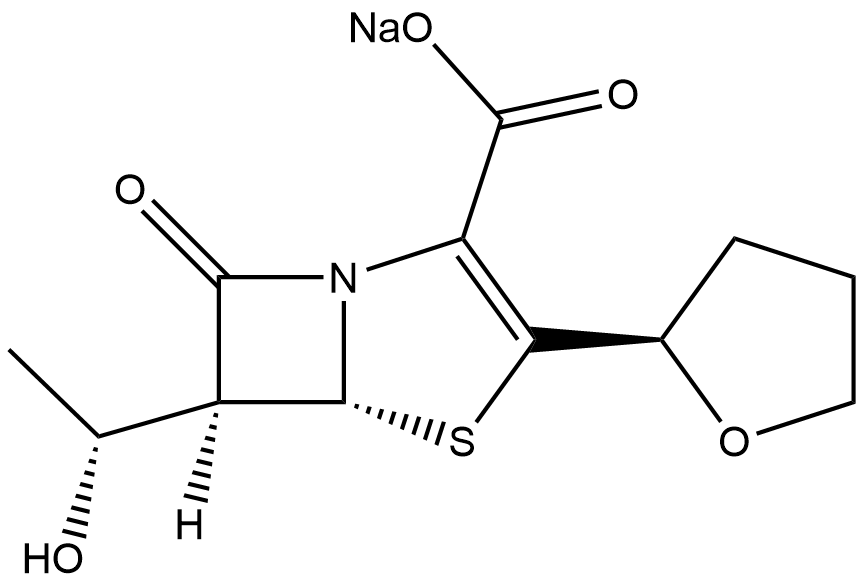
Faropenem sodium
Faropenem sodium (CAS No. 122547-49-3) is a non-classical β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the class of penem derivatives. Its mechanism of action involves blocking the synthesis of bacterial cell walls; specifically, it exhibits strong binding affinity to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), thereby exerting bactericidal effects. This agent possesses a broad antimicrobial spectrum, and it is stable to both β-lactamases and dehydropeptidase-I (DHP-I). It demonstrates favorable oral absorption, with its antimicrobial activity remaining unaffected by food intake. Following parenteral administration, faropenem sodium achieves high concentrations in serum and interstitial fluid. In vivo, it is absorbed through the small intestine via a carrier-mediated transport system.
With the exception of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, faropenem sodium exerts potent inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., and a wide range of Gram-negative bacteria including Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Branhamella catarrhalis, manifesting robust biological activity. It is particularly efficacious against anaerobic bacteria. In vitro antimicrobial activity assays have been conducted to compare faropenem sodium with a panel of antibiotics, namely cefteram, cefixime, cefaclor, amoxicillin, cefotaxime, cefuroxime, clindamycin, imipenem, cefpodoxime, ciprofloxacin, piperacillin, Augmentin, metronidazole, tobramycin, and vancomycin. The results indicated that faropenem sodium exhibited superior anaerobic inhibitory activity over all the tested antibiotics, rendering it the most potent anti-anaerobic antibiotic reported to date. Additionally, it demonstrates greater efficacy against Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus spp., and most Gram-negative bacteria compared to cefteram, cefixime, cefaclor, and amoxicillin, and its potency is 5–10 times higher than that of third-generation cephalosporins.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of faropenem sodium against all clinically isolated strains tested was determined to be 0.78 μg/mL. It showed significantly higher efficacy against Campylobacter spp. than erythromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin, and ofloxacin. Faropenem sodium also displayed marked inhibitory effects on Streptococcus spp. and Clostridioides difficile, with an MIC₉₀ value ≤ 1 μg/mL; for Bacteroides fragilis, the MIC₉₀ value was ≤ 4 μg/mL. As noted previously, its bactericidal activity is not influenced by food.
| Storage | Seal and dry at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 307.30 |
| Cas No. | 122547-49-3 |
| Formula | C12H14NNaO5S |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | sodium (5R,6S)-6-((R)-1-hydroxyethyl)-7-oxo-3-((R)-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(O[Na])C1=C([C@@H]2OCCC2)S[C@@H](N31)[C@]([C@H](O)C)([H])C3=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |