Enterocin
Enterocin is an antibiotic isolated from cultures of two strains of Streptomyces, Streptomyces candidus var. enterostaticus WS-8096 and variant M-127 of Streptomyces viridochromogenes. This antibiotic shows activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, especially against the Enterobacteriaceae [1]. Enterocin was named for its strong activity against Enterobacteriaceae.
The elementary analysis and mass spectroscopic measurement suggested that the molecular formula was C72H20O10. The ultraviolet absorption gave two maximal peaks at 250 nm and 283 nm in methanol [1]. The mechanism of enterocin is unknown. Enterocin acts synergistically with streptomycin and chloramphenicol. The genetics of enterocin biosynthesis has been extensively investigated. Enterocin is a small molecular weight secondary metabolite [1].
Reference:
[1] Miyairi N, SAKAI H E I I, KONOMI T, et al. Enterocin, a new antibiotic [J]. The Journal of antibiotics, 1976, 29(3): 227-235.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 444.4 |
| Cas No. | 59678-46-5 |
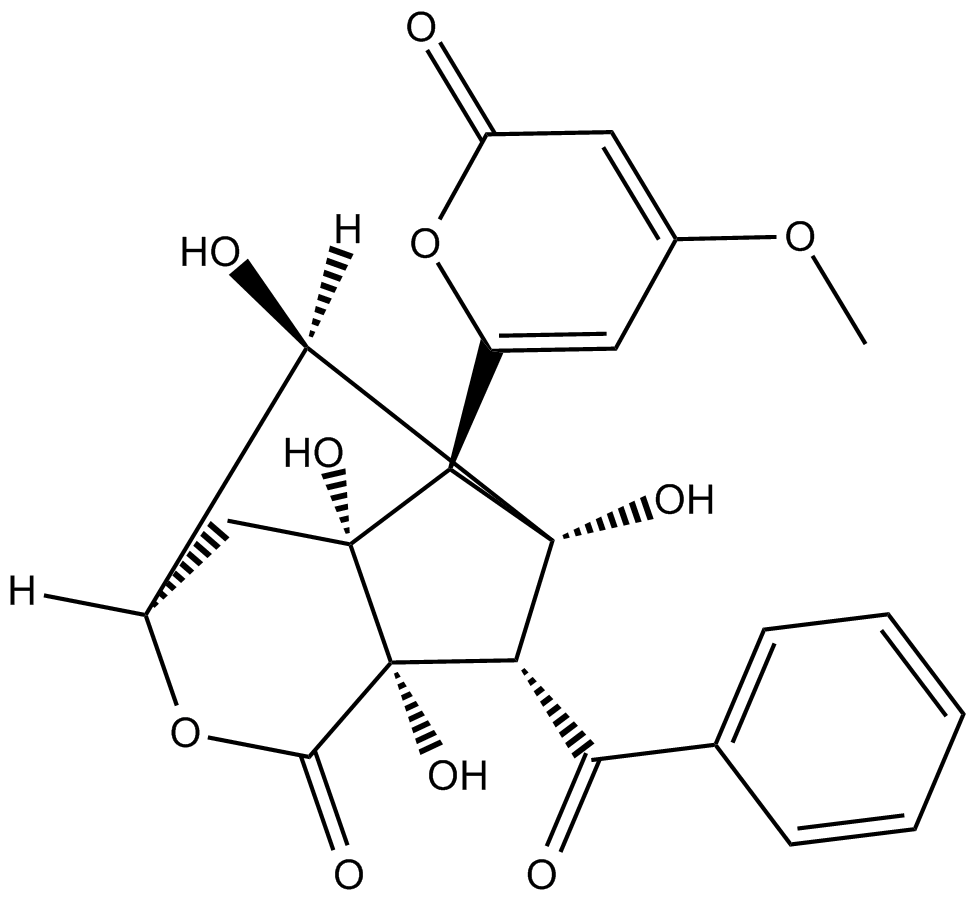
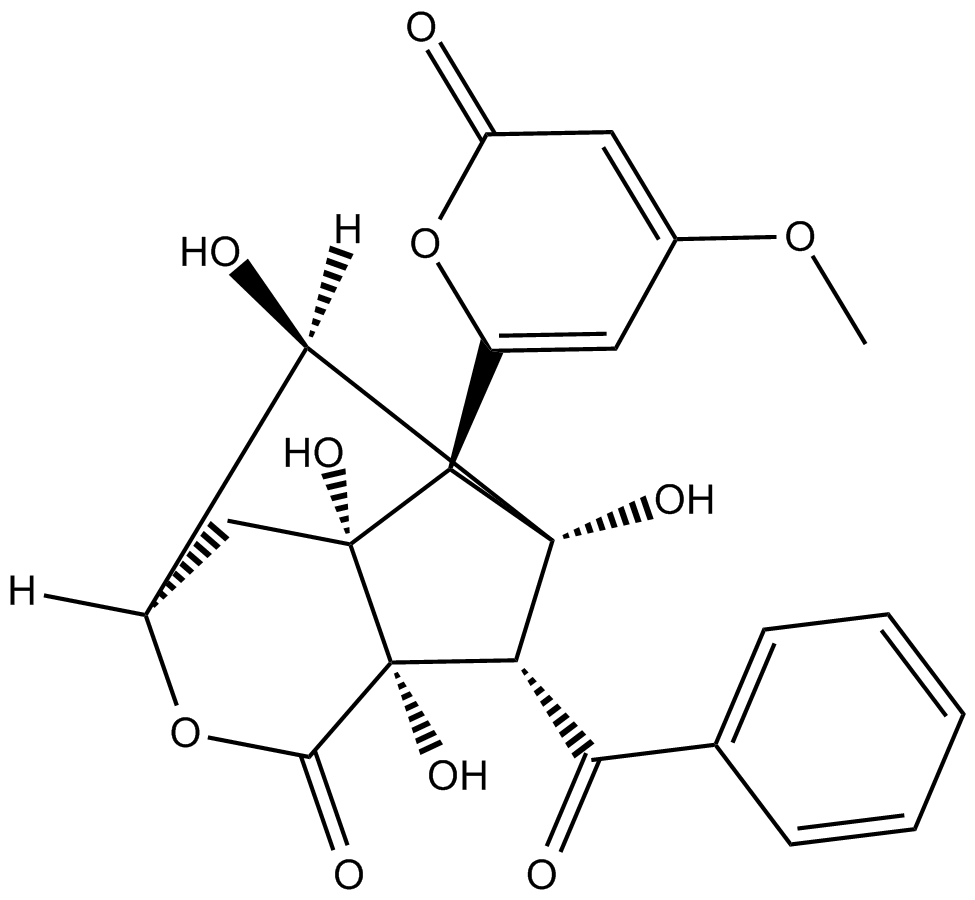
| Formula | C22H20O10 |
| Synonyms | Vulgamycin |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | (3R,4aR,5S,6S,7S,7aS,8R)-7-benzoylhexahydro-4a,6,7a,8-tetrahydroxy-5-(4-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-pyran-6-yl)-3,6-methanocyclopenta[c]pyran-1(3H)-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COC(C=C([C@H]([C@](C[C@H]([C@H]1O)OC2=O)([C@]2([C@H]2C(c3ccccc3)=O)O)O)[C@@]12O)O1)=CC1=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure