EGTA
EGTA, also known as egtazic acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid, a calcium chelator. It can protects against cell death caused by nitric oxide-induced calcium influx into nerve cells[1,2].
References:
[1]. Boullerne A I, Nedelkoska L, Benjamins J A. Role of calcium in nitric oxide-induced cytotoxicity: EGTA protects mouse oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 2001, 63(2): 124-135.
[2]. Fisher A E O, Hague T A, Clarke C L, et al. Catalytic superoxide scavenging by metal complexes of the calcium chelator EGTA and contrast agent EHPG. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2004, 323(1): 0-167.
- 1. Yingzi Wang, Haozhong Huang, et al. "Talin1 modulates the Piezo1–YAP axis to regulate endothelial cell inflammation and atherosclerosis." Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Dec 26;83(1):40. PMID: 41452468
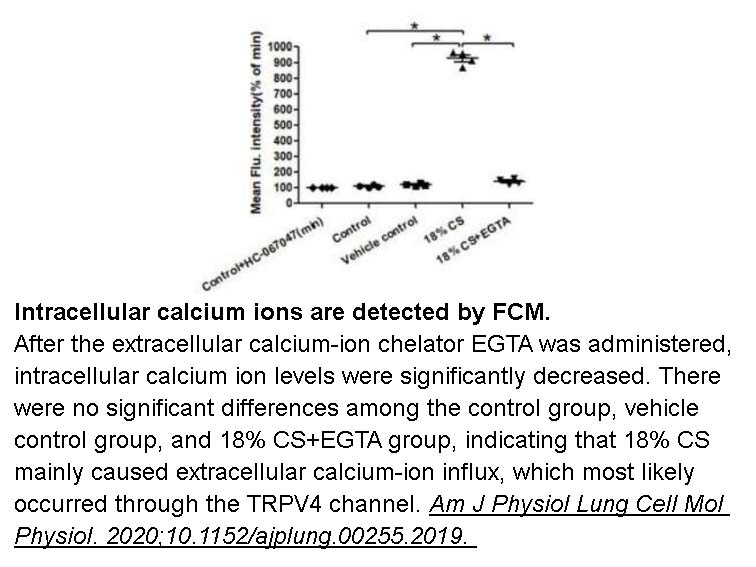
- 2. Yu Q, Wang D, et al. "Adipose-derived Exosomes Protect the Pulmonary Endothelial Barrier in Ventilator-induced Lung Injury by Inhibiting the TRPV4/Ca2+ Signaling Pathway." Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;10.1152/ajplung.00255.2019 PMID: 32073873
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at RT |
| M.Wt | 380.35 |
| Cas No. | 67-42-5 |
| Formula | C14H24N2O10 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; insoluble in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 3,12-bis(carboxymethyl)-6,9-dioxa-3,12-diazatetradecane-1,14-dioic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
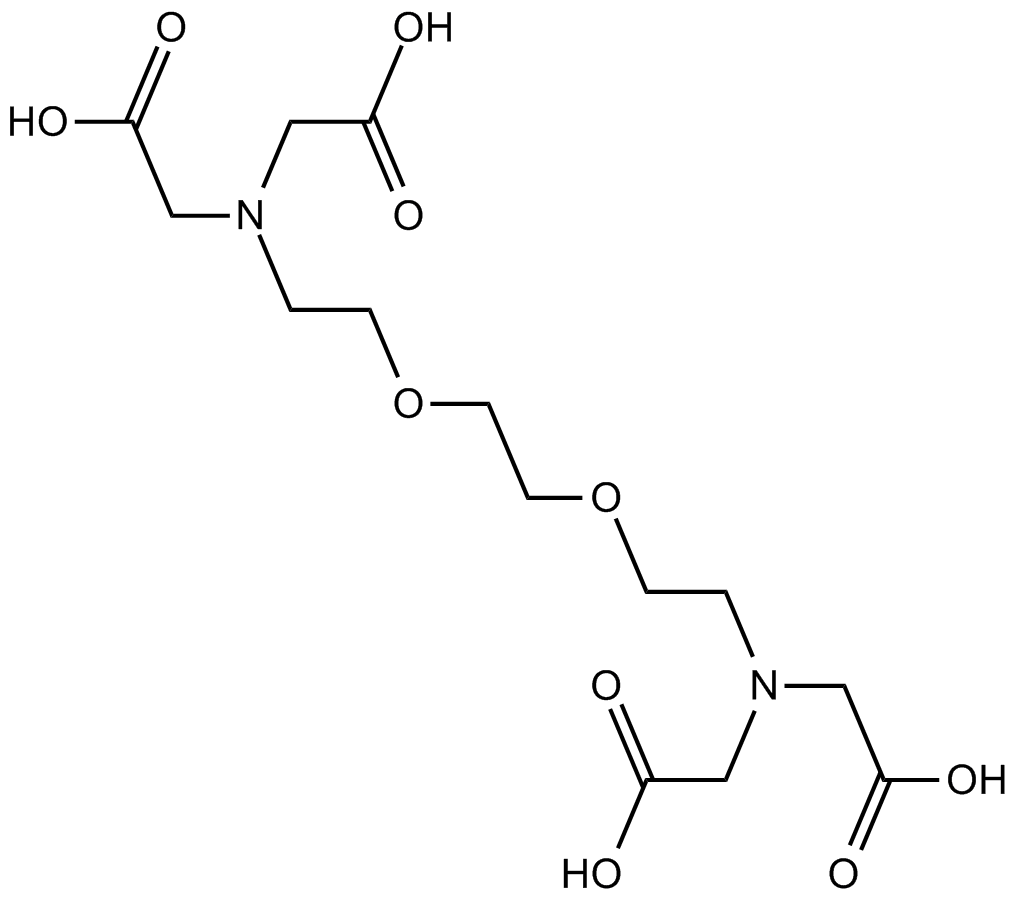
| Canonical SMILES | OC(CN(CCOCCOCCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure

Related Biological Data