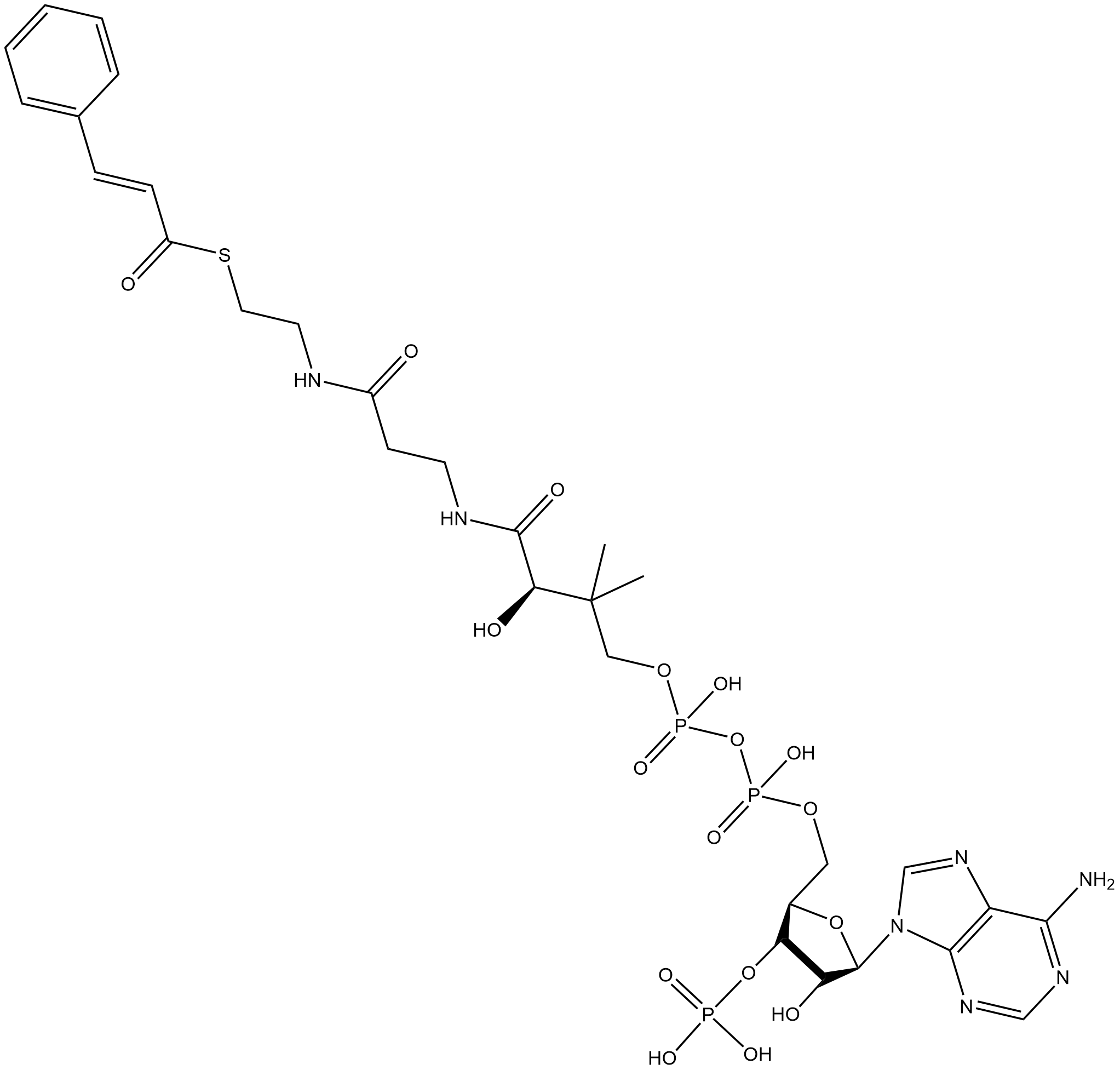
(E)-Cinnamoyl-coA
(E)-Cinnamoyl-CoA (CAS 76109-04-1) is a thioester conjugate of trans-cinnamic acid and CoA, found in microorganisms and plants, and serves as a key intermediate in aromatic metabolism. In microorganisms, it is a crucial intermediate in anaerobic phenylalanine fermentation, where the transfer and regeneration of the CoA group are mediated by specific CoA transferases such as FldA, acting as an "active carrier" in the metabolic cycle. In plants, it represents a critical node in lignin biosynthesis, with its metabolic flux and monomer diversity regulated by cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR); it also participates in plant defense and natural product synthesis, with its levels controlled by enzyme activity, gene expression, and environmental signals. Its unique structure and multifunctionality make it an important link between carbon and energy metabolism, biosynthetic pathways, and stress responses, highlighting its significant research and application potential.
Reference:
[1] Ye P, Su J, Lin J, Li Y, Wu H. Identification of a cinnamoyl-CoA reductase from Cinnamomum cassia involved in trans-cinnamaldehyde biosynthesis. Planta. 2024 Apr 30;259(6):138. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04419-w. PMID: 38687380.
[2] Sattler SA, Walker AM, Vermerris W, Sattler SE, Kang C. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of Cinnamoyl-CoA Reductases. Plant Physiol. 2017 Feb;173(2):1031-1044. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01671. Epub 2016 Dec 12. PMID: 27956488; PMCID: PMC5291045.
[3] Dickert S, Pierik AJ, Linder D, Buckel W. The involvement of coenzyme A esters in the dehydration of (R)-phenyllactate to (E)-cinnamate by Clostridium sporogenes. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Jun;267(12):3874-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01427.x. PMID: 10849007.
[4] Heider J. A new family of CoA-transferases. FEBS Lett. 2001 Dec 14;509(3):345-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03178-7. PMID: 11749953.
[5] J. Ralph, R.D. Hatfield, J. Piquemal, N. Yahiaoui, M. Pean, C. Lapierre, & A.M. Boudet, NMR characterization of altered lignins extracted from tobacco plants down-regulated for lignification enzymes cinnamylalcohol dehydrogenase and cinnamoyl-CoA reductase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (22) 12803-12808, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.22.12803 (1998).
[6] Ma QH, Tian B. Biochemical characterization of a cinnamoyl-CoA reductase from wheat. Biol Chem. 2005 Jun;386(6):553-60. doi: 10.1515/BC.2005.065. PMID: 16006242.
[7] Wang JP, Liu B, Sun Y, Chiang VL, Sederoff RR. Enzyme-Enzyme Interactions in Monolignol Biosynthesis. Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jan 11;9:1942. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01942. PMID: 30693007; PMCID: PMC6340093.
| Physical Appearance | A Solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C away from light. |
| M.Wt | 897.68 |
| Cas No. | 76109-04-1 |
| Formula | C30H42N7O17P3S |
| Synonyms | (E)-Cinnamoyl coenzyme A; trans-Cinnamoyl-CoA |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | S-(2-(3-((2R)-4-(((((((2R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido)propanamido)ethyl) (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enethioate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(SCCNC(CCNC([C@H](O)C(C)(C)COP(OP(OC[C@@H]1C(OP(O)(O)=O)C(O)[C@H](N2C(N=CN=C3N)=C3N=C2)O1)(O)=O)(O)=O)=O)=O)/C=C/C4=CC=CC=C4 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |