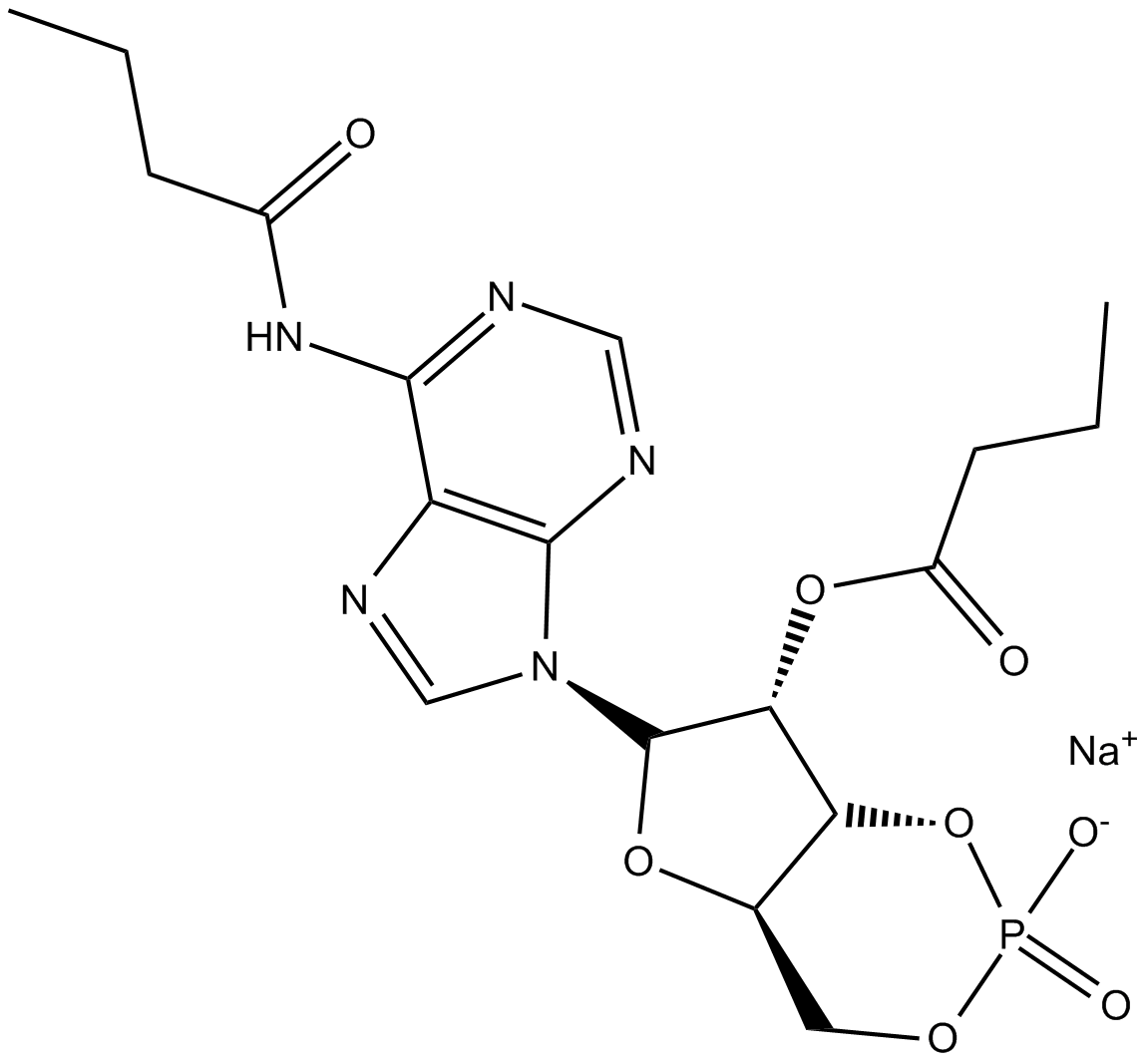
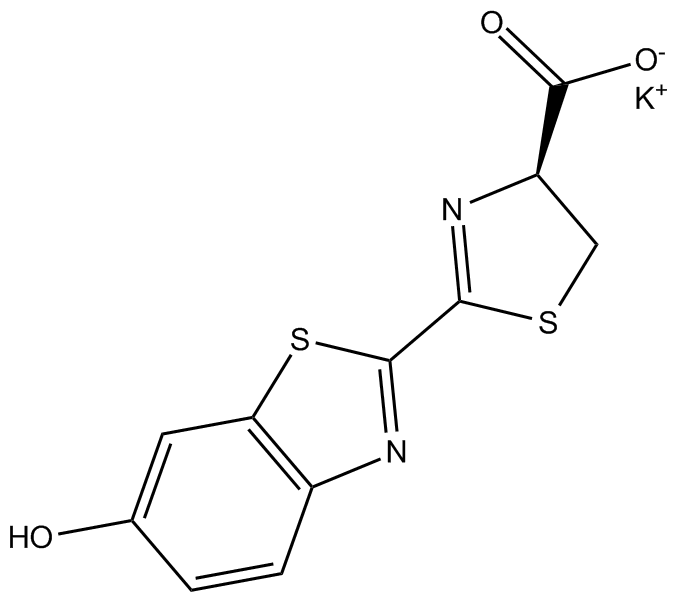
Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt
Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt (CAS 16980-89-5) is a cell-permeable, stable cyclic AMP (cAMP) analog, functioning as a selective activator of cAMP-dependent pathways in various cell types and exhibiting modulating activity on intracellular signaling processes in multiple tissues. Additionally, it serves as a phosphodiesterase () inhibitor, contributing to the regulation of cAMP levels within cells.
In experimental contexts, Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt elevates intracellular cAMP concentrations and enhances the activation of protein kinase A (PKA), as demonstrated by [IC50/EC50/other values], tested against [cell lines/organisms]. It can also induce differentiation, promote cellular proliferation, or modulate inflammatory responses by mimicking endogenous cAMP actions and bypassing some of the regulatory constraints imposed on native cyclic nucleotides.
In research and application settings, Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt is widely used as a tool compound for investigating cAMP-mediated cellular signaling, studying the mechanisms underlying cAMP-dependent gene expression, or evaluating the role of cAMP in processes such as inflammation, wound healing, and cell differentiation. Its usability in a broad range of experimental systems makes Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt a valuable agent for dissecting cAMP-regulated pathways and assessing pharmacological modulation of intracellular signaling cascades.
- 1. Xinyue Liao, Zhaoke Luo, et al. "Trigeminal nerve root compression induced neuroinflammatory response promotes mechanical allodynia through the CGRP/SP-Piezo2 axis via Ca 2+ signaling." Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Dec 3;31(1):3. PMID: 41340091
- 2. Robert I. McGeachan, Soraya Meftah, et al. "Divergent actions of physiological and pathological amyloid-β on synapses in live human brain slice cultures." Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 30;16(1):3753. PMID: 40307257
- 3. Li Li, Binglin Zhu, et al. "Identifying key regulators in neuronal transdifferentiation by gene regulatory network analysis." PNAS Nexus, pgaf365
- 4. Haoyang Zhuang, Shuhong Han, et al. "MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 mediated lung endothelial injury and altered hemostasis promote diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in murine lupus." bioRxiv. 2024 May 10:2024.05.07.593006. PMID: 38766226
- 5. Philipp Pottmeier, Danai Nikolantonaki, et al. "Sex-biased gene expression during neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells." Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 1:12:1341373. PMID: 38764741
- 6. Hongshuo Zhang, Qianyi Sun, et al. "Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase-4 regulates endometrial decidualization through a fatty acid β-oxidation pathway rather than lipid droplet accumulation." Mol Metab. 2024 Jun:84:101953. PMID: 38710444
- 7. Lewis W. Taylor, Elizabeth M. Simzer, et al. "p-tau Ser356 is associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology and is lowered in brain slice cultures using the NUAK inhibitor WZ4003." Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Jan 4;147(1):7. PMID: 38175261
- 8. Binglin Zhu, Emily Fisher, et al. "PTBP2 attenuation facilitates fibroblast to neuron conversion by promoting alternative splicing of neuronal genes." Stem Cell Reports. 2023 Nov 14;18(11):2268-2282. PMID: 37832540
- 9. Lewis W. Taylor, Elizabeth M. Simzer, et al. "Tau phosphorylated at serine 356 is associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology and can be lowered in mouse and human brain tissue using the NUAK inhibitor WZ4003." bioRxiv. August 29, 2023
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 491.37 |
| Cas No. | 16980-89-5 |
| Formula | C18H23N5NaO8P |
| Synonyms | Dibutyryl cAMP sodium salt; DBcAMP sodium salt |
| Solubility | ≥49.1 mg/mL in H2O; ≥23.7 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥3.21 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | sodium (4aR,6S,7R,7aR)-6-(6-butyramido-9H-purin-9-yl)-7-(butyryloxy)tetrahydro-4H-furo[3,2-d][1,3,2]dioxaphosphinin-2-olate 2-oxide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(CCC)O[C@H]1[C@H](N2C(N=CN=C3NC(CCC)=O)=C3N=C2)O[C@@](CO4)([H])[C@@]1([H])OP4(O[Na])=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Hippocampal neurons from 17E Sprague-Dawley rats |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 and 50 μM dibutyryl cAMP for 1 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Dibutyryl cAMP significantly inhibited neuronal glucose uptake in a dose-dependent manner. Neurons exposed to 50 μM dibutyryl cAMP showed only 13% of glucose uptake by the control neurons. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Mice, 20 ~ 25 g |
|
Dosage form |
600 nM/mouse Injected intraperitoneally for 4 days |
|
Applications |
Treatment with intraperitoneal injection of dibutyryl cAMP (600 nM/mouse) reversed zinc chloride- and lead acetate-induced avoidance memory retention impairments in mice. Thus, dibutyryl cAMP could be used to explore the potential role of protein kinase A pathways in zinc chloride- and lead acetate-induced avoidance memory alterations. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Prapong T, Uemura E, Hsu WH. G protein and cAMP-dependent protein kinase mediate amyloid beta-peptide inhibition of neuronal glucose uptake. Experimental Neurology, 2001, 167(1): 59-64. 2. Tabrizian K, Yazdani A, Baheri B, et al. Zinc chloride and lead acetate-induced passive avoidance memory retention deficits reversed by nicotine and bucladesine in mice. Biological Trace Element Research, 2016, 169(1): 106-113. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure