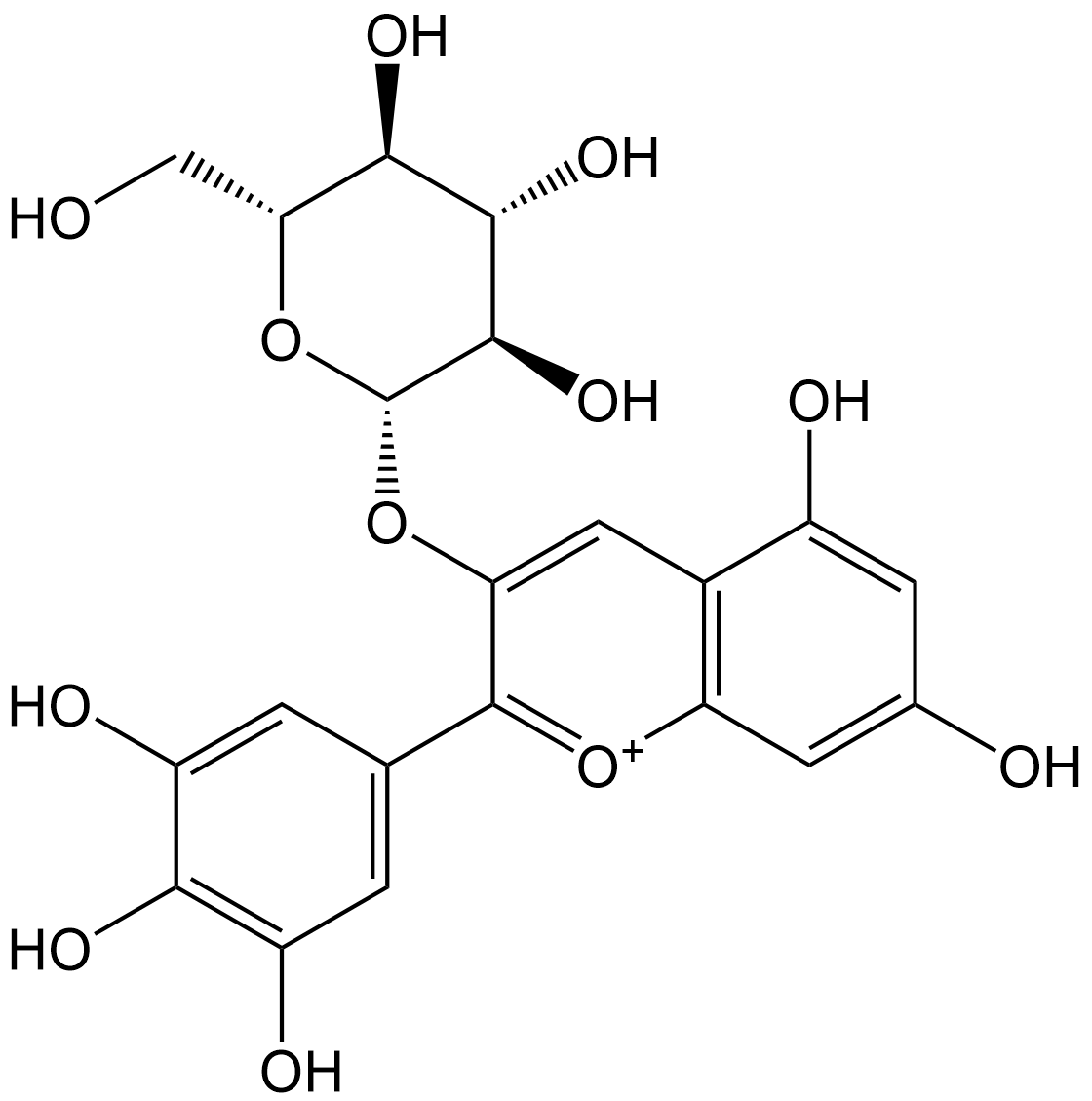
Delphinidin-3-B-D-glucoside
Delphinidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside (D3G, CAS 50986-17-9) primarily exerts its biological effects through the regulation of oxidative stress (reactive oxygen species [ROS], free radicals), inflammatory signaling pathways, and metabolism-related pathways. Its core bioactivity data are closely associated with its content, as well as its in vivo metabolic characteristics. D3G is one of the major anthocyanin components in black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.), with a content of 2.6±0.02 mg/g (peak area 343.7±2.5 mAU) in the Geomjeongkong-2 (G2) variety, and a higher content of 3.8±0.03 mg/g (peak area 504.1±3.4 mAU, p<0.001) in the Tawonkong (TW) variety. Notably, the total anthocyanin content in the G2 variety is significantly higher than that in TW (19.7±0.09 mg/g vs. 13.1±0.08 mg/g, p<0.001).
Regarding in vivo metabolism, following oral administration in rats, D3G is absorbed in its intact glycoside form, with two plasma concentration peaks observed at 15 and 60 minutes. The primary metabolite identified is 4'-O-methyl delphinidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside (MDp3G), which predominates in the liver. Both the parent compound and its metabolite are detected in the kidney. Methylation occurs exclusively at the 4'-OH position during metabolism, with no 3'-O-methyl derivatives detected, indicating that methylation at the 4'-position is the principal metabolic pathway.
In terms of bioactivity, D3G exhibits antioxidant, anticancer, hypoglycemic, and anti-inflammatory properties. It confers protective effects by scavenging ROS and inhibiting free radical-induced damage, and also participates in metabolic regulation. As a naturally occurring plant-derived compound, D3G is abundant in black soybean, making it a potential natural colorant and functional food ingredient. Its rapid absorption and well-defined metabolic profile in vivo provide a solid foundation for further studies on its biological activities.
References:
[1] Ichiyanagi T, Rahman MM, Kashiwada Y, Ikeshiro Y, Shida Y, Hatano Y, Matsumoto H, Hirayama M, Konishi T. Absorption and metabolism of delphinidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside in rats. Biofactors. 2004;21(1-4):411-3. doi: 10.1002/biof.552210181. PMID: 15630238.
[2] Koh K, Youn JE, Kim HS. Identification of anthocyanins in black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) varieties. J Food Sci Technol. 2014 Feb;51(2):377-81. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0493-y. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PMID: 24493899; PMCID: PMC3907645.
| Storage | -20℃, sealed storage, away from moisture and light |
| M.Wt | 465.39 |
| Cas No. | 50986-17-9 |
| Formula | C21H21O12+ |
| Synonyms | Delphinidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside, D3G |
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chromenylium |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC1=CC(C2=[O+]C(C=C(O)C=C3O)=C3C=C2O[C@H]4[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O4)=CC(O)=C1O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure