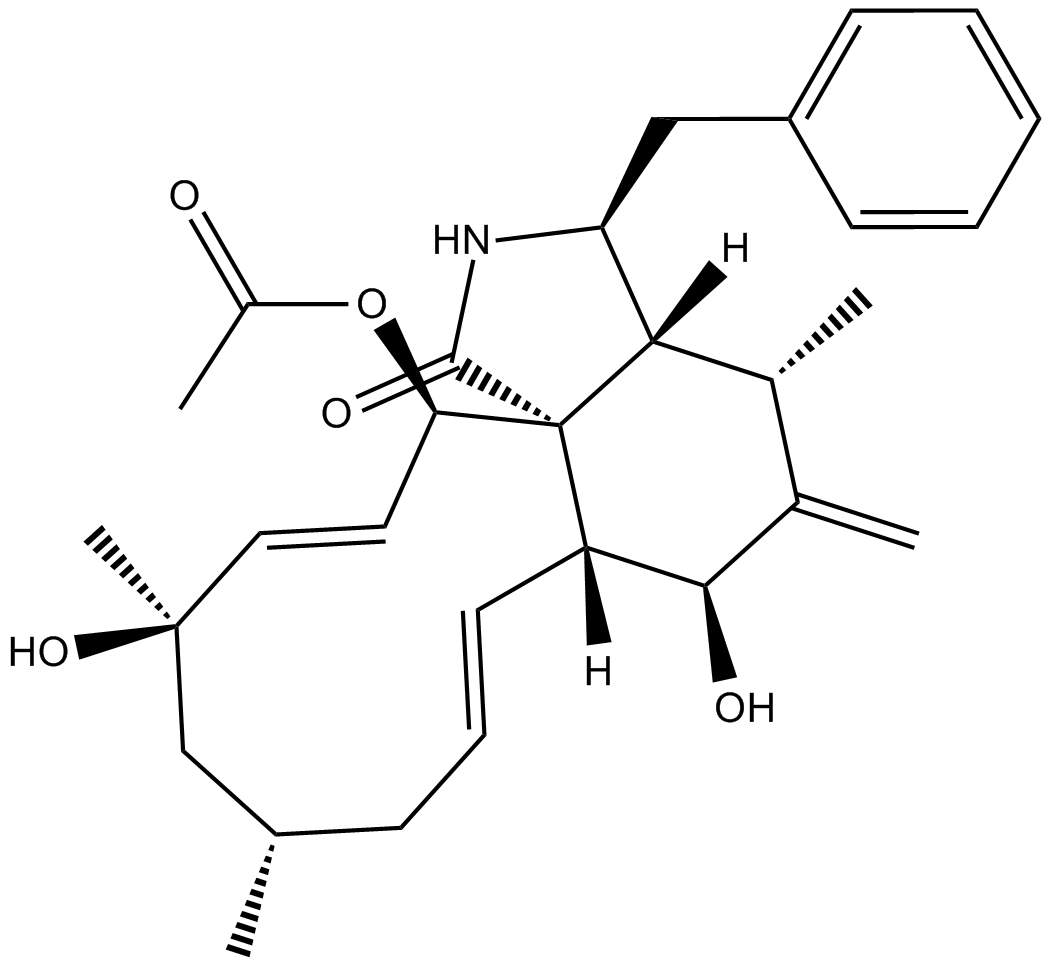
Cytochalasin H
Cytochalasin H is a potent inhibitor of actin incorporation into filaments [5].
The cytochalasins are a group of cell-permeable cytotoxic fungal metabolites that disrupt actin filaments and actin-associated structures in a wide variety of cell types. Cytochalasins have been valuable agents in the study of the actin self-assembly mechanism [1][2][3][4].
Cytochalasin H is a potent inhibitor of actin incorporation into filaments. Cytochalasin H, the active constituent of an ethanolic extract of Gleditsia sinensis thorns (EEGS), had anti-angiogenic activity in vitro and in vivo via suppression of pro-angiogenic proteins, such as endothelin-1 (ET-1) and metallopeptidase 2 (MMP2). In chicken embryos, the calculated LD50 for cytochalasin H was 6.2 μg per egg [6][7].
In an in ovo tumor xenograft model, cytochalasin H significantly decreased tumor weight by 40%. In a chick CAM assay, cytochalasin H at 125 ng per egg effectively inhibited the angiogenesis by 50%. Intraperitoneal injections of cytochalasin H at 2.5 mg/kg/d inhibited A549-xenografed tumor growth without any signs of toxicity [6][7].
References:
[1]. Brenner SL, Korn ED. The effects of cytochalasins on actin polymerization and actin ATPase provide insights into the mechanism of polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):841-4.
[2]. Lin DC, Tobin KD, Grumet M, et al. Cytochalasins inhibit nuclei-induced actin polymerization by blocking filament elongation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):455-60.
[3]. Flaumenhaft R, Dilks JR, Rozenvayn N, et al. The actin cytoskeleton differentially regulates platelet alpha-granule and dense-granule secretion. Blood. 2005 May 15;105(10):3879-87.
[4]. Walling EA1, Krafft GA, Ware BR. Actin assembly activity of cytochalasins and cytochalasin analogs assayed using fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jul;264(1):321-32.
[5]. Yahara I, Harada F, Sekita S, et al. Correlation between effects of 24 different cytochalasins on cellular structures and cellular events and those on actin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):69-78.
[6]. Lee J, Yi JM, Kim H, et al. Cytochalasin H, an active anti-angiogenic constituent of the ethanol extract of Gleditsia sinensis thorns. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(1):6-12.
[7]. Yi JM, Kim J, Park JS, et al. In Vivo Anti-tumor Effects of the Ethanol Extract of Gleditsia sinensis Thorns and Its Active Constituent, Cytochalasin H. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(6):909-12.
| Physical Appearance | A white lyophilisate |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 493.6 |
| Cas No. | 53760-19-3 |
| Formula | C30H39NO5 |
| Synonyms | 17-Deoxo-21-acetylzygosporin D,Kodocytochalasin 1,Paspalin P1 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | (3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7E,10S,12R,13E,15R,15aR)-15-(acetyloxy)-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,9,10,11,12,15-dodecahydro-6,12-dihydroxy-4,10,12-trimethyl-5-methylene-3-1H-cycloundec[d]isoindol-1-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1N[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)[C@]([C@]31[C@H](OC(C)=O)/C=C/[C@](C)(O)C[C@@H](C)C/C=C/[C@@]3([H])[C@@H]4O)([H])[C@H](C)C4=C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity ≥ 95.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure