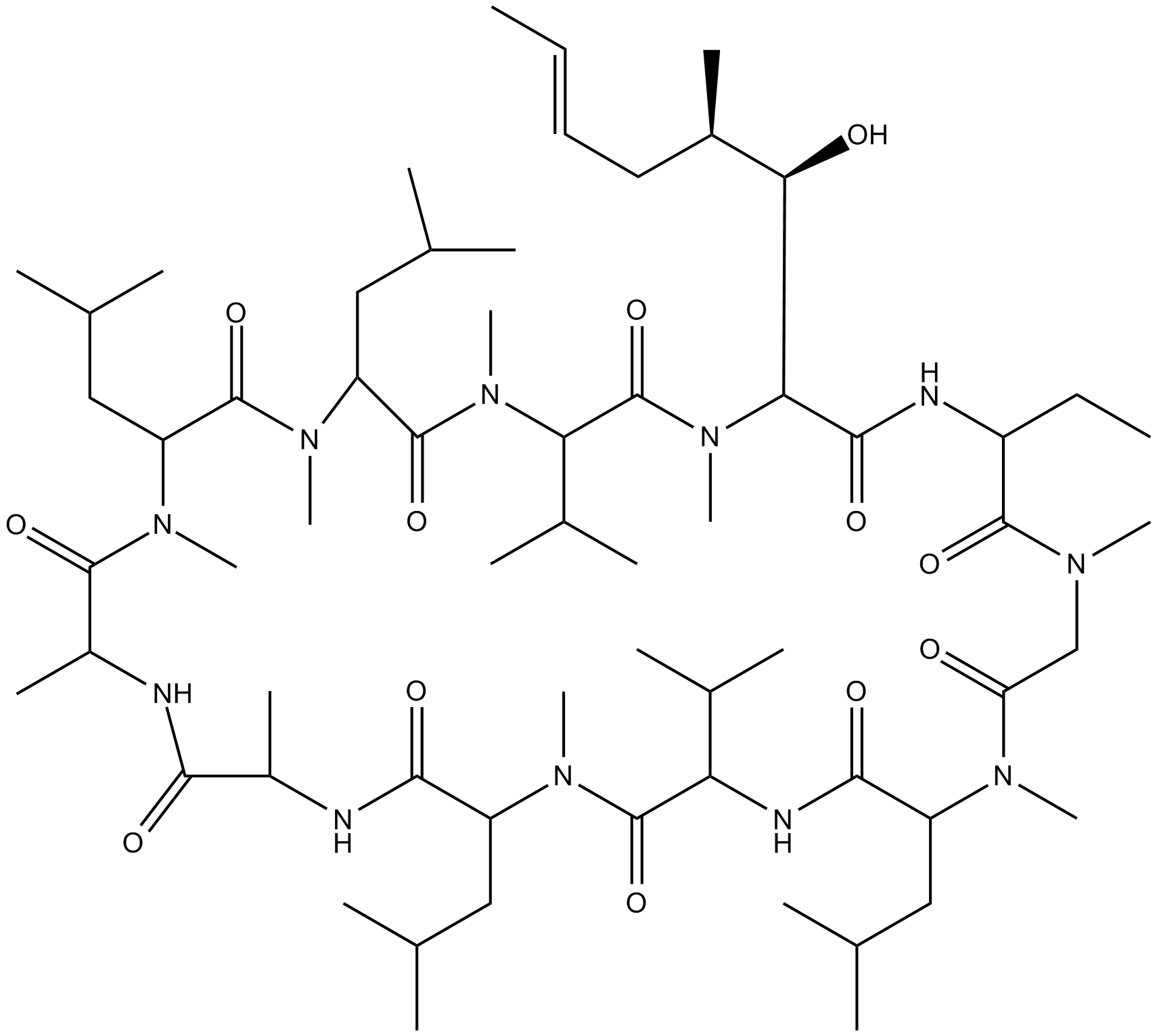
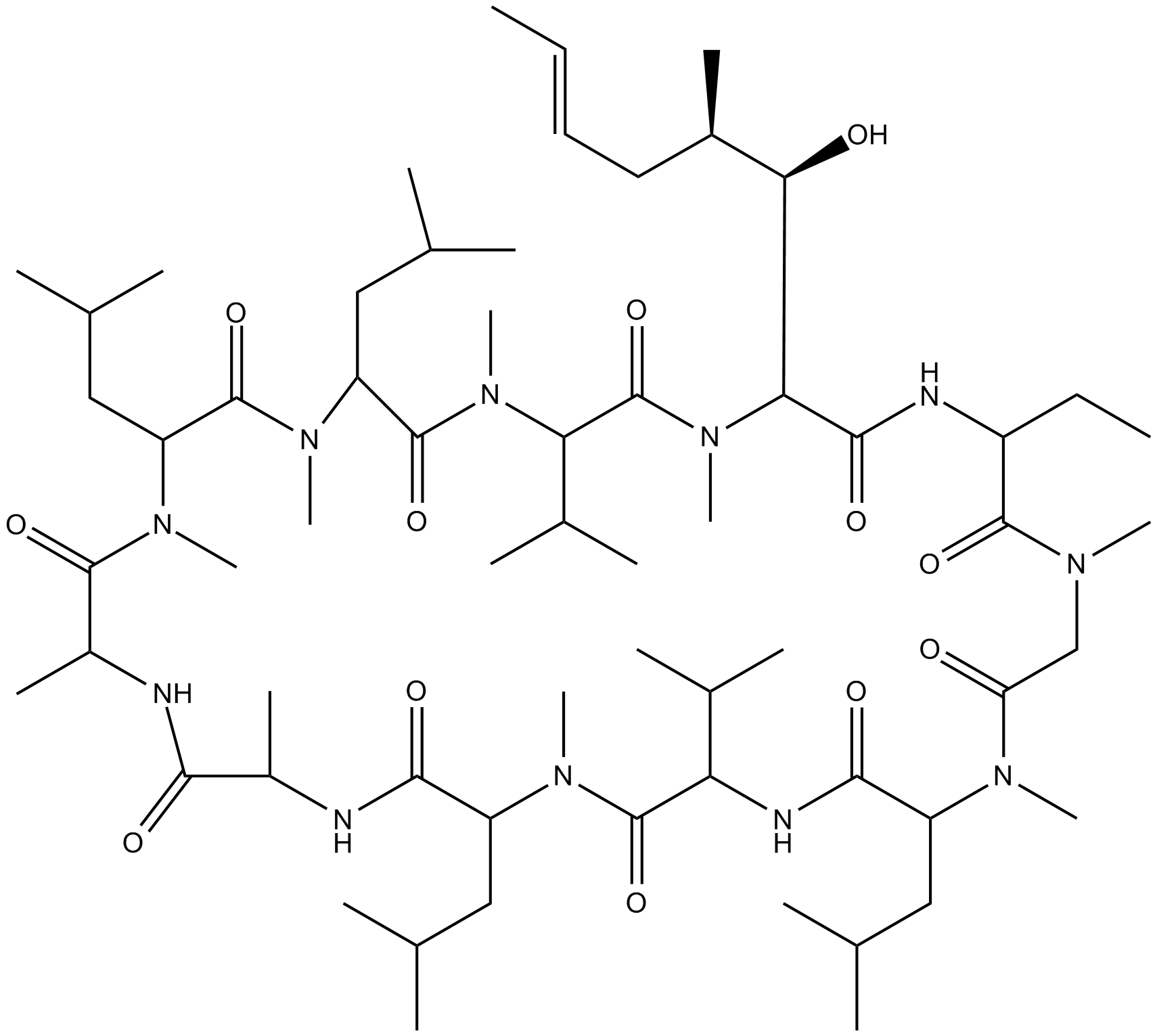
Cyclosporin
Cyclosporin (CAS No. 79217-60-0) is a class of cyclic undecapeptides produced by soil fungi, comprising several variants (A, B, C, D, E, etc.), among which Cyclosporin A (CsA) represents the principal bioactive member. Its core biological functions include immunosuppression and modulation of mitochondrial function. The primary molecular targets are members of the cyclophilin family, especially Cyclophilin A (CypA). By forming a drug–cyclophilin complex, CsA inhibits the activity of the phosphatase calcineurin, thereby blocking the dephosphorylation of the transcription factor NF-AT and suppressing the expression of cytokines such as IL-2. In addition, CsA inhibits p38 MAPK activation in a CypA-dependent manner. CsA can also bind specifically to Cyclophilin D, thereby blocking the mitochondrial Ca²⁺-dependent permeability transition (MPT) pore.
The IC₅₀ of CsA exhibits marked cell type- and target-specificity. For example, the IC₅₀ for inhibition of splenocyte proliferation in Ppia⁺/⁺ mice is 25 nM (with complete inhibition at 100 nM), whereas the IC₅₀ in Ppia⁻/⁻ cells is at least an order of magnitude higher. The effective concentration for inhibition of the mitochondrial MPT pore is 100–300 nM, a range in which CsA, CsB, CsC, and CsD are active, whereas CsE is inactive.
Commonly used experimental concentrations include 0.1 nM–2.5 μM for in vitro cell-based assays (e.g., inhibition of T-cell proliferation and signaling pathway studies). In animal models, typical dosing regimens in mice involve intraperitoneal injection of 30 mg/kg/day to suppress immune responses in wild-type animals and 70–90 mg/kg/day to suppress immune responses in Ppia⁻/⁻ mice. Clinically, cyclosporin is administered orally and is primarily used as an anti-rejection agent in organ transplantation. The therapeutic concentration is usually defined with reference to CsA, adjusted according to the patient’s immune status. The principal immunosuppressive effect is achieved through inhibition of T-cell activation, and CsA is characterized by high membrane permeability and suitability for oral administration.
References:
[1] Colgan J, Asmal M, Yu B, Luban J. Cyclophilin A-deficient mice are resistant to immunosuppression by cyclosporine. J Immunol. 2005 May 15;174(10):6030-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6030. PMID: 15879096.
[2] Efimov SV, Dubinin MV, Kobchikova PP, Zgadzay YO, Khodov IA, Belosludtsev KN, Klochkov VV. Comparison of cyclosporin variants B-E based on their structural properties and activity in mitochondrial membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 11;526(4):1054-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.184. Epub 2020 Apr 16. PMID: 32307084.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C away from light for 2 years |
| M.Wt | 1202.61 |
| Cas No. | 79217-60-0 |
| Formula | C62H111N11O12 |
| Solubility | ≥60.15mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 30-ethyl-33-((1R,2R,E)-1-hydroxy-2-methylhex-4-en-1-yl)-6,9,18,24-tetraisobutyl-3,21-diisopropyl-1,4,7,10,12,15,19,25,28-nonamethyl-1,4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28,31-undecaazacyclotritriacontan-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29,32-undecaone |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CN(C(C(C)NC(C(C)NC(C(N(C)C(C(C(C)C)NC(C(N(C(CN(C(C(NC(C([C@H](O)[C@H](C)C/C=C/C)N(C)C(C(C(C)C)N(C)C(C1CC(C)C)=O)=O)=O)CC)=O)C)=O)C)CC(C)C)=O)=O)CC(C)C)=O)=O)=O)C(CC(C)C)C(N1C)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure