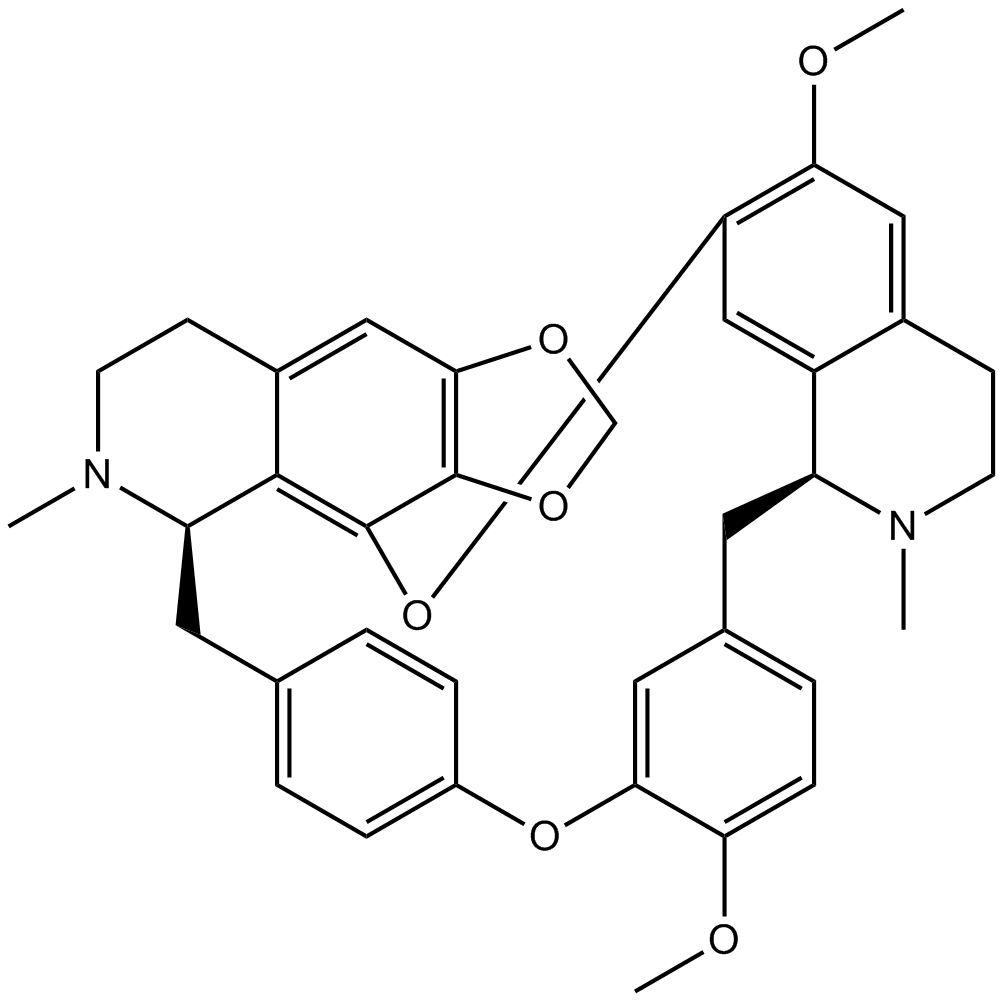
Cepharanthine
IC50: 90 microM for the antiperoxidant potency
Cepharanthine is a biscoclaurine alkaloid extracted from Stephania cepharantha Hayata, which is widely used for the treatment of many acute and chronic diseases. The extract of Stephania cepharantha Hayata contains biscoclaurine alkaloids such as cepharanthine, which have been used widely for the treatment of radiation-induced leukopenia.
In vitro: Cepharanthine was found to exert antitumor effects by augmenting the immunological responses of the host, or by exerting apoptosis-inducing effects [1].
In vivo: Combined therapy of cepharanthine and S-1 (a new oral antineoplastic agent) showed antitumor effects on human OSCC xenografts and induced apoptotic cells in tumors significantly. Immunohistochemistry results showed TS and DPD expressions down-regulated and OPRT expression up-regulated in tumors treated with cepharanthine plus S-1 [2].
Clinical trial: In order to examine the clinical efficacy of cepharanthin for preventing chemotherapy-caused leukopenia in lung cancer patients, a randomized trial was carried out. The results suggested that administration of cepharanthin had an obvious antileukopenic effect in anticancer treatment, which made it possible to reduce the period of risk for infection and allow effective regimens to be repeatedly administered in a shorter interval [3].
References:
[1] Furusawa S,Wu J. The effects of biscoclaurine alkaloid cepharanthine on mammalian cells: implications for cancer, shock, and inflammatory diseases. Life Sci.2007 Feb 27;80(12):1073-9.
[2] Harada K,Ferdous T,Itashiki Y,Takii M,Mano T,Mori Y,Ueyama Y. Effects of cepharanthine alone and in combination with fluoropyrimidine anticancer agent, S-1, on tumor growth of human oral squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Anticancer Res.2009 Apr;29(4):1263-70.
[3] Saito R,Tsuchiya S,Ishizuka T,Fueki N,Ezawa K,Minato K,Nakano H,Takise A,Kurihara M,Fueki R. Clinical effects of cepharanthin (Ceph.) on leukopenia by chemotherapy in lung cancer patients. Nihon Gan Chiryo Gakkai Shi.1989 Dec 20;24(11):2587-93.
- 1. Yang Y, Ji N, et al. "Modulating the function of ABCB1: in vitro and in vivo characterization of sitravatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor." Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020;10.1002/cac2.12040. PMID:32525624
- 2. Wu ZX, Teng QX, et al. "Tepotinib reverses ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells." Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Aug;166:120-127. PMID:31078601
- 3. Zhang XY, Zhang YK, et al. "Osimertinib (AZD9291), a Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor, Reverses ABCB1-Mediated Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells." Molecules. 2016 Sep 15;21(9). pii: E1236. PMID:27649127
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 606.71 |
| Cas No. | 481-49-2 |
| Formula | C37H38N2O6 |
| Solubility | ≥21.9 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥24.6 mg/mL in EtOH |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CN(CC1)[C@H](CC(C=C2)=CC=C2OC3=CC(C[C@@H](C4=C5)N(C)CCC4=C6)=CC=C3OC)C(C1=CC7=C8OCO7)=C8OC5=C6OC |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
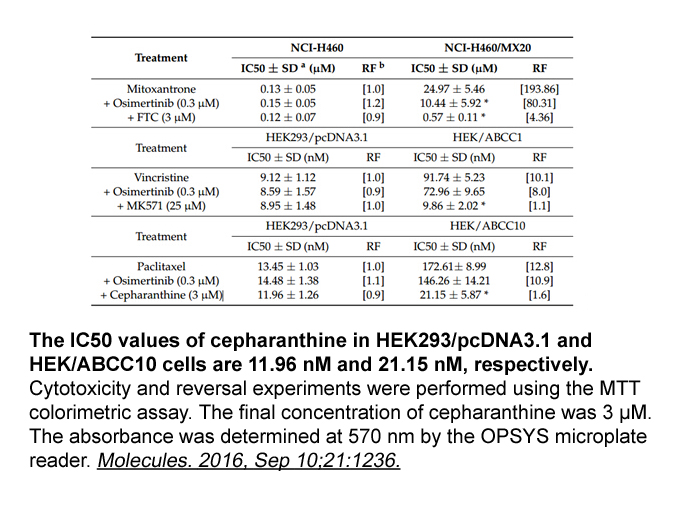
Related Biological Data









