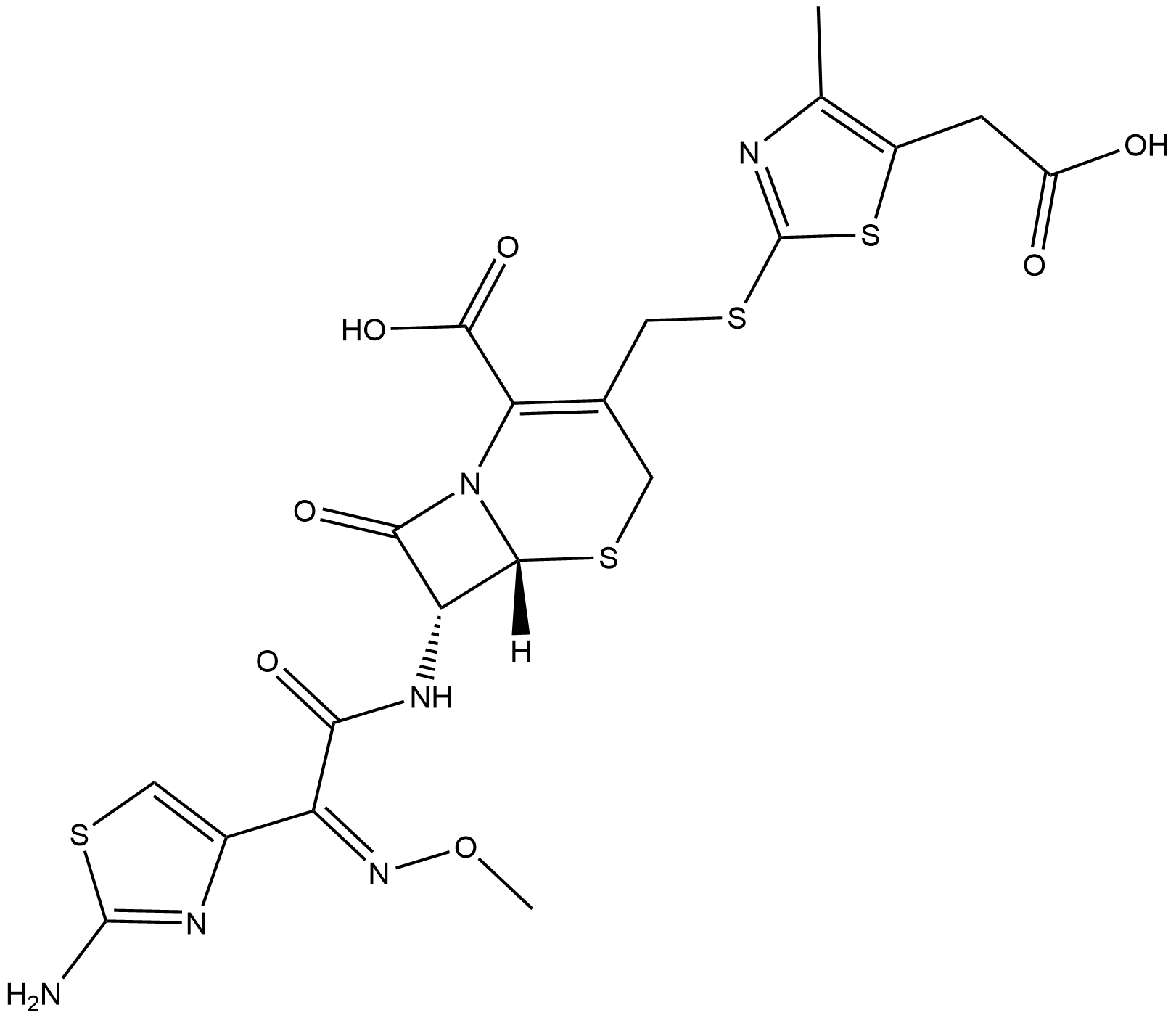
Cefodizime
Cefodizime (CAS No. 69739-16-8) is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that targets bacterial penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)—with particularly high affinity for PBPs 1A/B, 2 and 3 of Escherichia coli—and exerts bactericidal effects by disrupting bacterial cell wall synthesis; its antibacterial activity is characterized by the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), with MIC₉₀ values against common pathogens as follows: 0.40 mg/L for Escherichia coli, < 0.01 mg/L for Haemophilus influenzae, 1.76 mg/L for Klebsiella pneumoniae, 0.28 mg/L for Streptococcus pneumoniae and 0.008–0.016 mg/L for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, while it is ineffective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other non-susceptible strains; in vitro, its effective concentration ranges from 0.008 to 64 mg/L consistent with MIC values, and for in vivo therapy, the daily dosage is 1–4 g for adults (administered intramuscularly or intravenously in 1–2 divided doses), a single dose of 0.25–1 g for uncomplicated gonorrhea, 60 mg/kg/day for children (in 3–4 divided doses) and 200 mg/kg/day for meningitis cases; this agent exhibits broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci) and most Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Enterobacteriaceae, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria spp.), is stable to β-lactamases and has immunomodulatory properties by enhancing phagocytic cell function; it is mainly excreted via the kidneys with a 24-hour urinary excretion rate of 56%–80%, has a plasma protein binding rate of 81% and an elimination half-life of 2–5 hours; common adverse reactions include gastrointestinal discomfort, cutaneous reactions and injection site irritation, it is contraindicated in patients with cephalosporin hypersensitivity, and some extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing strains as well as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are resistant to it.
References:
[1] Barradell LB, Brogden RN. Cefodizime. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992 Nov;44(5):800-34. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199244050-00008. Erratum in: Drugs 1993 Jan;45(1):130. PMID: 1280568.
[2] LE Huy H, Koizumi N, Ung TTH, LE TT, Nguyen HLK, Hoang PVM, Nguyen CN, Khong TM, Hasebe F, Haga T, LE MTQ, Hirayama K, Miura K. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from urban rodents in Hanoi, Vietnam. J Vet Med Sci. 2020 May 20;82(5):653-660. doi: 10.1292/jvms.19-0697. Epub 2020 Mar 30. PMID: 32224554; PMCID: PMC7273608.
[3] Jiang Y, Lu R, Shen Y, Zhou Q, Ou M, Du Z, Zhu H. Analysis of antibacterial drug use and bacterial resistance in psychiatric hospital in the epidemic. Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 10;15(1):4984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88260-5. PMID: 39929904; PMCID: PMC11811061.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | -20°C |
| M.Wt | 584.67 |
| Cas No. | 69739-16-8 |
| Formula | C20H20N6O7S4 |
| Solubility | ≥51.1 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
| Chemical Name | (6R,7R)-7-((Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamido)-3-(((5-(carboxymethyl)-4-methylthiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(C1=C(CSC2=NC(C)=C(CC(O)=O)S2)CS[C@@]([C@@H]3NC(/C(C4=CSC(N)=N4)=N\OC)=O)([H])N1C3=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |