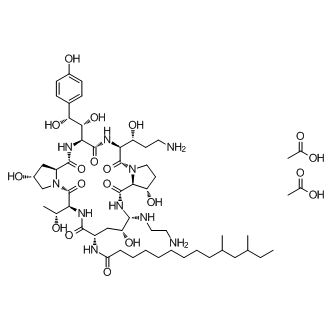
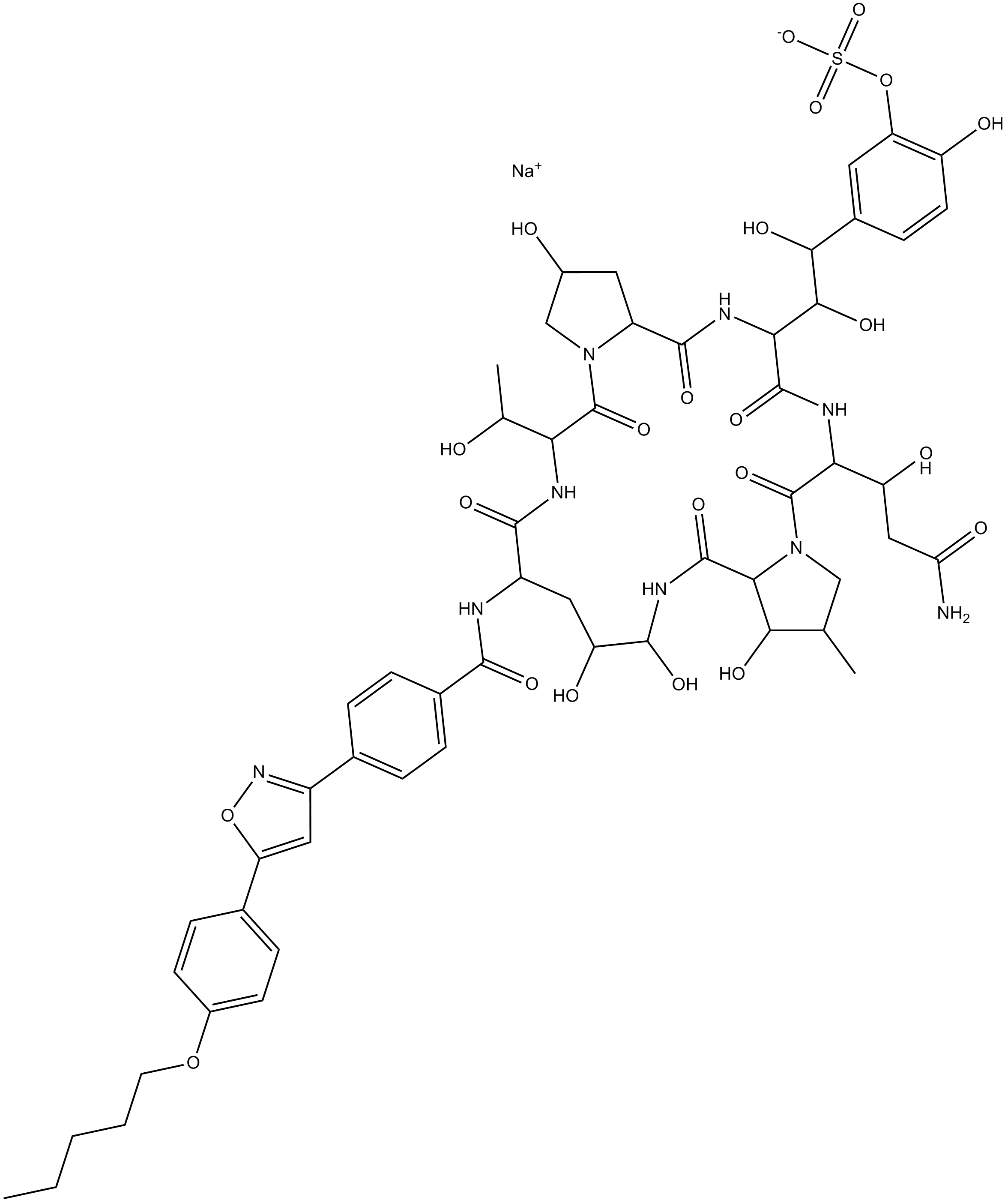
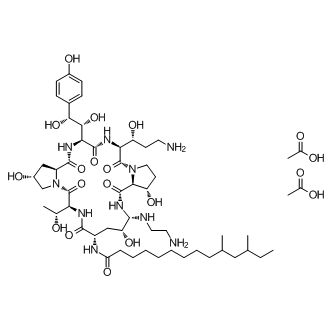
Caspofungin Acetate
Caspofungin acetate (MK-0991; CAS 179463-17-3) is an antifungal lipopeptide compound targeting fungal cell wall synthesis by inhibiting 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase, thereby disrupting structural integrity. This inhibition mechanism leads to the blockage of glucan polymer production essential for fungal growth. In vitro analyses indicate Caspofungin acetate demonstrates antifungal activity against species including Aspergillus fumigatus and several Candida species, with MIC90 values around 0.5 µg/mL for C. albicans and C. parapsilosis, 1.0 µg/mL for C. glabrata and C. tropicalis, and 2.0 µg/mL for C. krusei. Caspofungin is utilized in biomedical research to explore cell wall synthesis pathways, fungal susceptibility tests, and mechanistic antifungal studies.
References:
[1] Bowman J C, Hicks P S, Kurtz M B, et al. The antifungal echinocandincaspofungin acetate kills growing cells of Aspergillus fumigatus in vitro [J]. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 2002, 46 (9): 3001-3012.
[2] Hoang A. Caspofungin acetate: an antifungal agent [J]. American journal of health-system pharmacy, 2001, 58 (13): 1206-1214.
[3] Pacetti S A, Gelone S P. Caspofungin acetate for treatment of invasive fungal infections [J]. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 2003, 37 (1): 90-98.
[4] Bartizal K, Gill C J, Abruzzo G K, et al. In vitro preclinical evaluation studies with the echinocandin antifungal MK-0991 (L-743,872) [J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1997, 41 (11): 2326-2332.
- 1. Rehema Nakiwala, Noopur Dasgupta, et al. "Access to Substituted Tricyclic Heteroarenes by an Oxidative Cyclization Reaction and Their Antifungal Performance." Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;18(2):249. PMID: 40006062
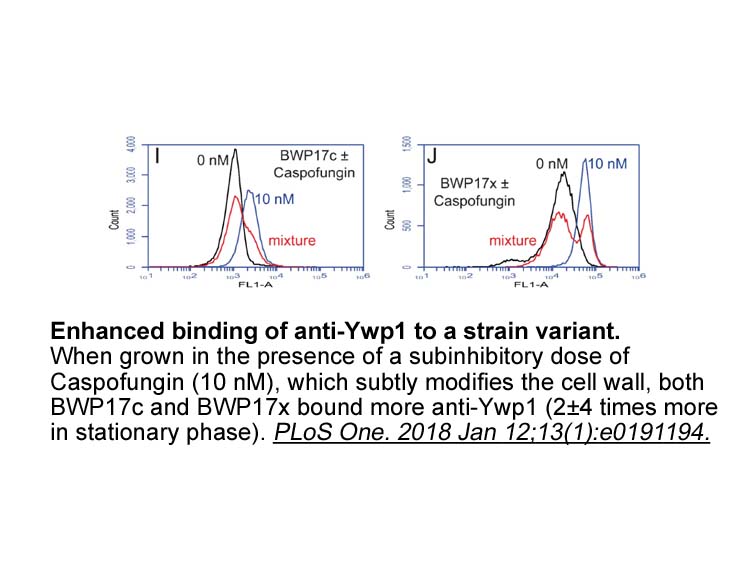
- 2. Granger BL. "Accessibility and contribution to glucan masking of natural and genetically tagged versions of yeast wall protein 1 of Candida albicans." PLoS One. 2018 Jan 12; 13 (1): e0191194. PMID: 29329339
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1213.42 |
| Cas No. | 179463-17-3 |
| Formula | C56H96N10O19 |
| Solubility | ≥60.67 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥21.5 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | acetic acid compound with (Z)-N-((2R,6S,7Z,9S,11R,12S,13E,14aS,15S,20S,21Z,23S,24Z,25aS)-20-((R)-3-amino-1-hydroxypropyl)-12-((2-aminoethyl)amino)-23-((1S,2S)-1,2-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl)-2,8,11,14,15,22,25-heptahydroxy-6-((R)-1-hydroxyethyl)-5 |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)CC(C)CCCCCCCCC(=O)NC1CC(C(NC(=O)C2C(CCN2C(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C3CC(CN3C(=O)C(NC1=O)C(C)O)O)C(C(C4=CC=C(C=C4)O)O)O)C(CCN)O)O)NCCN)O.CC(=O)O.CC(=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Aspergillus fumigates |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37°C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
32 μg/mL for 6 h; or 2 μg/mL for 12 h |
|
Applications |
Caspofungin suppressed the synthesis of cell wall β-1,3-glucan, which triggered a compensatory stimulation of chitin synthesis. Caspofungin induced morphological changes in Aspergillus fumigates. Moreover, Treatment with caspofungin induced ChsG-dependent upregulation of chitin synthesis and the formation of chitin-rich microcolonies in Aspergillus fumigates. |
|
References: 1 Walker, L. A., Lee, K. K., Munro, C. A. and Gow, N. A. (2015) Caspofungin Treatment of Aspergillus fumigatus Results in ChsG-Dependent Upregulation of Chitin Synthesis and the Formation of Chitin-Rich Microcolonies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 59, 5932-5941 |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data