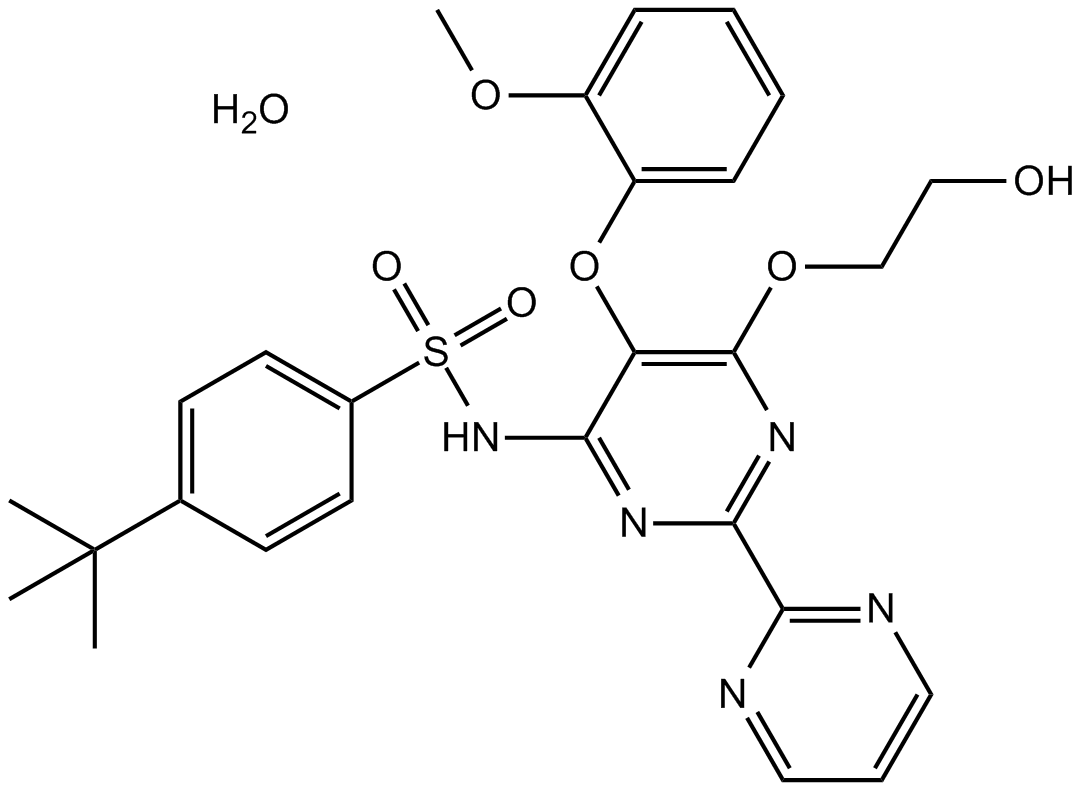
Bosentan monohydrate
Bosentan Hydrate (CAS No.157212-55-0) is a sulfonamide-derived competitive and specific endothelin receptor antagonist, with relatively higher affinity for endothelin A (ETA) receptors than endothelin B (ETB) receptors. In P388/dx cells, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) for ETA and ETB receptors is 15.1 ± 1.6 μM.
Its mechanism of action is as follows: by competitively binding to ETA and ETB receptors in endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, it counteracts the effects of endothelin—a potent endogenous vasoconstrictor and bronchoconstrictor. This further reduces pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance, making it particularly suitable for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension [1].
In vitro experiments investigated the effect of Bosentan on the angiogenic function of dermal microvascular endothelial cells (MVECs) and its ability to counteract the anti-angiogenic effect of systemic sclerosis serum. The results showed that Bosentan significantly enhanced cell viability and could effectively reverse the anti-angiogenic inhibitory effect of systemic sclerosis serum on dermal MVECs [2].
In vivo experiments using Wistar rats explored the regulatory effect of Bosentan on plasma leptin levels in rats after myocardial infarction. After oral administration of 100 mg/kg Bosentan once daily for 2 consecutive days, the plasma leptin concentration increased significantly. This study indicated that Bosentan plays an important role in regulating leptin concentration in ischemic cardiovascular diseases [1].
A double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the effect of Bosentan on exercise capacity in a large sample of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. A total of 213 patients first received 62.5 mg Bosentan twice daily for 4 consecutive weeks, followed by 125 mg or 250 mg twice daily for at least 12 weeks. The results showed that the 125 mg dose of Bosentan was well-tolerated and had definite benefits for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension [3].
References:
[1] Ostrowski RP, Januszewski SA, Kowalska ZA and Kapuscinski A. Effect of endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan on plasma leptin concentration in acute myocardial infarction in rats. Pathophysiology. 2003 Sep; 9(4): 249-56.
[2]Romano E, Bellando-Randone S, Manetti M, Bruni C, Lepri G, Matucci-Cerinic M, Guiducci S. Bosentan blocks the antiangiogenic effects of sera from systemic sclerosis patients: an in vitro study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Aug; 33(4 Suppl 91): S148-52.
[3]Rubin LJ, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Galiè N, Black CM et, al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. New Engl J Med. 2002 Mar; 346 (12): 896-903.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 569.63 |
| Cas No. | 157212-55-0 |
| Formula | C27H31N5O7S |
| Synonyms | Tracleer; Stayveer; Safebo |
| Solubility | ≥57.21 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥2.45 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrimidin-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide;hydrate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC2=C(C(=NC(=N2)C3=NC=CC=N3)OCCO)OC4=CC=CC=C4OC.O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure