Tyrosine Kinase
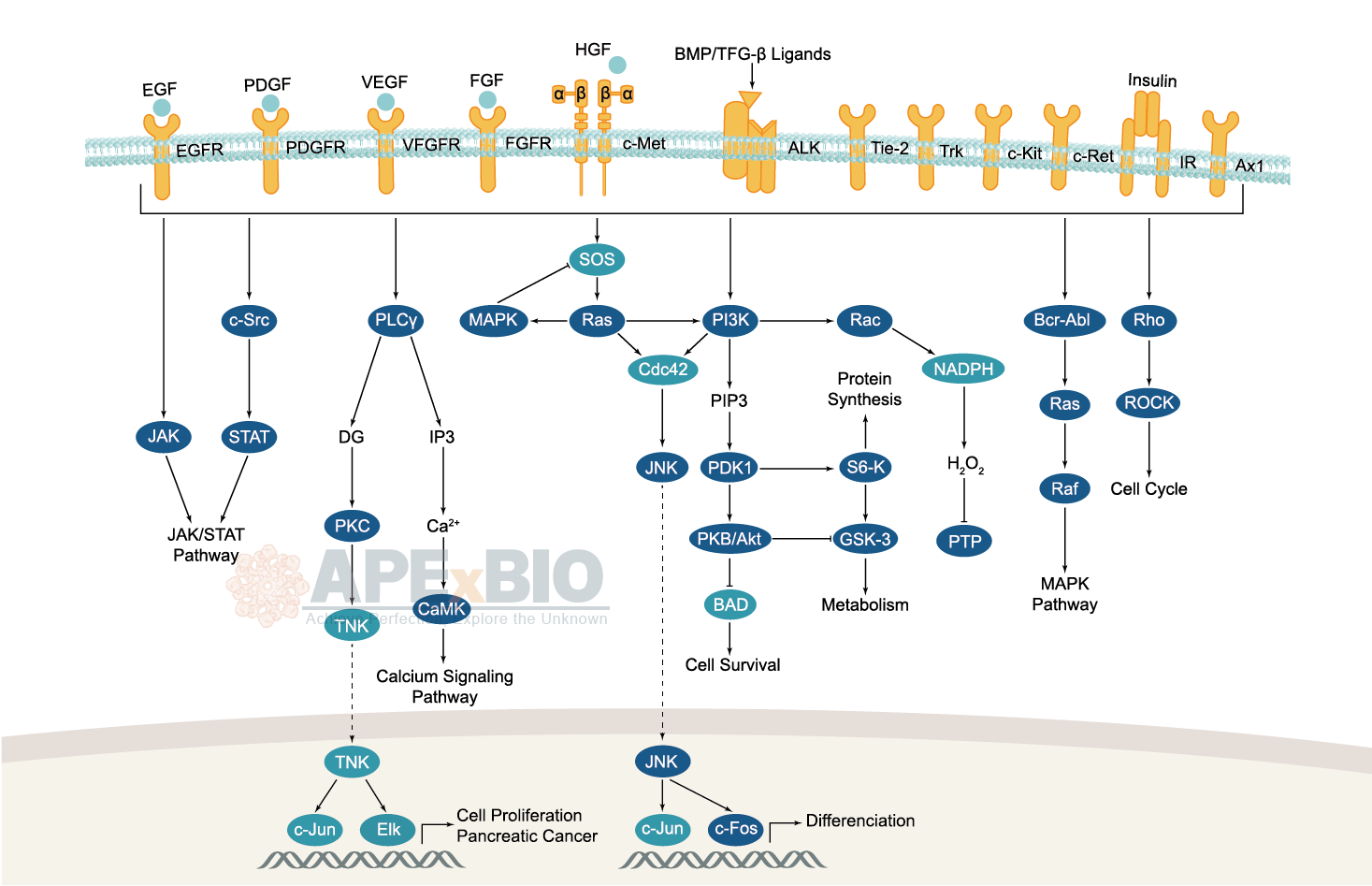

Receptor tyrosine kinases bind to extracellular ligands/growth factors, which promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine residues. This triggers a cascade of downstream events through phosphorylation of intracellular proteins that ultimately transduce the extracellular signal to the nucleus, causing changes in gene expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases include EGFR/ErbB, PDGFR, VEGFR, FGFR and MET subfamilies etc. Dysfunctions in tyrosine phosphorylation are linked to oncogenic transformation. In additions, various adaptor and effector proteins couple to carboxy-terminal of an active kinase. For instance, binding of the GRB2 adaptor protein activates EGFR and MAPK/ERK signaling.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases involve many well-defined proteins (e.g. the Src family kinases, c-Abl, and Jak kinases) and other kinases which regulates cell growth and differentiation. For example, Src family kinases are curial for activating and inhibitory pathways in the innate immune response.
-
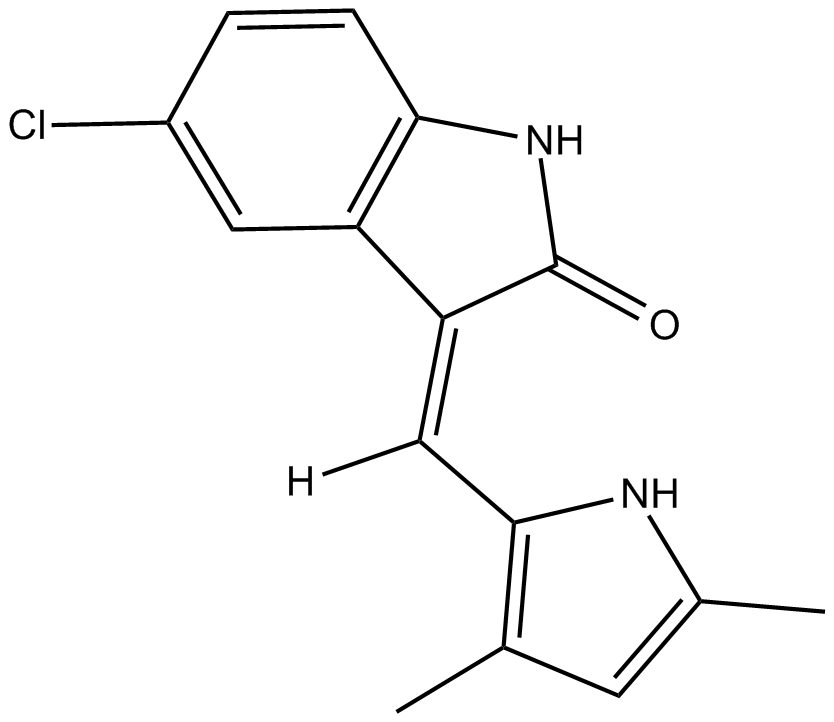 B6097 SU56141 CitationSummary: tyrosine kinase inhibitor
B6097 SU56141 CitationSummary: tyrosine kinase inhibitor -
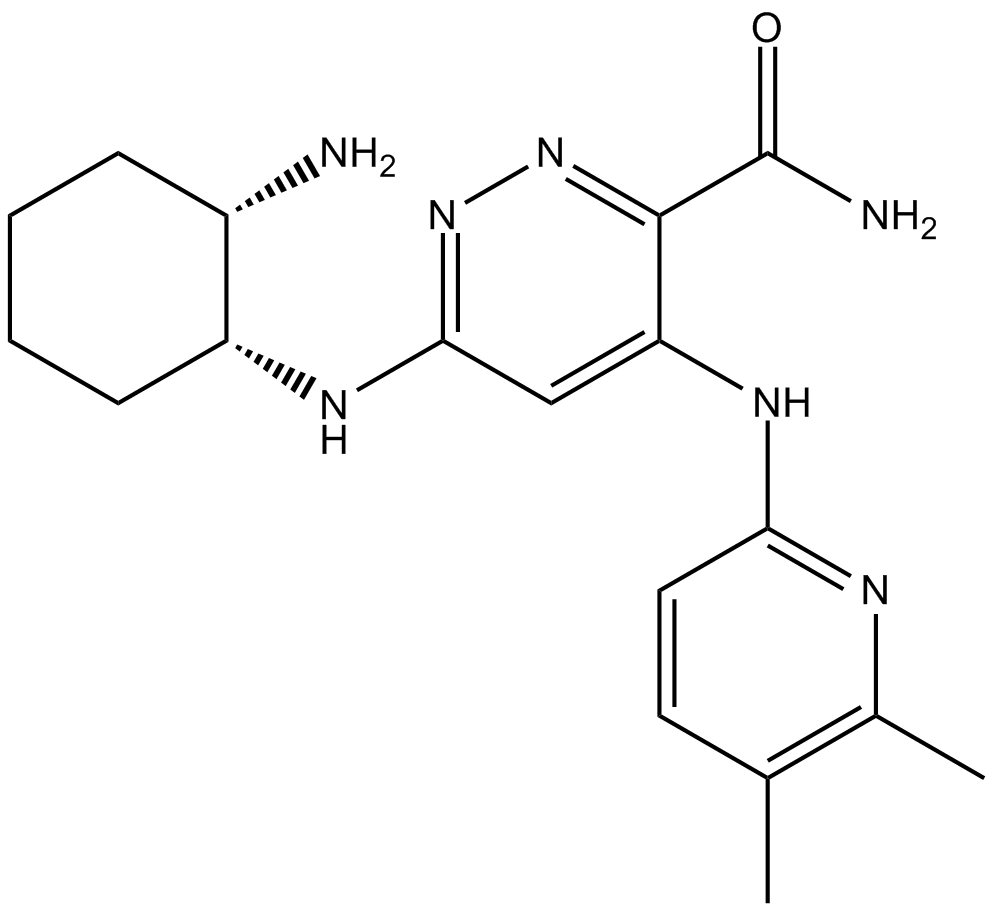 B6158 RO9021Summary: Syk inhibitor
B6158 RO9021Summary: Syk inhibitor -
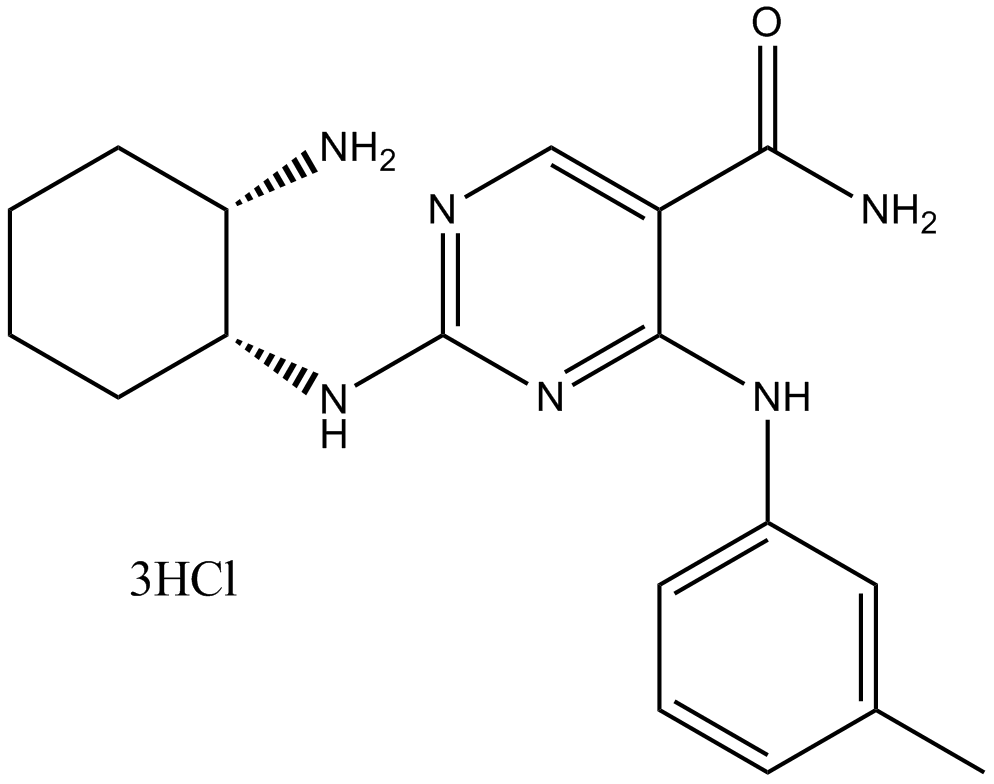 B6161 PRT-060318Summary: novel Syk inhibitor
B6161 PRT-060318Summary: novel Syk inhibitor -
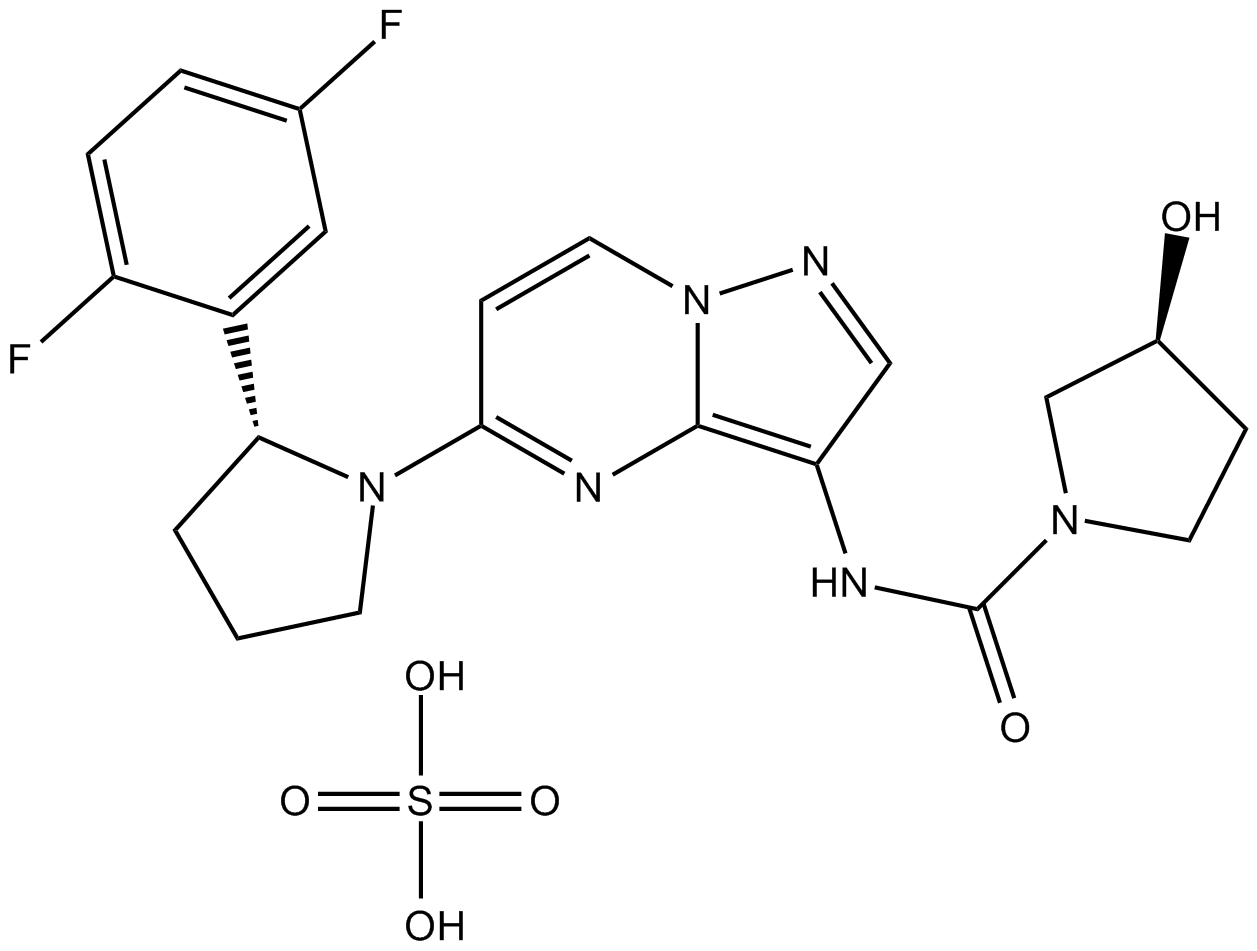 B6176 LOXO-101Target: tropomyosin receptor kinaseSummary: tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) inhibitor
B6176 LOXO-101Target: tropomyosin receptor kinaseSummary: tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) inhibitor -
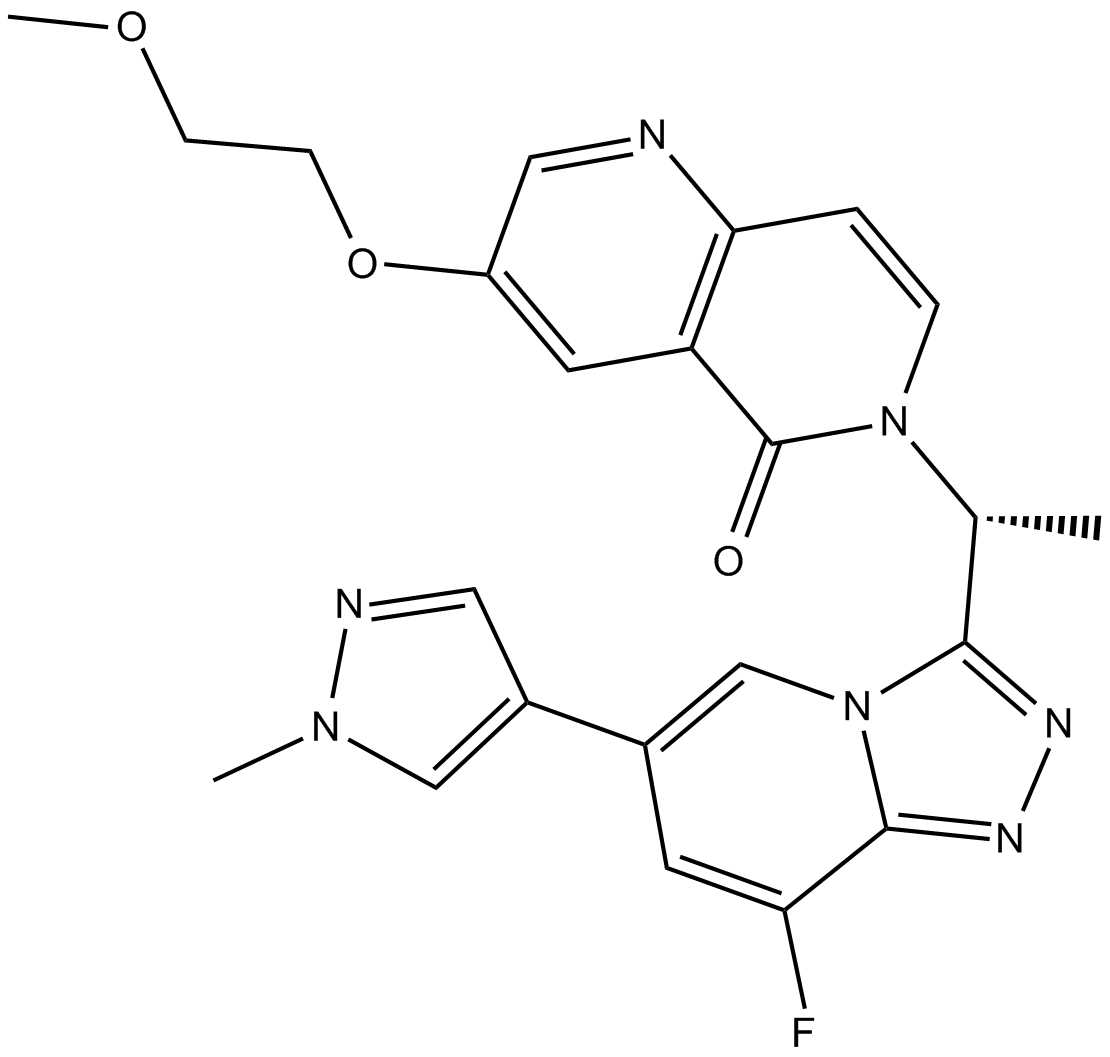 B6193 AMG 337Summary: MET inhibitor
B6193 AMG 337Summary: MET inhibitor -
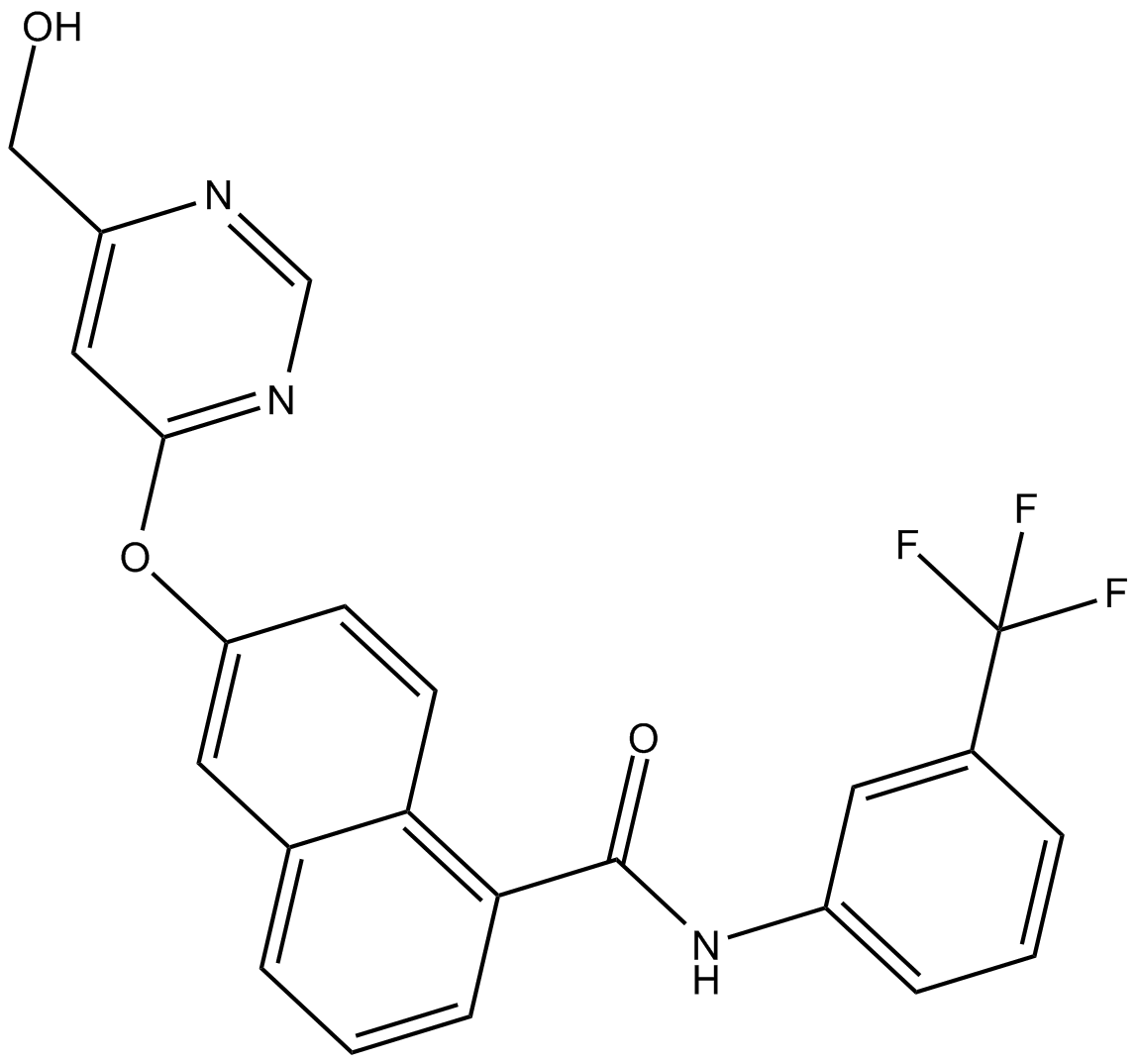 B6199 BFH772Summary: VEGFR2 inhibitor
B6199 BFH772Summary: VEGFR2 inhibitor -
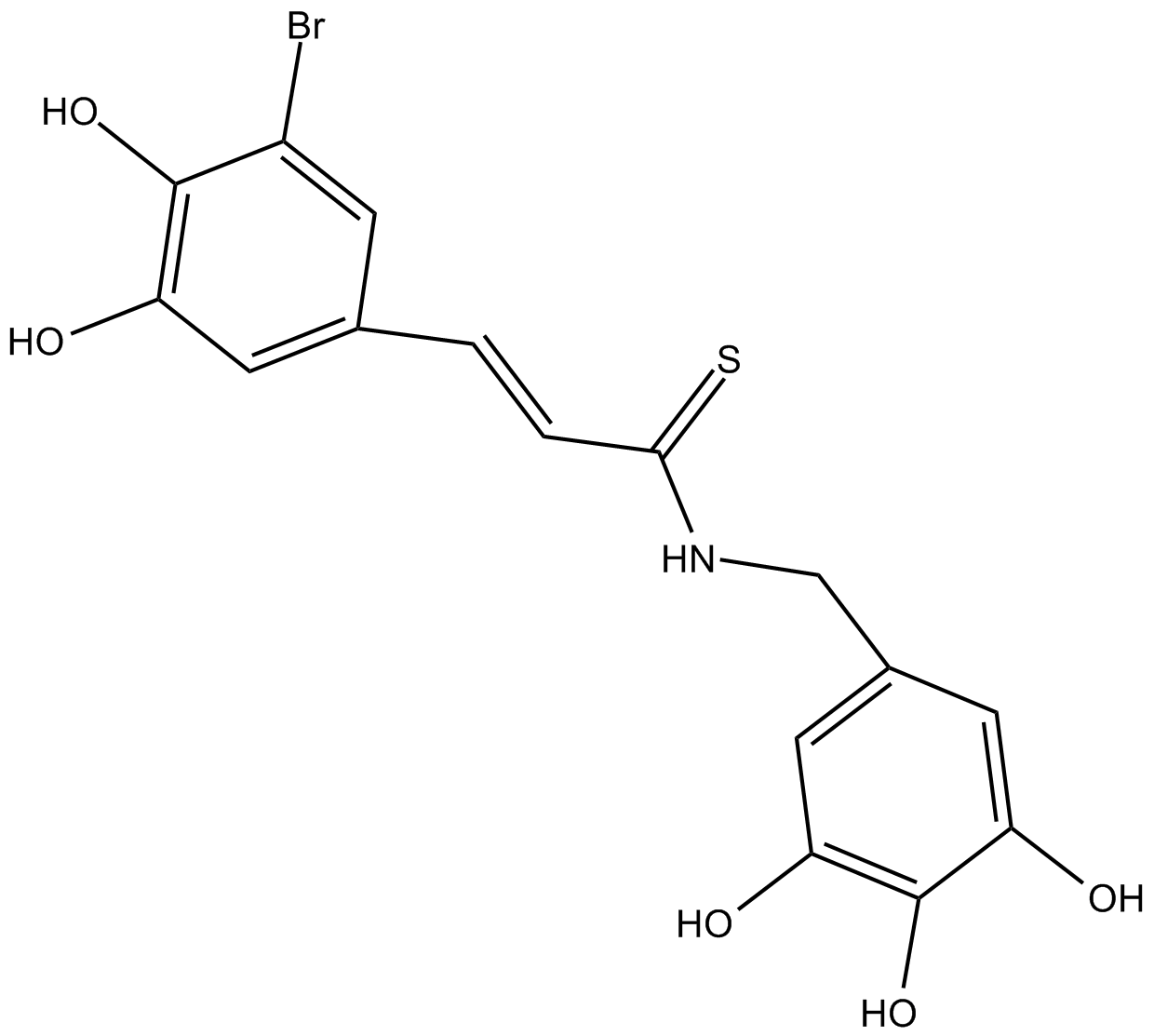 B7808 NT1571 CitationSummary: IRS-1/2 inhibitor, inhibits IGF-1R and STAT3 signaling pathway
B7808 NT1571 CitationSummary: IRS-1/2 inhibitor, inhibits IGF-1R and STAT3 signaling pathway -
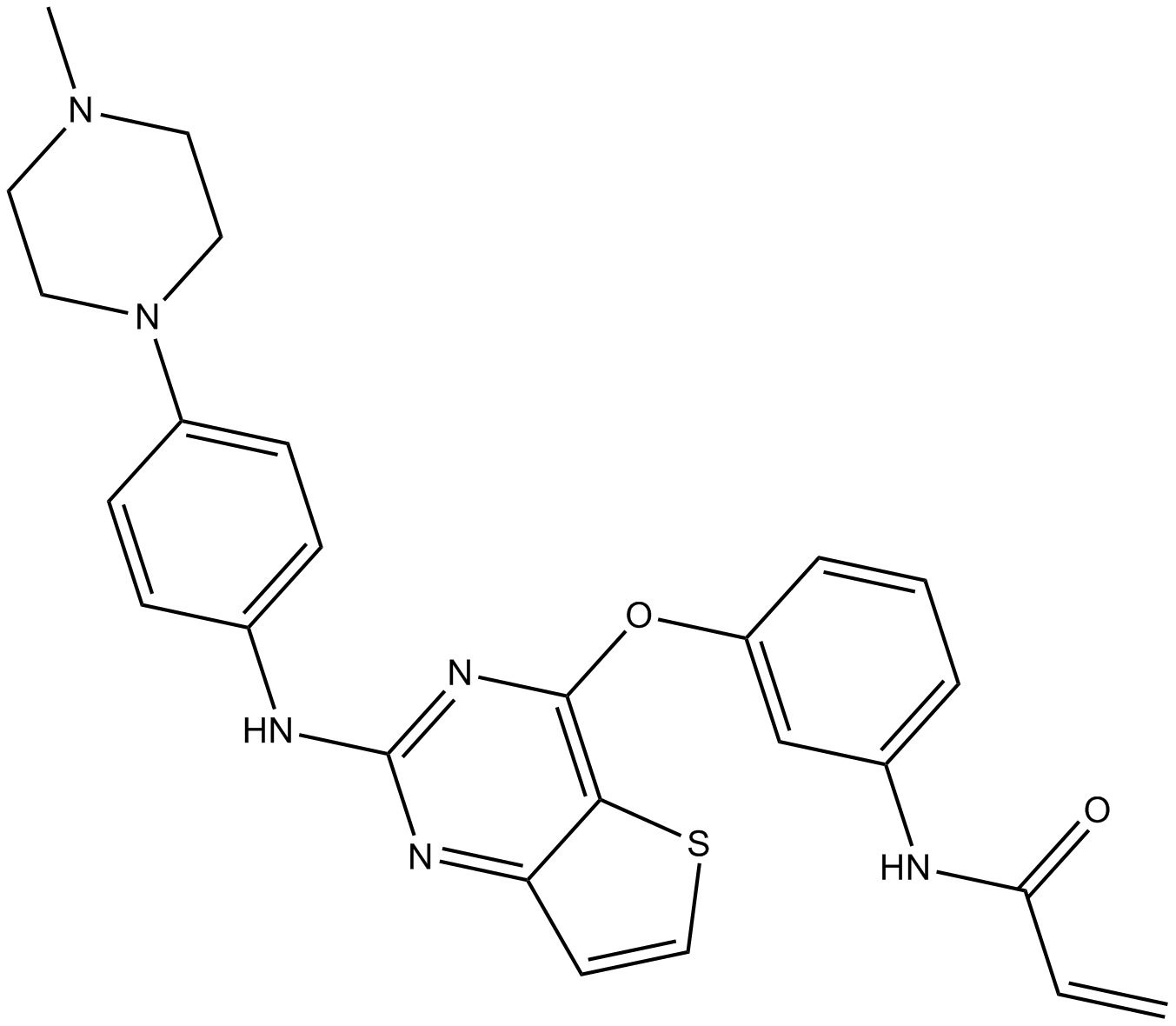 B7813 Olmutinib (HM61713, BI 1482694)Summary: EGFR mutant-specific inhibitor
B7813 Olmutinib (HM61713, BI 1482694)Summary: EGFR mutant-specific inhibitor -
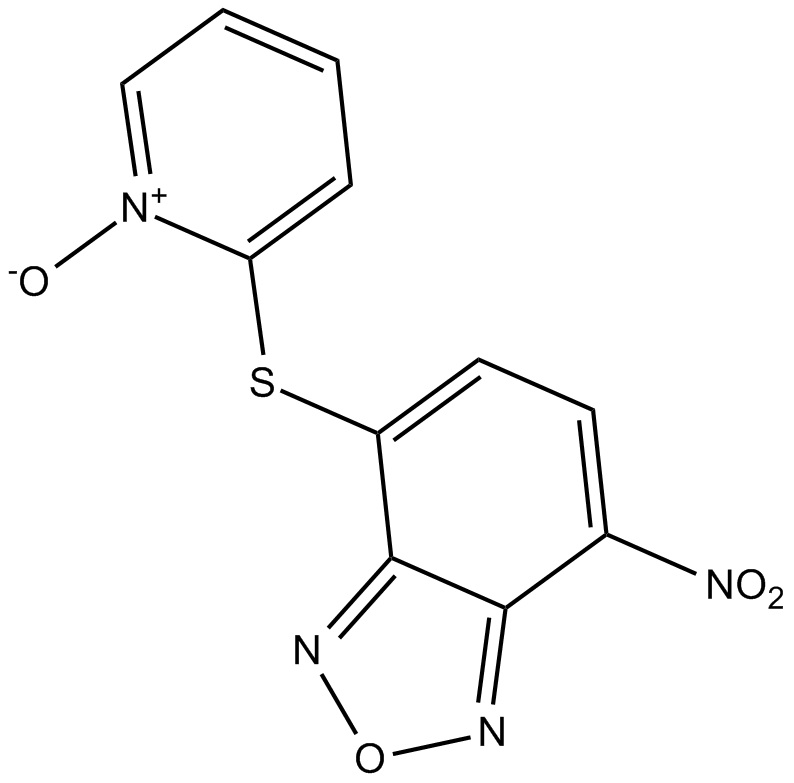 B7815 NSC228155Summary: EGFR activator
B7815 NSC228155Summary: EGFR activator -
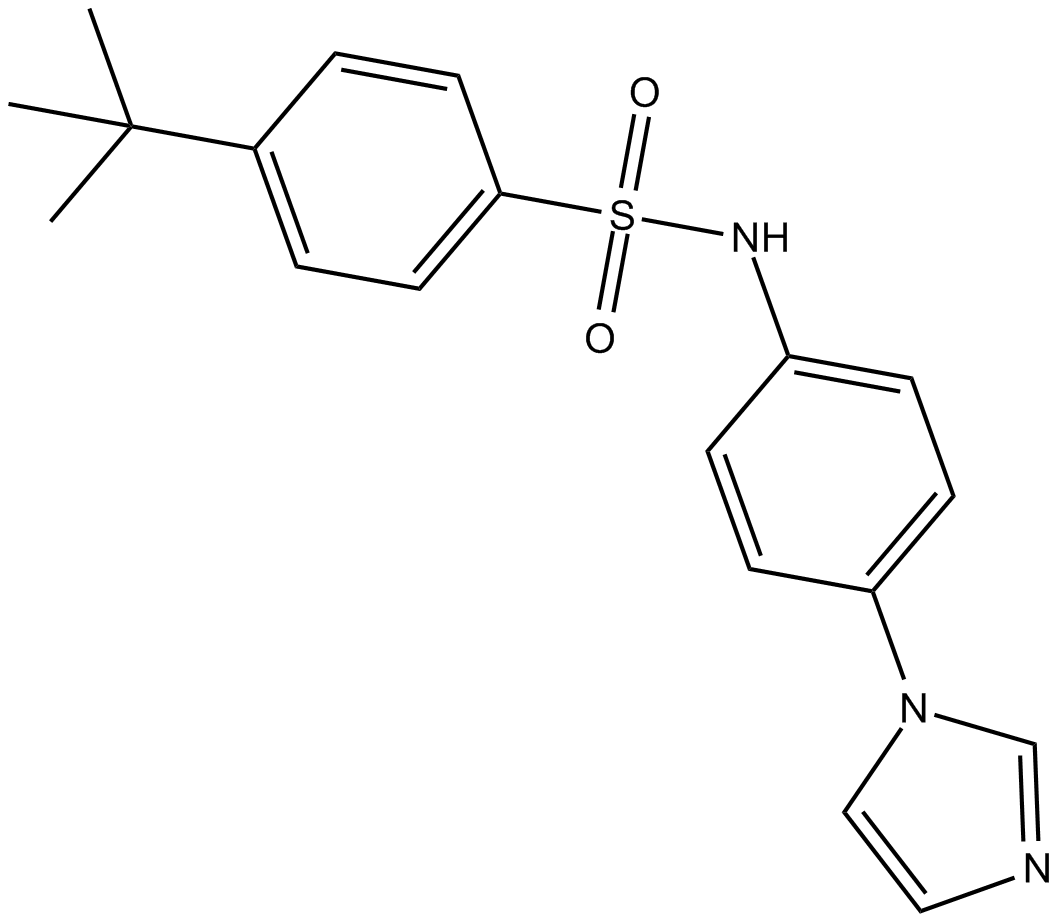 C3152 ISCK03Summary: inhibitor of SCF-mediated c-kit activation
C3152 ISCK03Summary: inhibitor of SCF-mediated c-kit activation


