Tyrosine Kinase
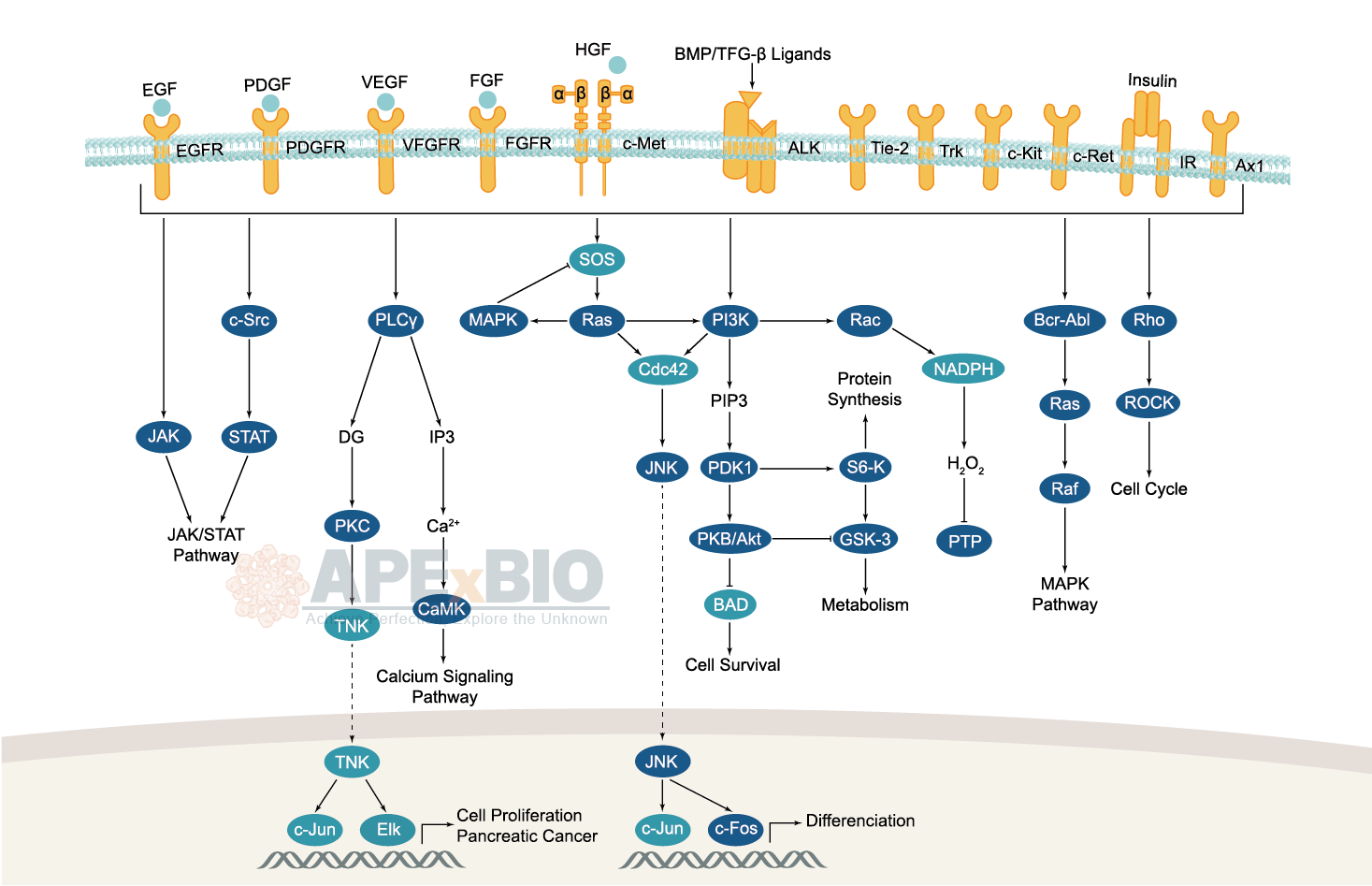

Receptor tyrosine kinases bind to extracellular ligands/growth factors, which promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine residues. This triggers a cascade of downstream events through phosphorylation of intracellular proteins that ultimately transduce the extracellular signal to the nucleus, causing changes in gene expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases include EGFR/ErbB, PDGFR, VEGFR, FGFR and MET subfamilies etc. Dysfunctions in tyrosine phosphorylation are linked to oncogenic transformation. In additions, various adaptor and effector proteins couple to carboxy-terminal of an active kinase. For instance, binding of the GRB2 adaptor protein activates EGFR and MAPK/ERK signaling.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases involve many well-defined proteins (e.g. the Src family kinases, c-Abl, and Jak kinases) and other kinases which regulates cell growth and differentiation. For example, Src family kinases are curial for activating and inhibitory pathways in the innate immune response.
-
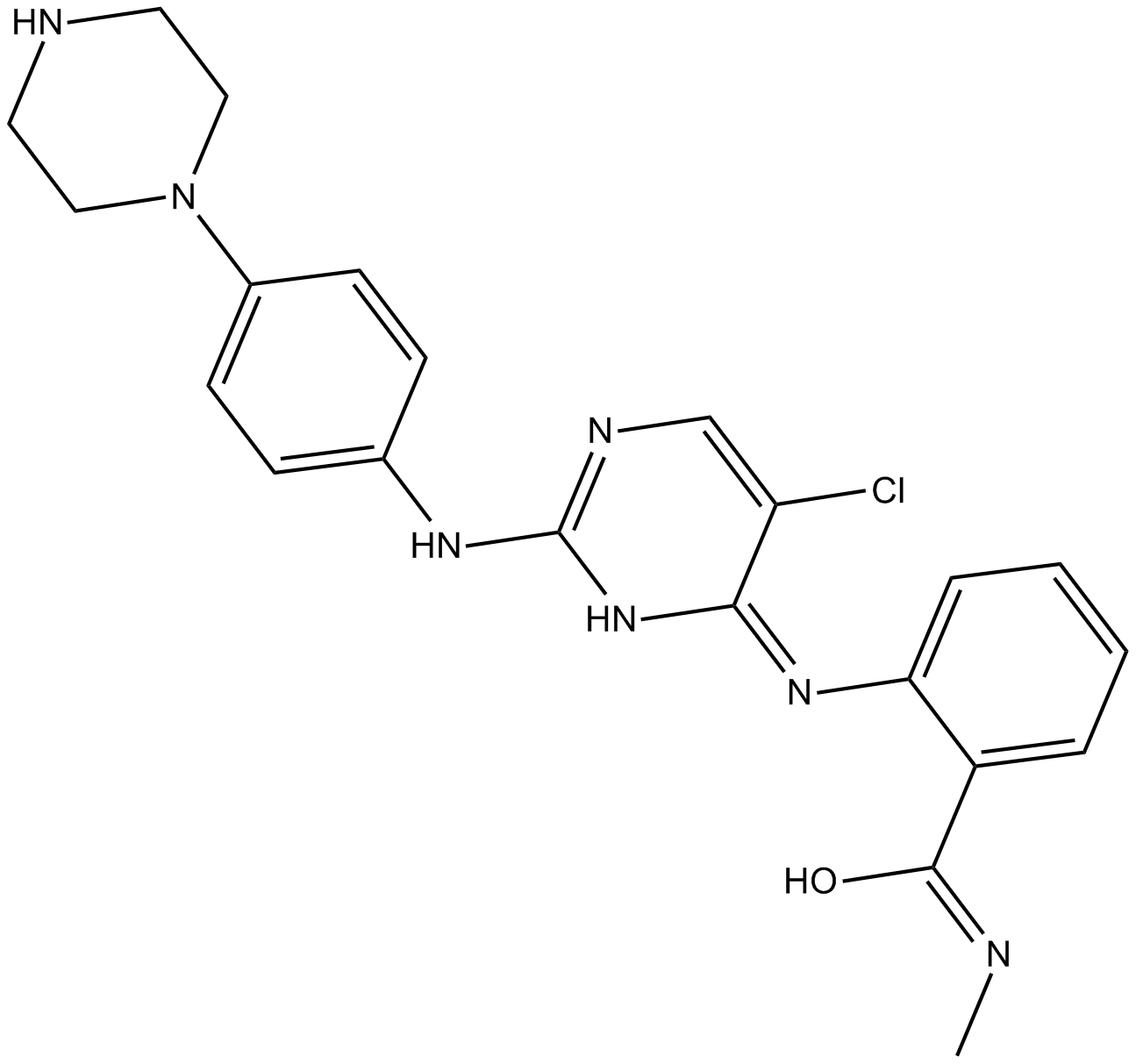 B5843 CTX0294885Target: KinasesSummary: Pan-kinase inhibitor
B5843 CTX0294885Target: KinasesSummary: Pan-kinase inhibitor -
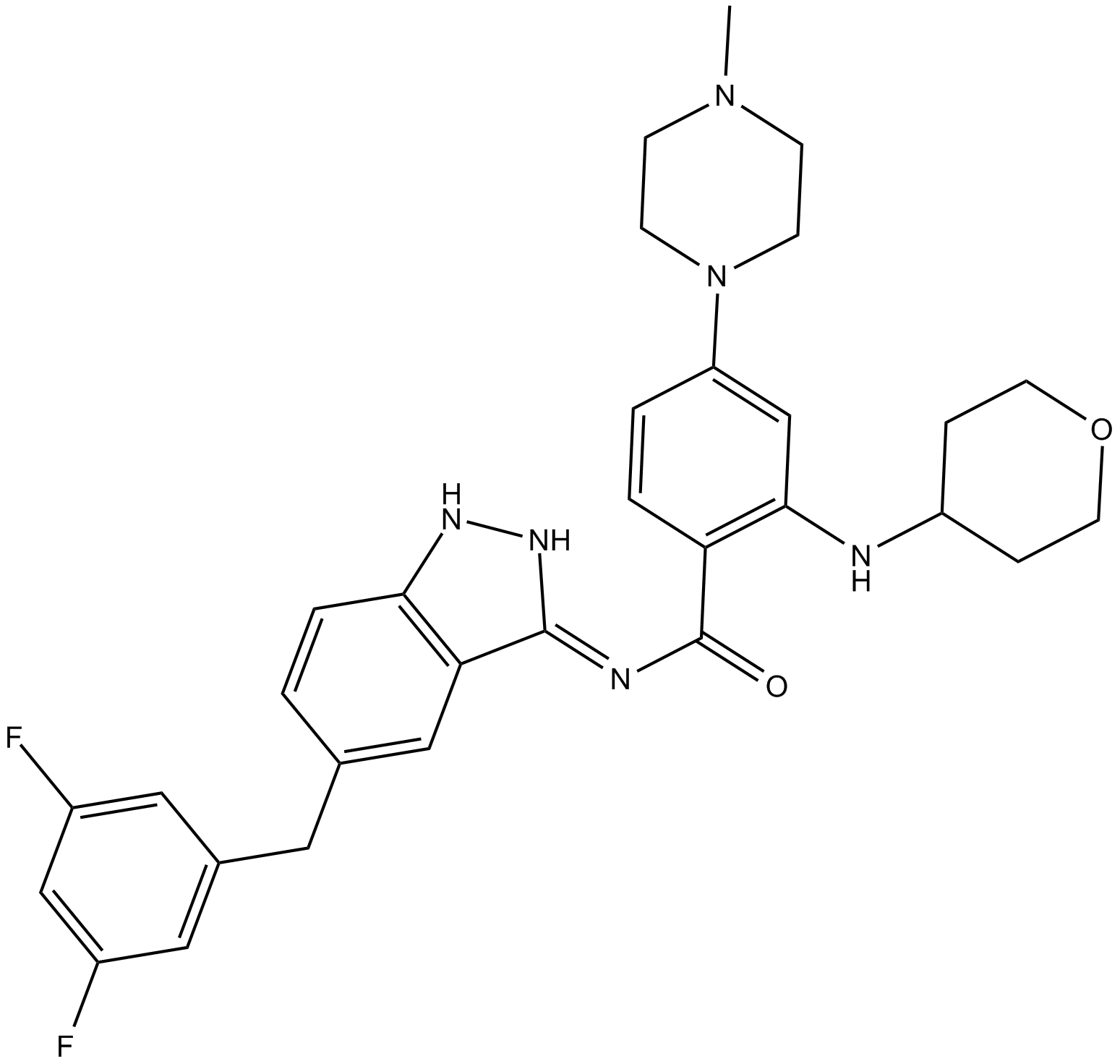 B5859 EntrectinibTarget: Trk Receptors|ALK|ROS1Summary: Orally active inhibitor of ALK kinase
B5859 EntrectinibTarget: Trk Receptors|ALK|ROS1Summary: Orally active inhibitor of ALK kinase -
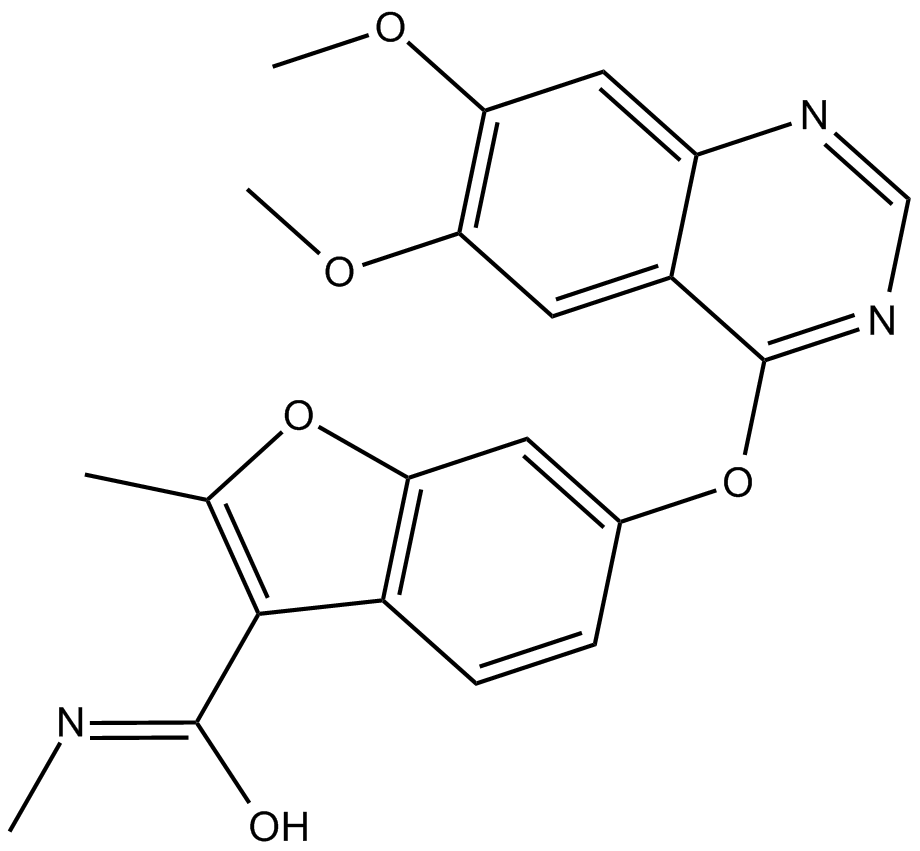 B5864 Fruquintinib(HMPL-013)Target: VEGFRSummary: Potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR 1, 2, 3
B5864 Fruquintinib(HMPL-013)Target: VEGFRSummary: Potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR 1, 2, 3 -
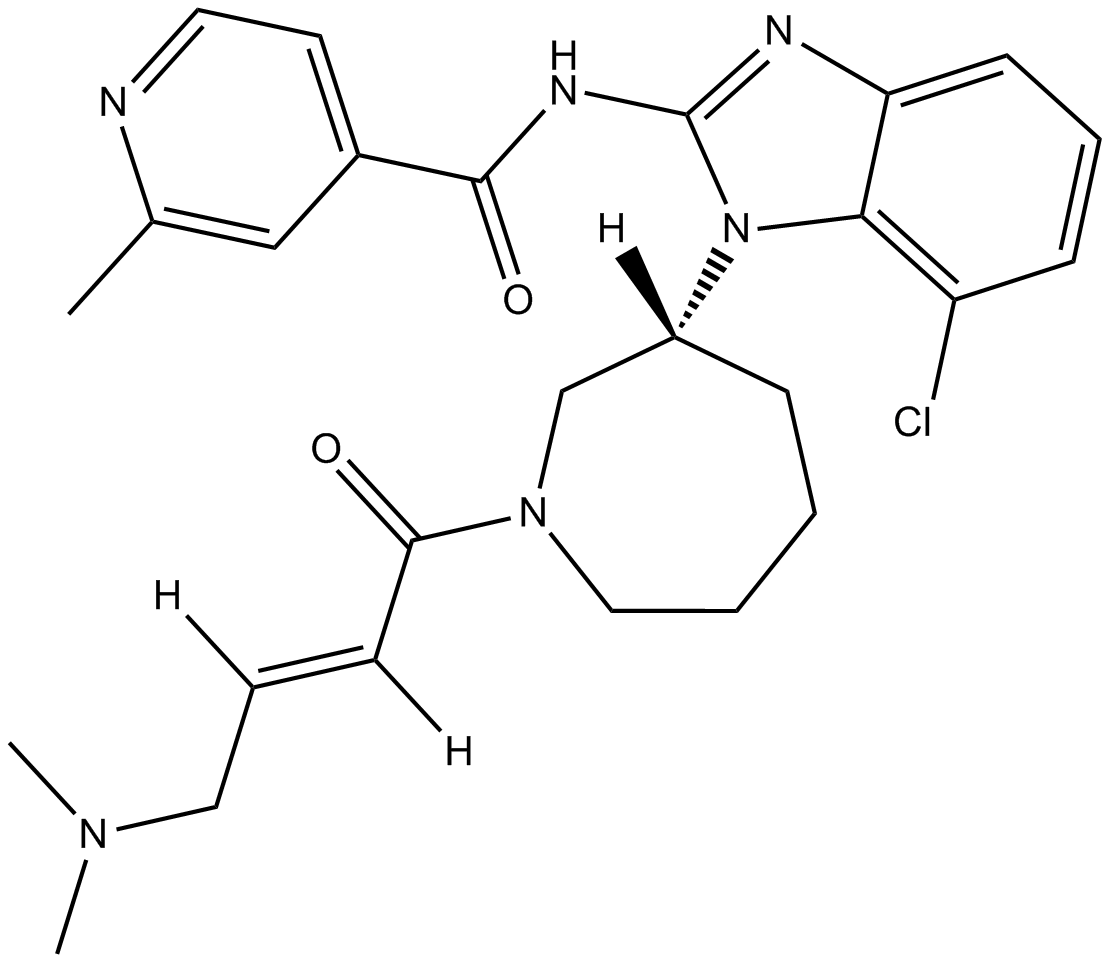 B5889 EGF8162 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Novel covalent inhibitor of mutant-selective EGFR
B5889 EGF8162 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Novel covalent inhibitor of mutant-selective EGFR -
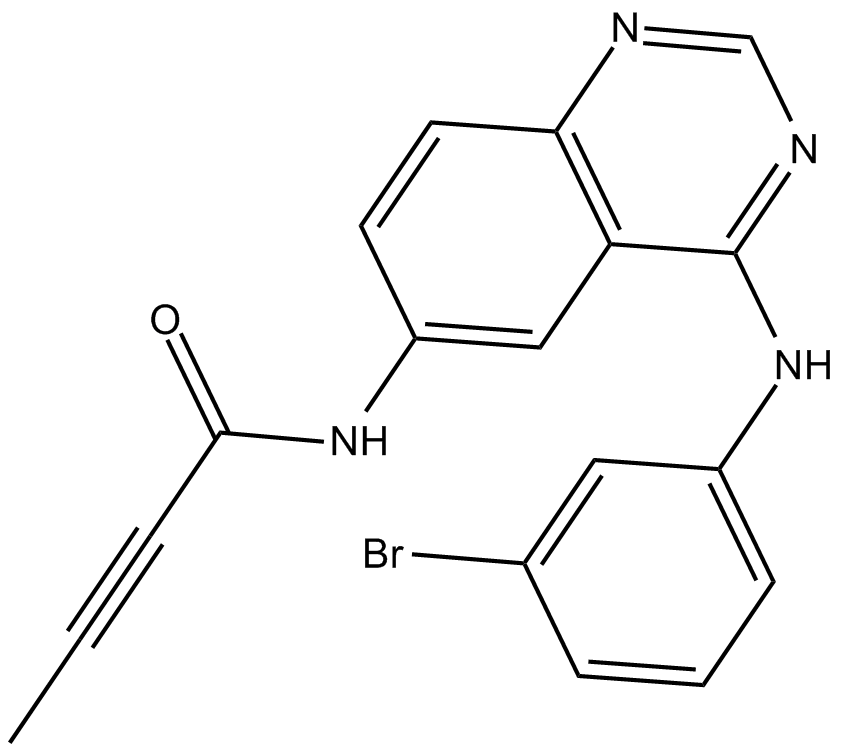 B5899 CL-387785 (EKI-785)Summary: Irreversible inhibiter of EGFR
B5899 CL-387785 (EKI-785)Summary: Irreversible inhibiter of EGFR -
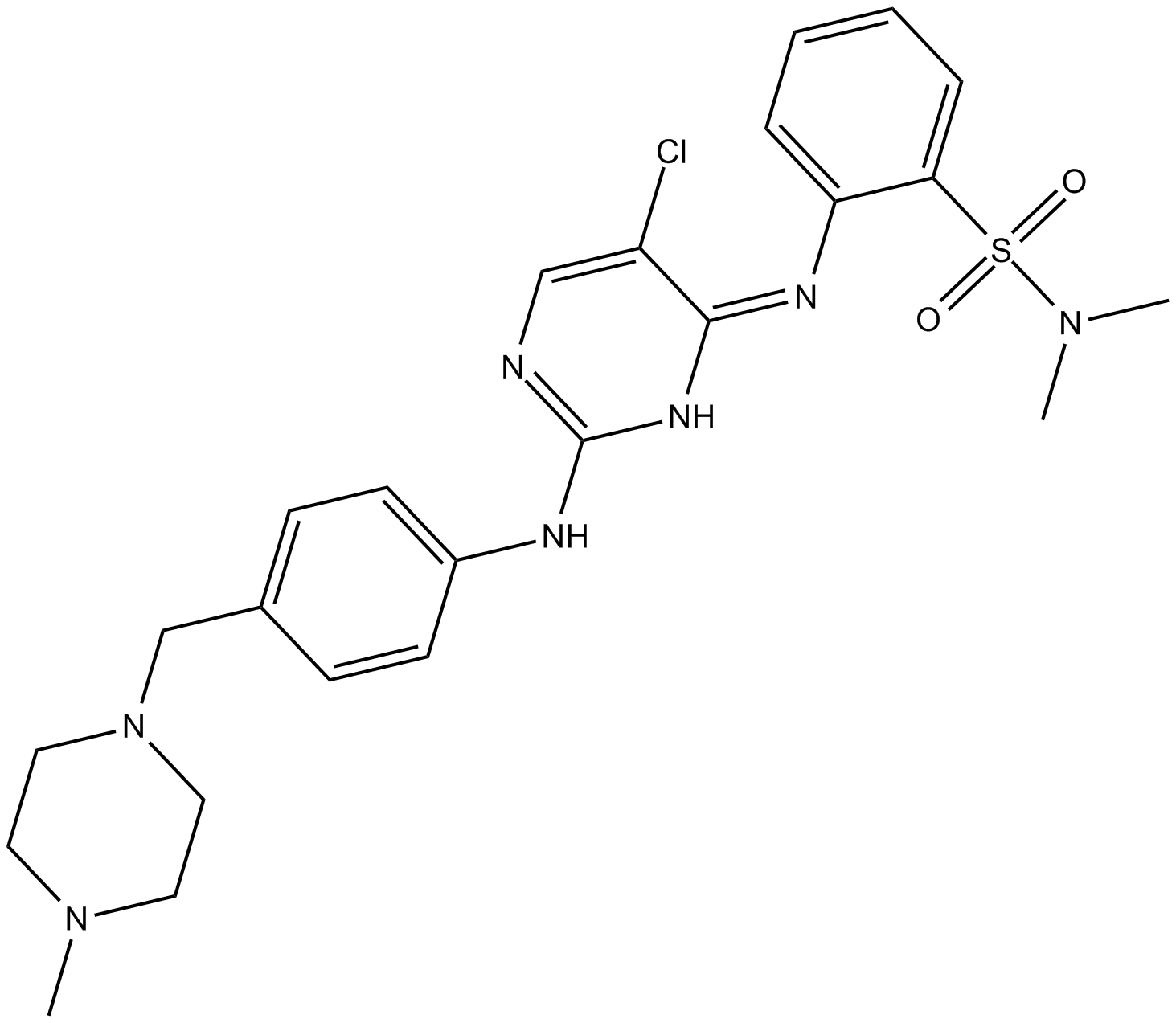 B5940 TP-0903Target: AXLSummary: AXL receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, anti-cancer agent
B5940 TP-0903Target: AXLSummary: AXL receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, anti-cancer agent -
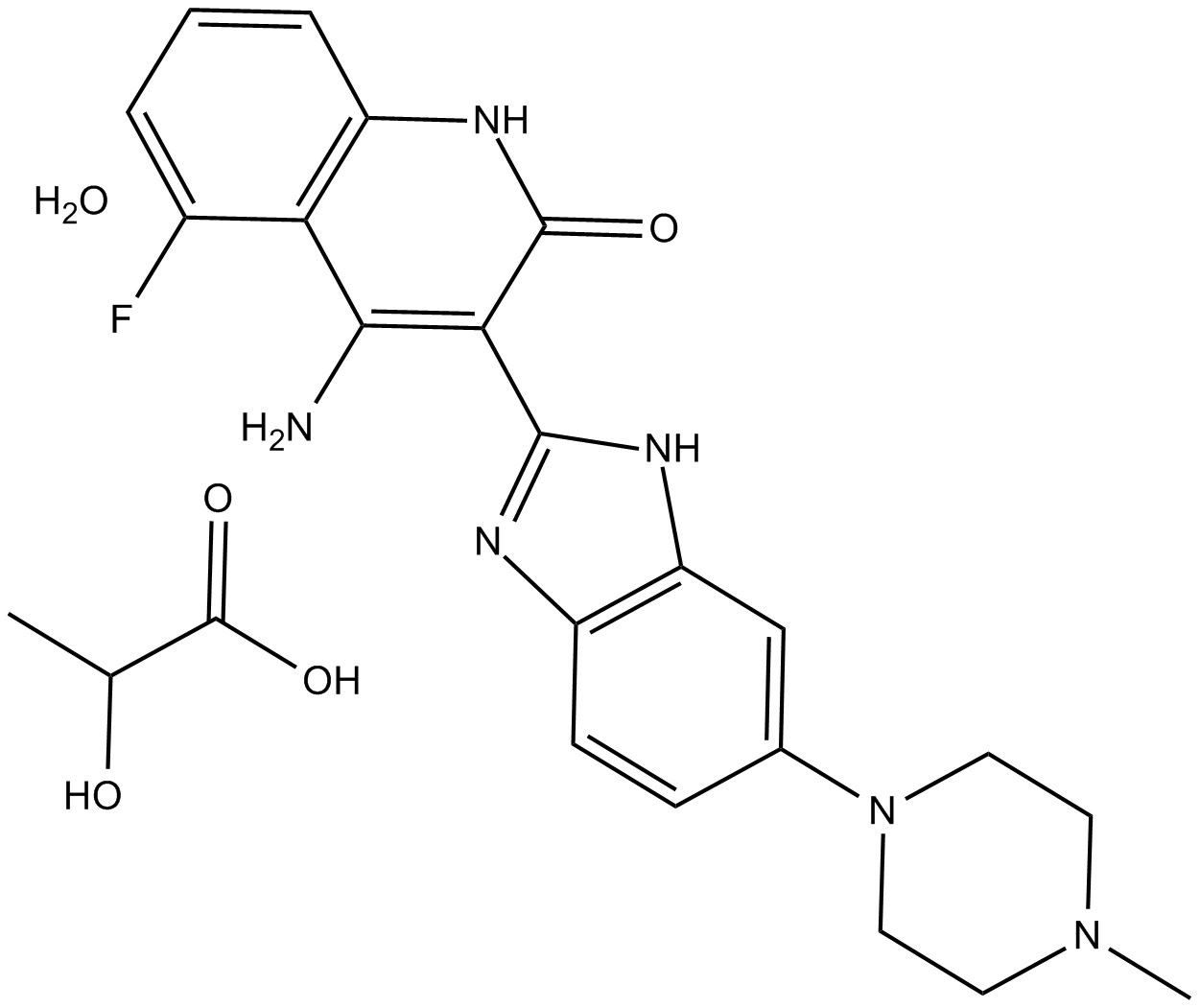 B5953 Dovitinib (TKI258) LactateTarget: CSF-1R|FLT3|VEGFR|PDGFR|c-Kit|FGFRSummary: Oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) against FGFR1–3, VEGFR1–3, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR).
B5953 Dovitinib (TKI258) LactateTarget: CSF-1R|FLT3|VEGFR|PDGFR|c-Kit|FGFRSummary: Oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) against FGFR1–3, VEGFR1–3, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR). -
 B6006 NPS-1034Summary: MET inhibitor
B6006 NPS-1034Summary: MET inhibitor -
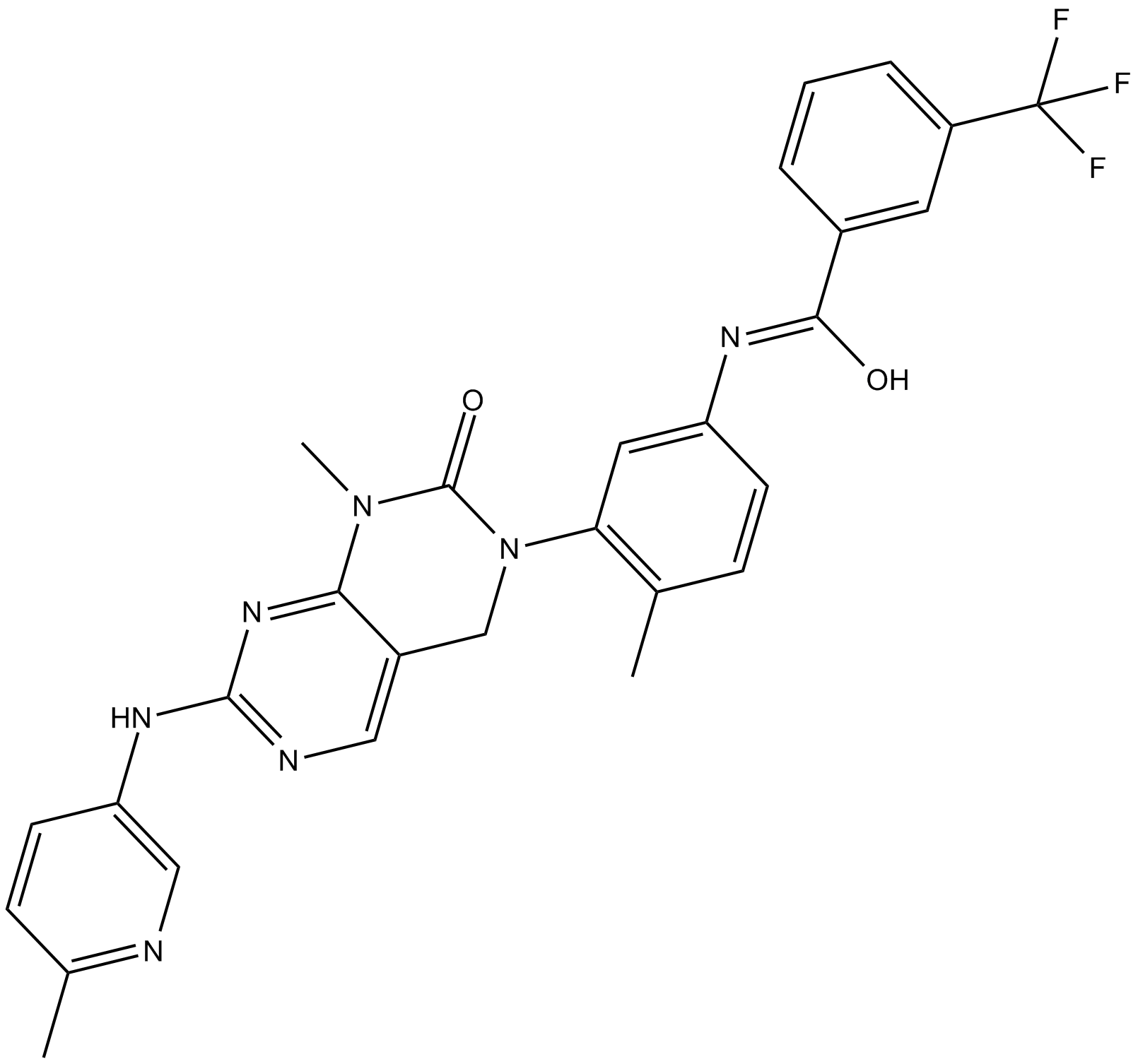 B6033 GNF-7Summary: Type II Bcr-Abl inhibitor
B6033 GNF-7Summary: Type II Bcr-Abl inhibitor -
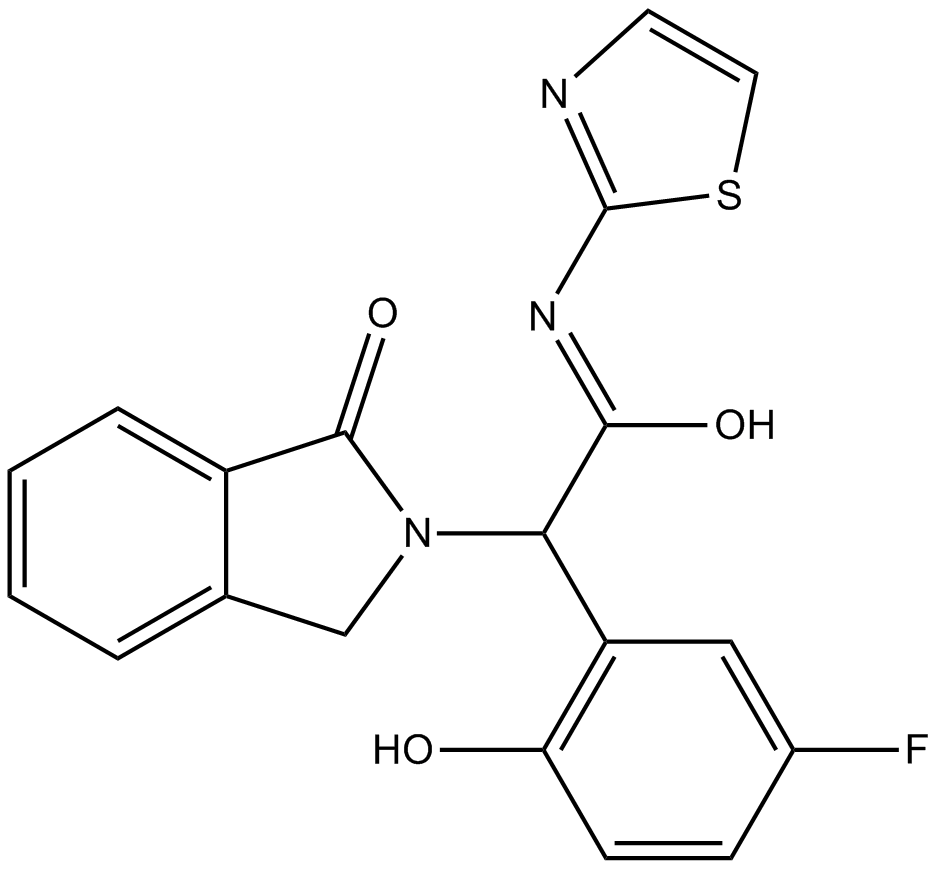 B6054 EAI045Summary: Inhibitor of L858R/T790M EGFR mutants
B6054 EAI045Summary: Inhibitor of L858R/T790M EGFR mutants


