TGF-β/Smad Signaling
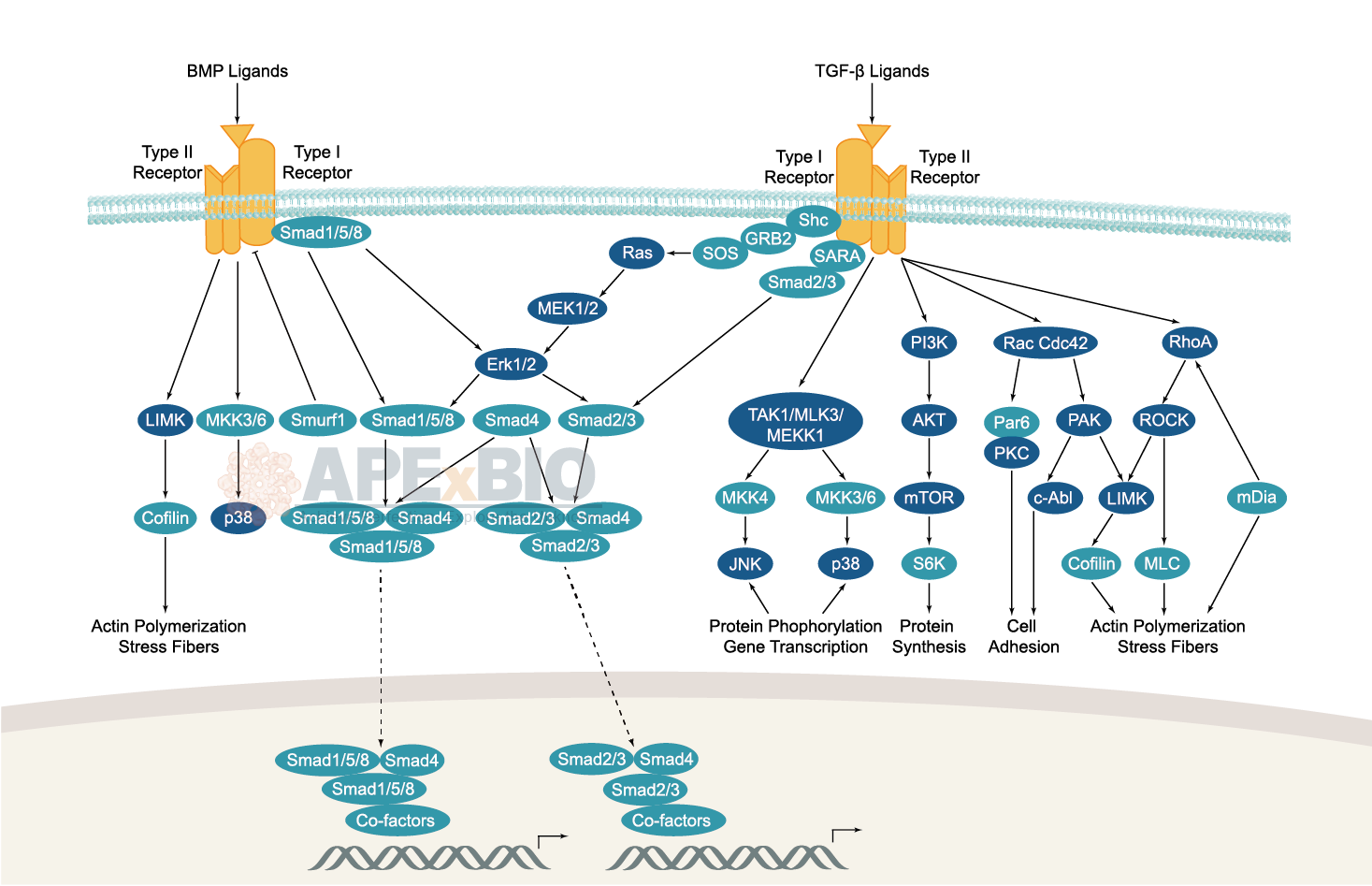

The TGF-β family is generally classified into two sub-families, TGF-β ligands, and bone morphogenic protein (BMP) ligands. In canonical signaling, receptor activation lead to phosphorylation of a group of transcription factors called Smads. TGF-β ligands bind to type II receptors (TGF-β II) which recruit and phosphorylate type I receptor (TGF-β I) on serine/threonine residues. The TGF-β I then recruits and phosphorylates a receptor regulated Smad (R-Smad). The R-Smad binds to the common Smad (Co-Smad) and forms a heterodimeric complex. This complex then translocates into the cell nucleus where it binds with nuclear co-factors to regulate the transcription of various target genes. Dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway is associated with a number of pathological conditions including fibrosis, cancer, immunodeficiency, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases etc.
-
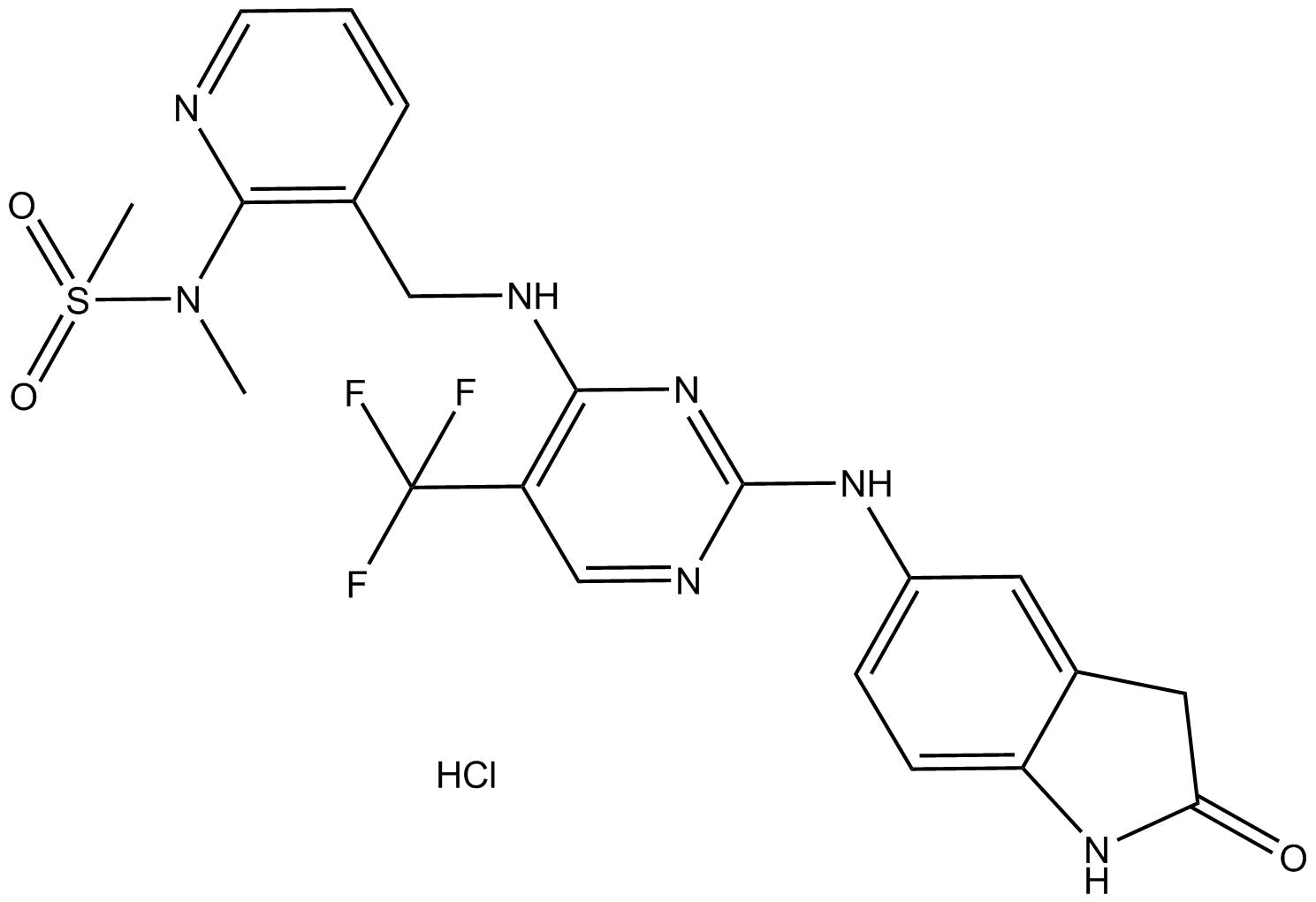 A8345 PF-562271 HClTarget: FAK|Pyk2Summary: FAK/Pyk2 inhibitor
A8345 PF-562271 HClTarget: FAK|Pyk2Summary: FAK/Pyk2 inhibitor -
 A8341 Go 6976Target: PKCSummary: PKCα/PKCβ1 inhibitor
A8341 Go 6976Target: PKCSummary: PKCα/PKCβ1 inhibitor -
 A8342 GF 109203X1 CitationTarget: PKCSummary: Protein kinase C,MLCK,PKG and PKA inhibitor
A8342 GF 109203X1 CitationTarget: PKCSummary: Protein kinase C,MLCK,PKG and PKA inhibitor -
 A8343 Go 69831 CitationSummary: pan-PKC inhibitor
A8343 Go 69831 CitationSummary: pan-PKC inhibitor -
 A8344 K-252cTarget: PKC|PKASummary: Protein kinase inhibitor
A8344 K-252cTarget: PKC|PKASummary: Protein kinase inhibitor -
 A8464 LY210976110 CitationSummary: TβRI/II kinase inhibitor
A8464 LY210976110 CitationSummary: TβRI/II kinase inhibitor -
 A8525 Sotrastaurin (AEB071)Target: PKCSummary: PKC inhibitor
A8525 Sotrastaurin (AEB071)Target: PKCSummary: PKC inhibitor -
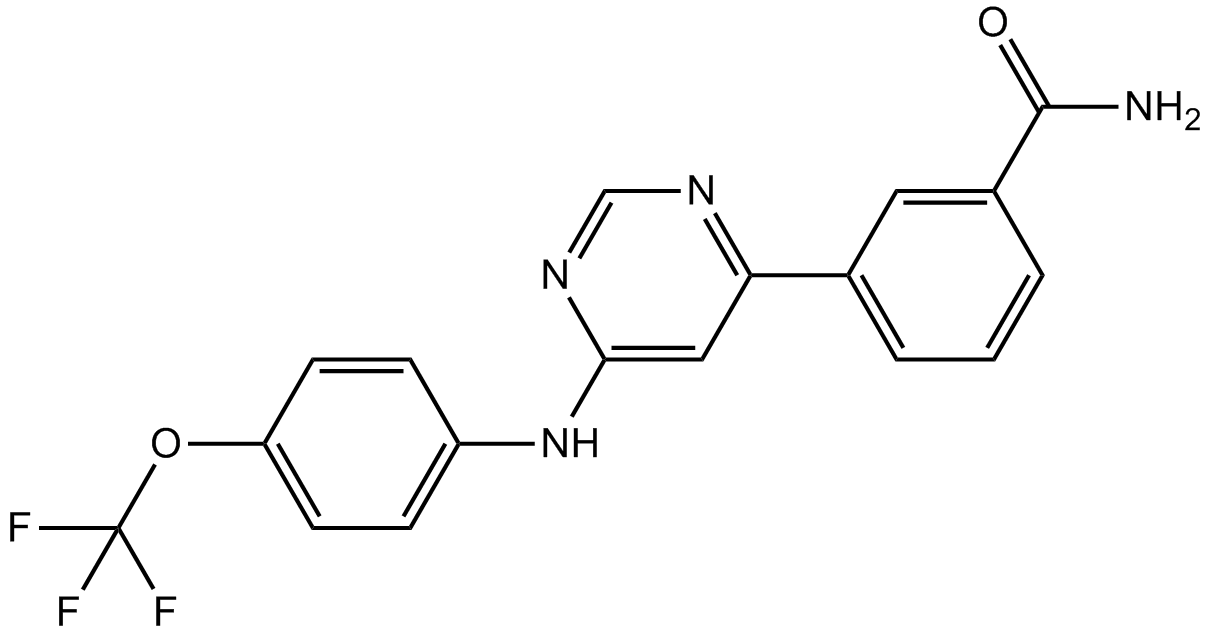 A8603 GNF 2Summary: Bcr-Abl inhibitor
A8603 GNF 2Summary: Bcr-Abl inhibitor -
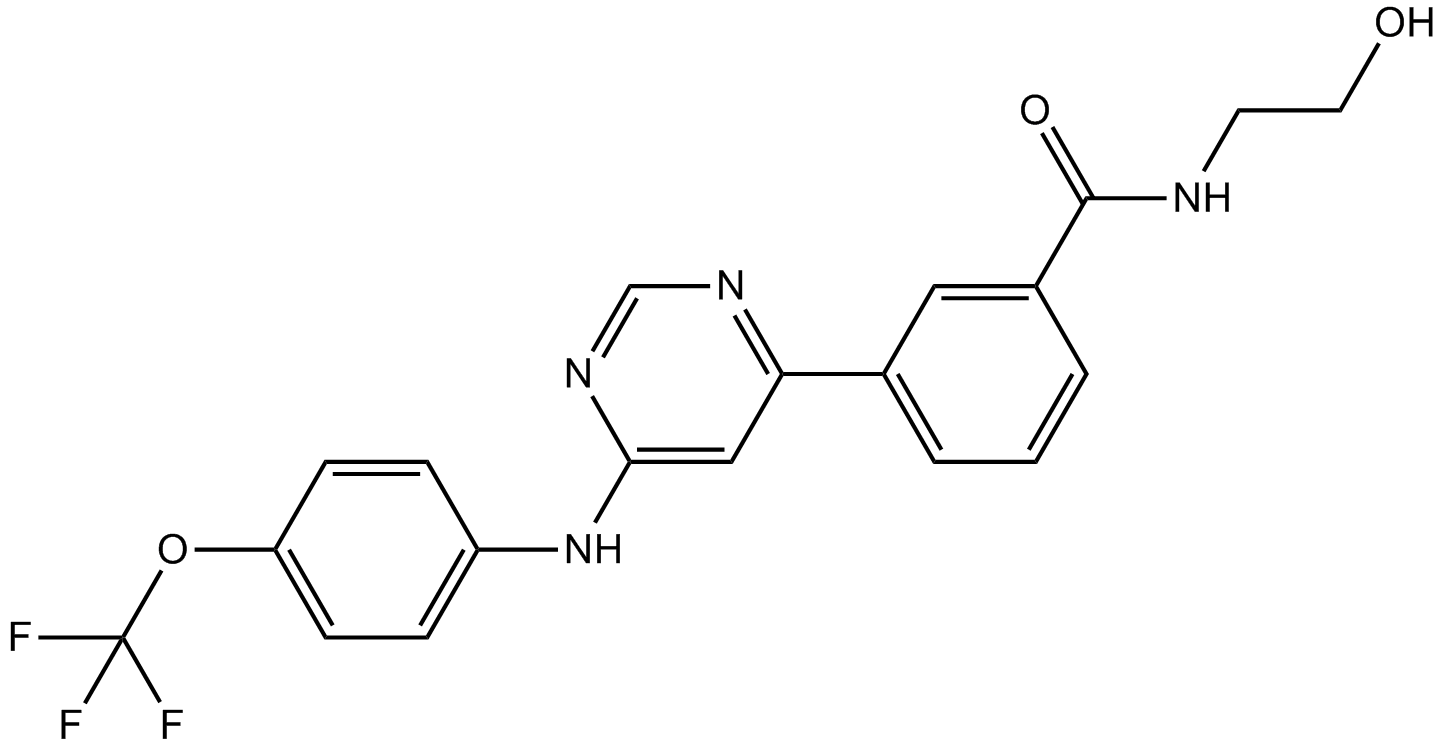 A8604 GNF 5Target: Bcr-AblSummary: Bcr-Abl inhibitor
A8604 GNF 5Target: Bcr-AblSummary: Bcr-Abl inhibitor -
 A8605 1-Naphthyl PP1Summary: Src family kinases inhibitor
A8605 1-Naphthyl PP1Summary: Src family kinases inhibitor


