Stem Cell
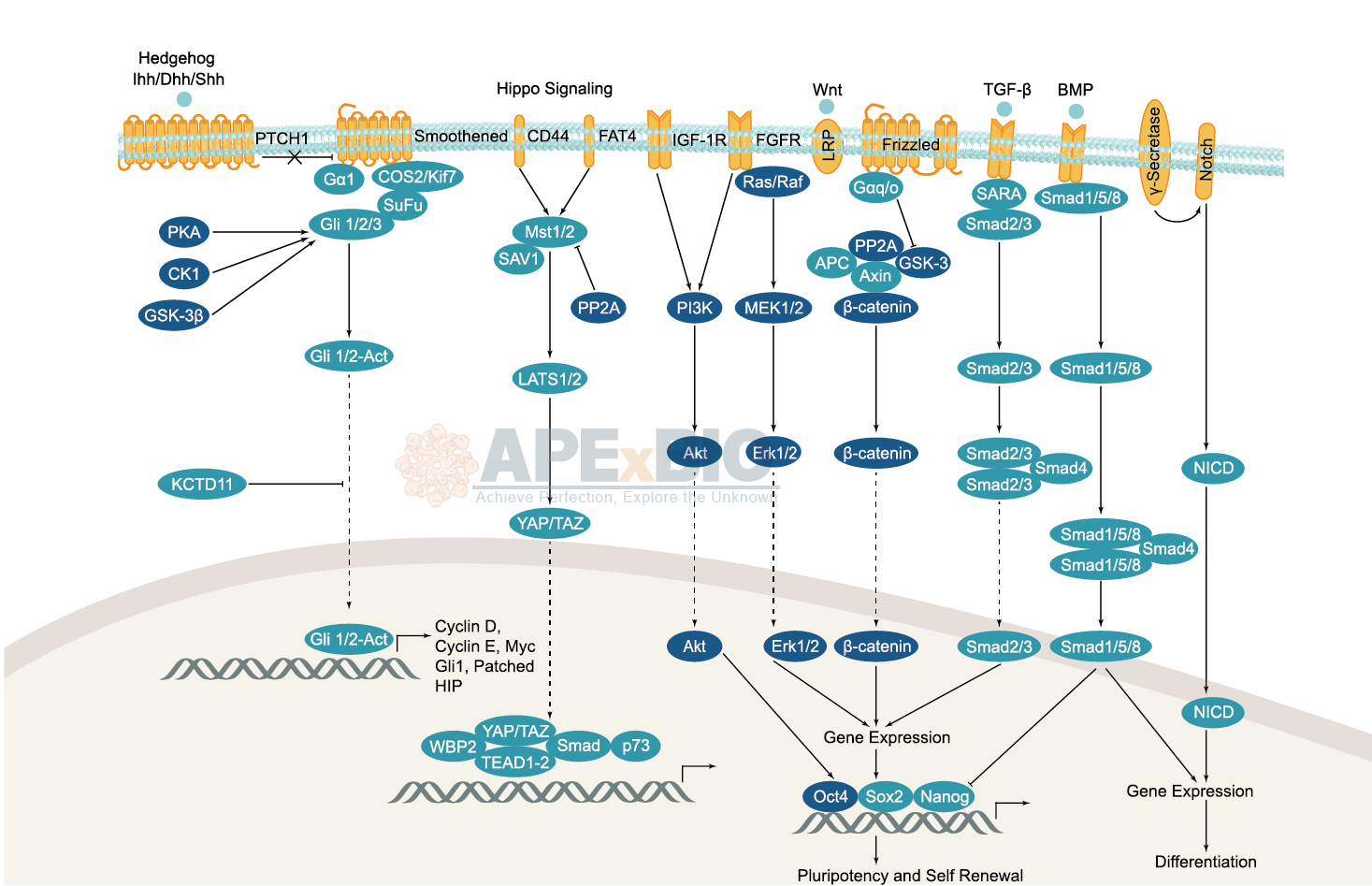

In ESC, BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway plays a key role in maintaining pluripotency and self-renewal. It signals through Smad proteins, and the FGF signaling pathway, which activates the MAPK and Akt pathways. The Wnt signaling pathway also promotes pluripotency. OCT-4, SOX2, and NANOG are three main transcription factors that are expressed and activated by these pathways. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) are pluripotent cells that can be generated from differentiated cells with forced expression of specific reprogramming factors. Both ESC and iPSC can be induced to develop into distinct cell types that associated with three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Signaling pathways that control the development of these cell lineages, including BMP/TGF-β, Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog and Hippo pathways, which regulate cell division, growth and differentiation. Defects in stem cell signaling are related to developmental disorders and cancer.
-
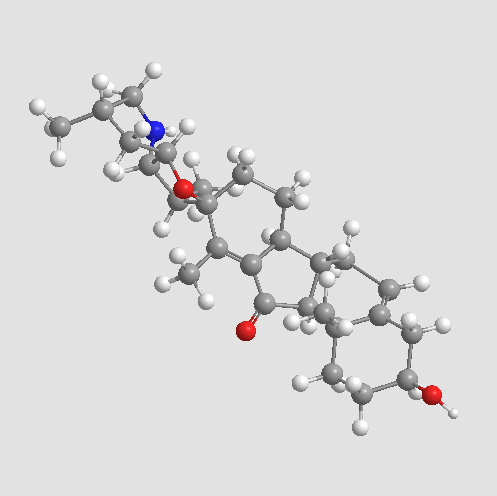 A8656 JervineSummary: Hedgehog signaling Inhibitor
A8656 JervineSummary: Hedgehog signaling Inhibitor -
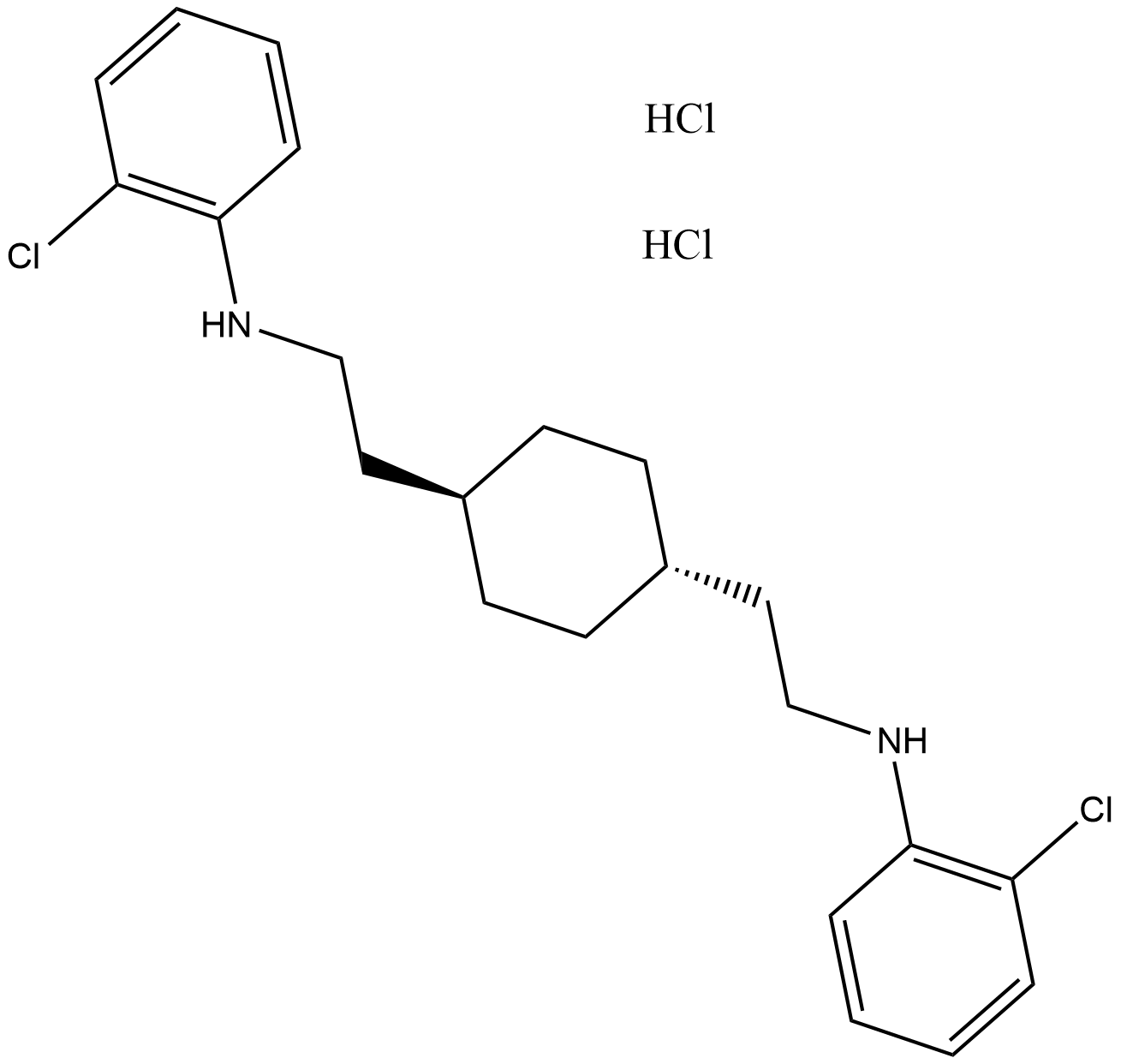 A8658 AY 9944 dihydrochlorideSummary: Hedgehog Inhibitor
A8658 AY 9944 dihydrochlorideSummary: Hedgehog Inhibitor -
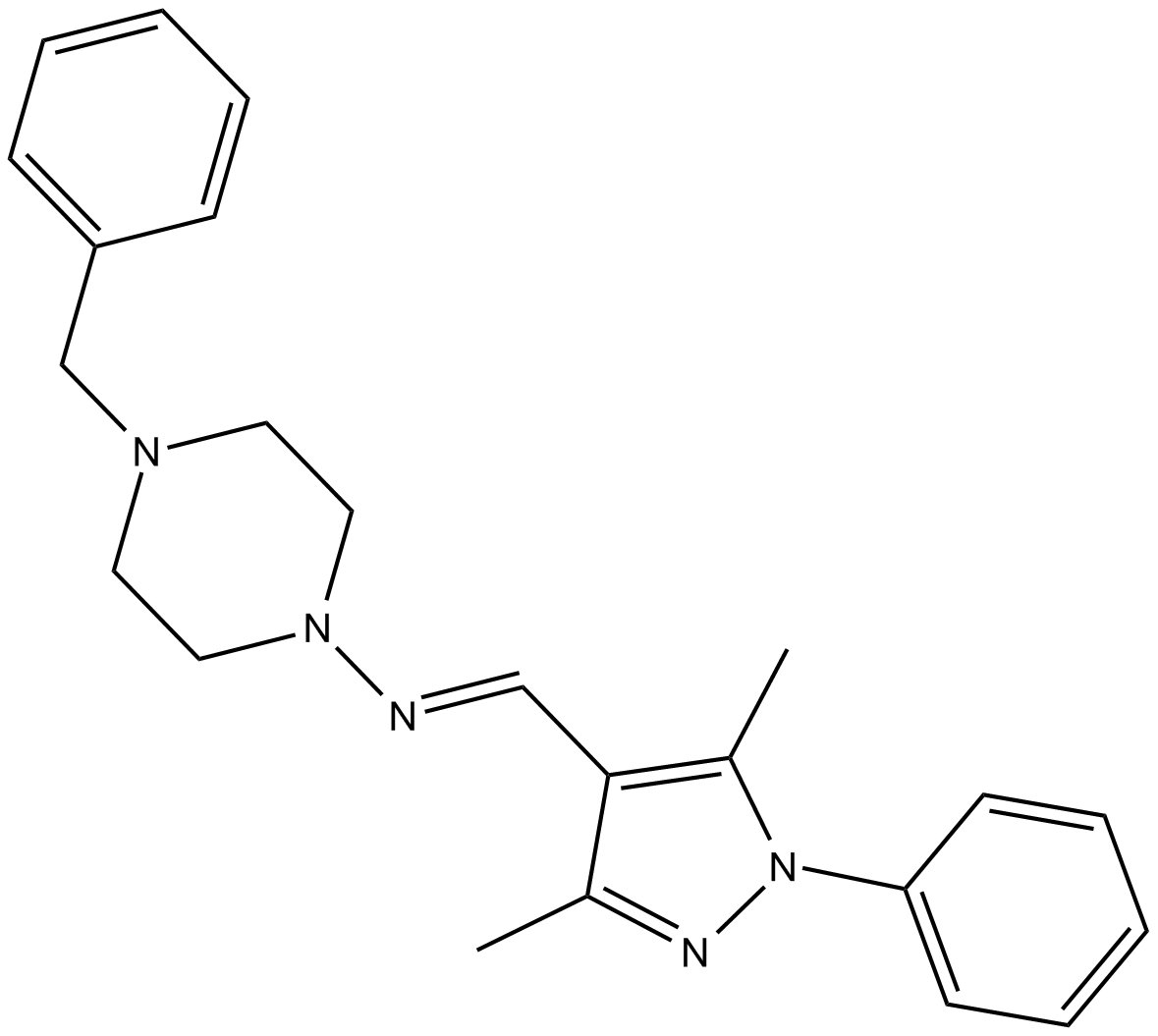 A8659 SANT-12 CitationSummary: Shh inhibitor,potent and cell-permeable
A8659 SANT-12 CitationSummary: Shh inhibitor,potent and cell-permeable -
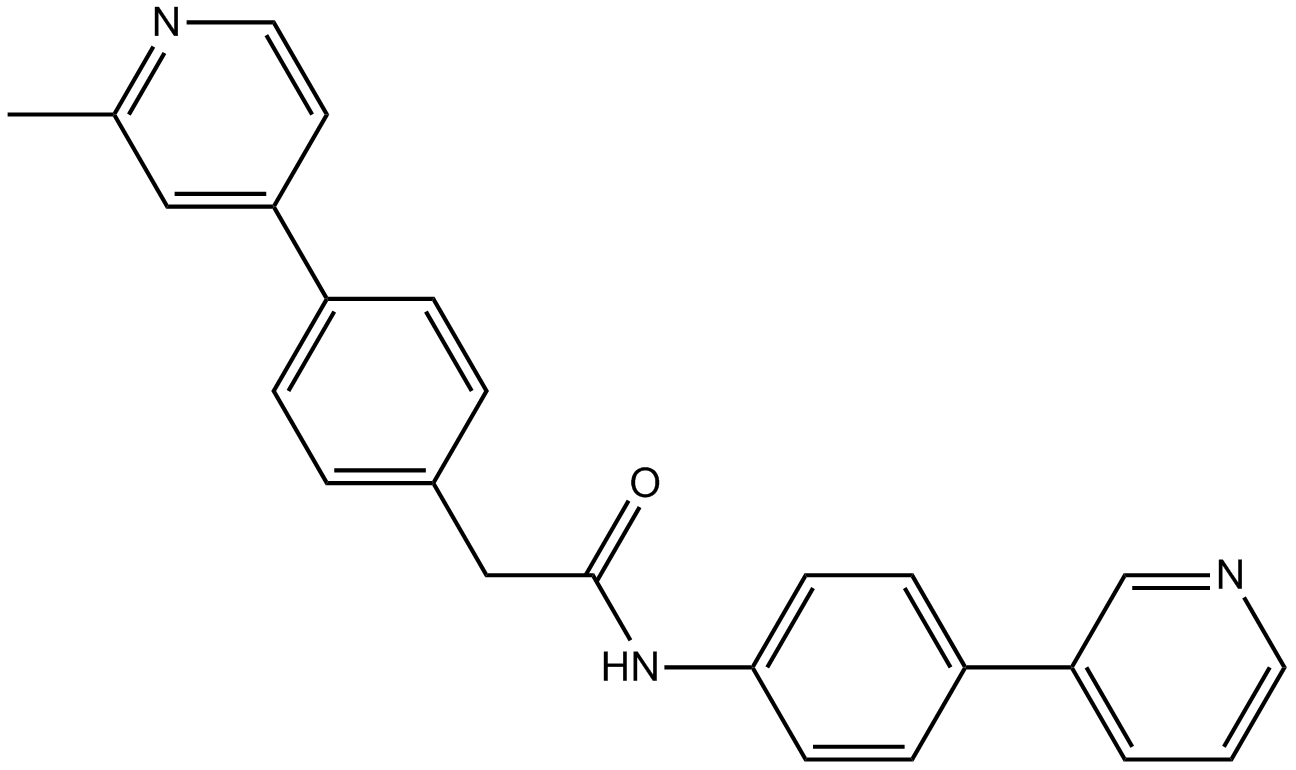 A8685 Wnt-C592 CitationTarget: PORCNSummary: PORCN inhibitor,highly potent and selective
A8685 Wnt-C592 CitationTarget: PORCNSummary: PORCN inhibitor,highly potent and selective -
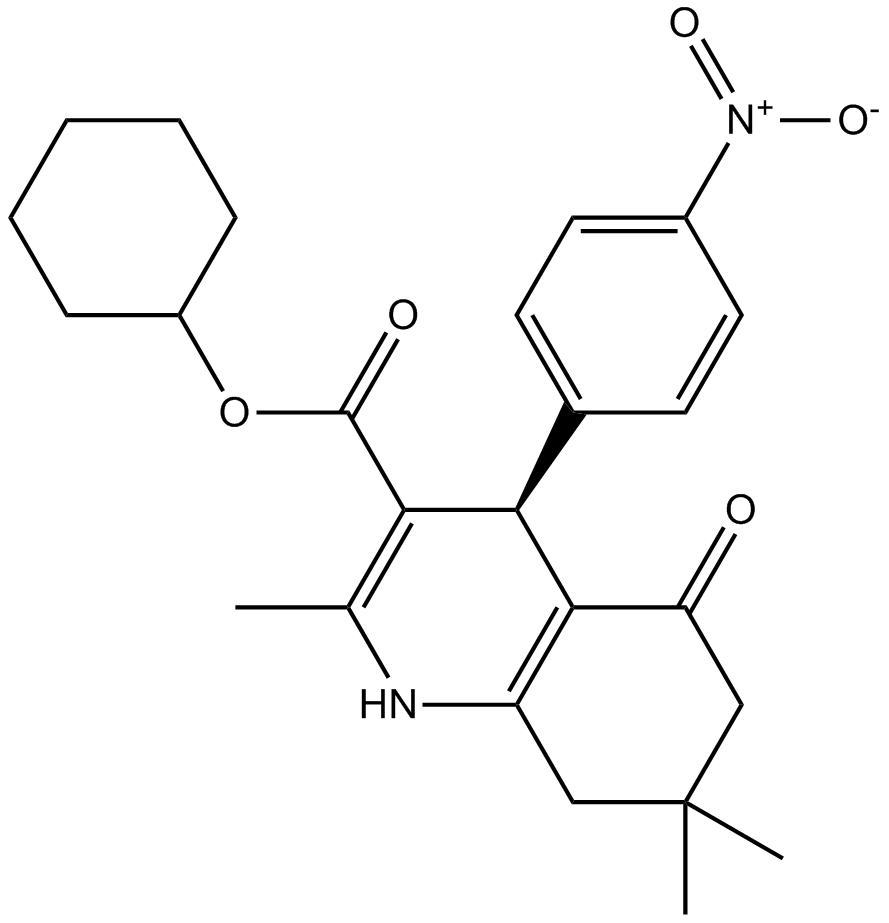
 A9905 Stem Cell Set ISummary: For inhibiting HDAC/ GSK-3α/β /histone methyltransferase /ALK5
A9905 Stem Cell Set ISummary: For inhibiting HDAC/ GSK-3α/β /histone methyltransferase /ALK5 -
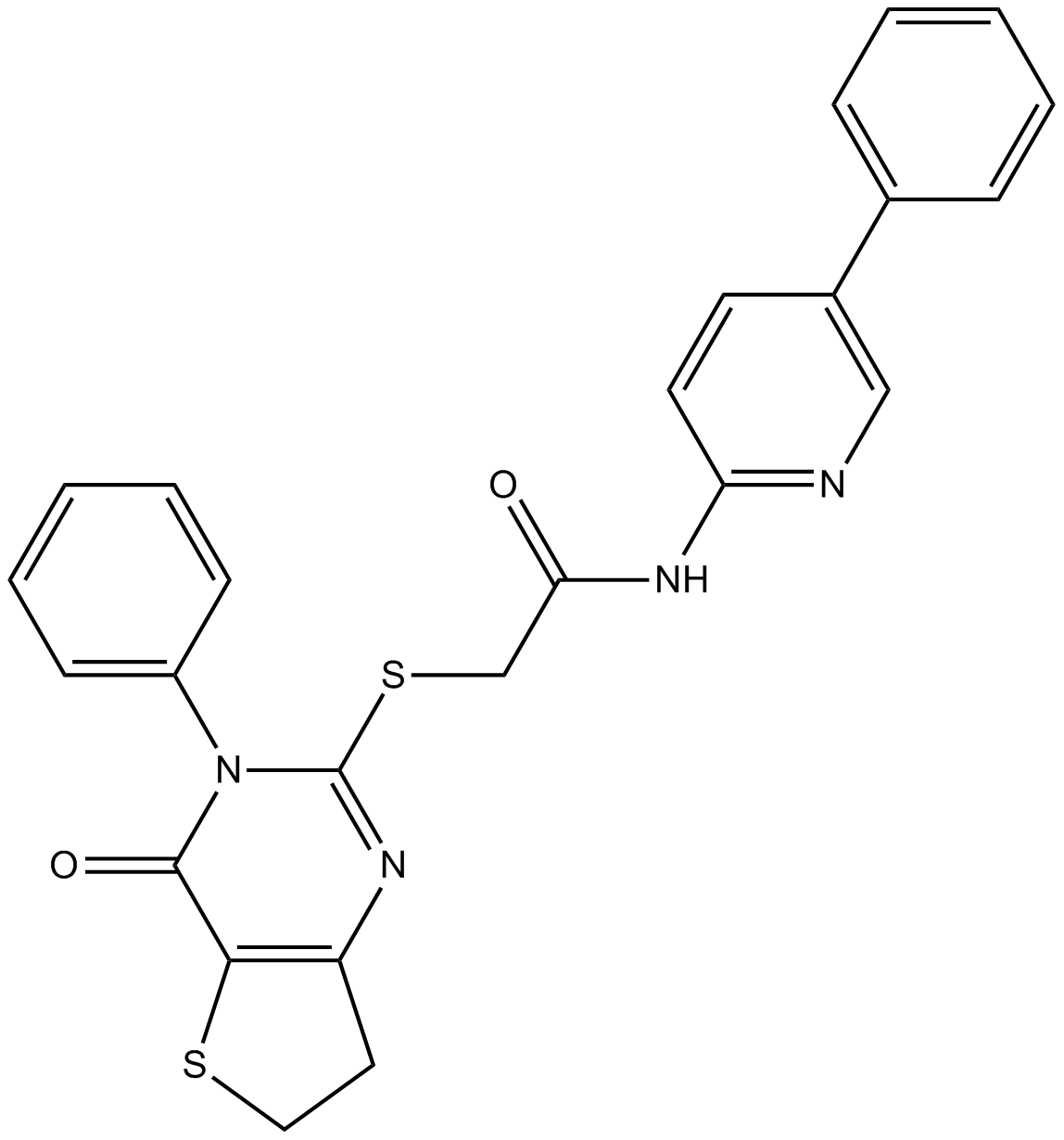
 B3083 FLI-06Summary: novel inhibitor of Notch signaling
B3083 FLI-06Summary: novel inhibitor of Notch signaling -
 B2305 IWP-L6Summary: Porcupine inhibitor,highy potent
B2305 IWP-L6Summary: Porcupine inhibitor,highy potent -
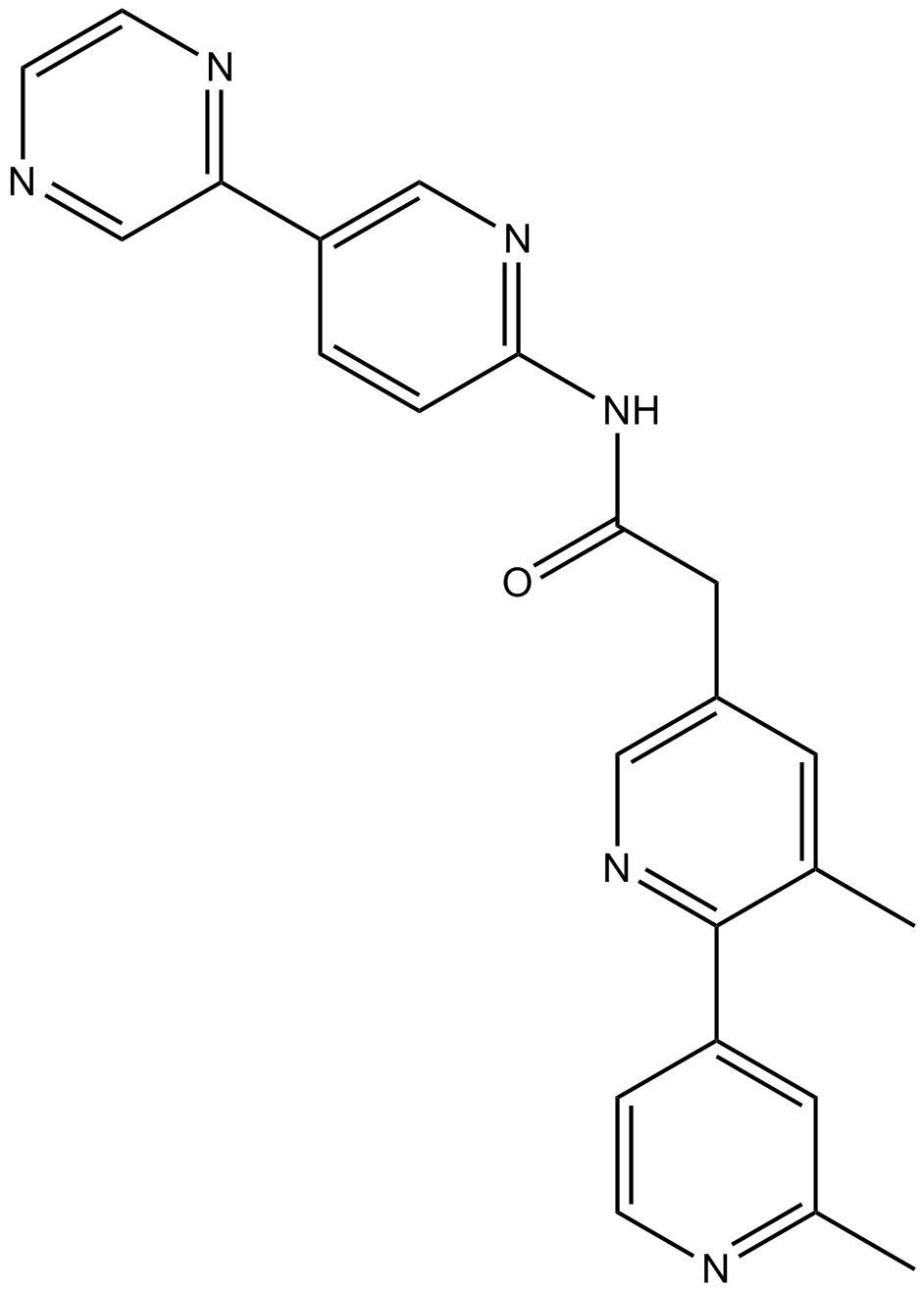 B2307 LGK-9744 CitationSummary: PORCN inhibitor,potent and specific
B2307 LGK-9744 CitationSummary: PORCN inhibitor,potent and specific -
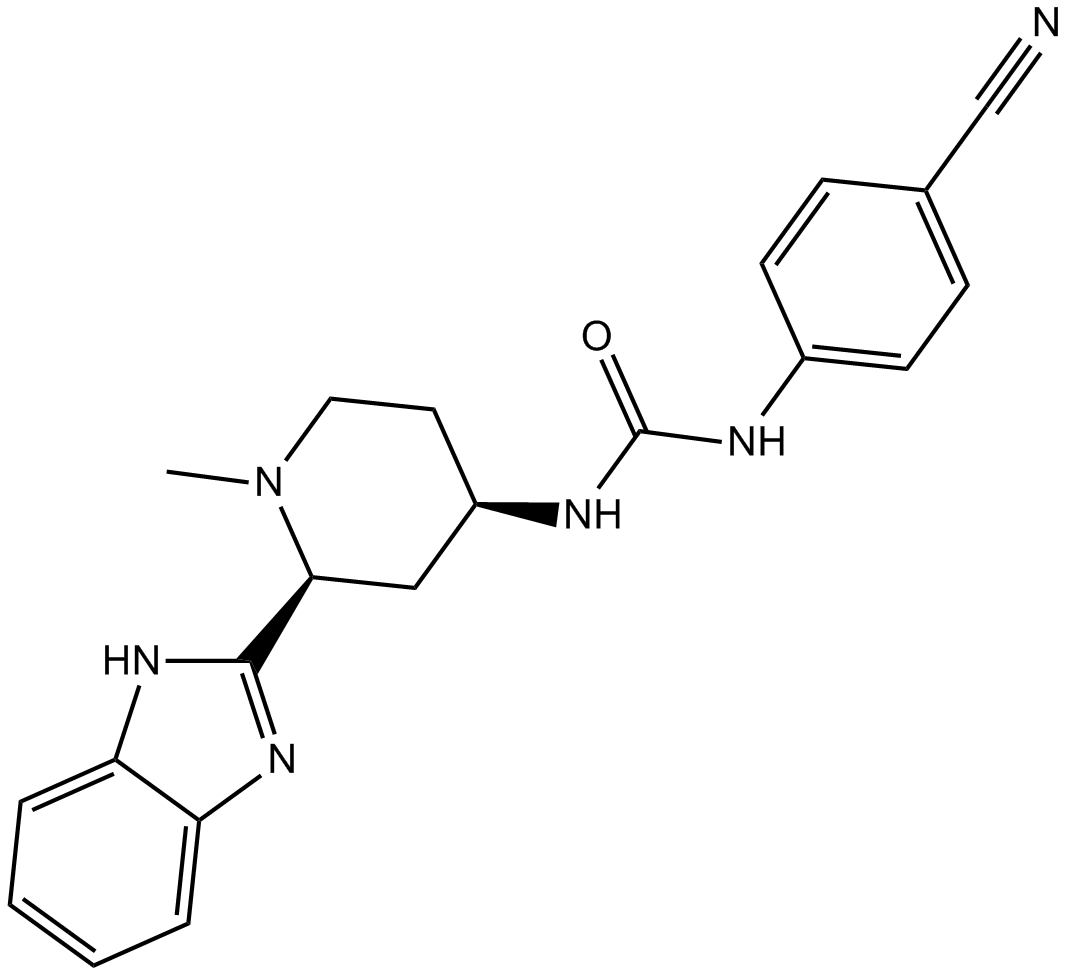 B3283 PF-04449913Target: SmoothenedSummary: Antagonist of smoothened
B3283 PF-04449913Target: SmoothenedSummary: Antagonist of smoothened -
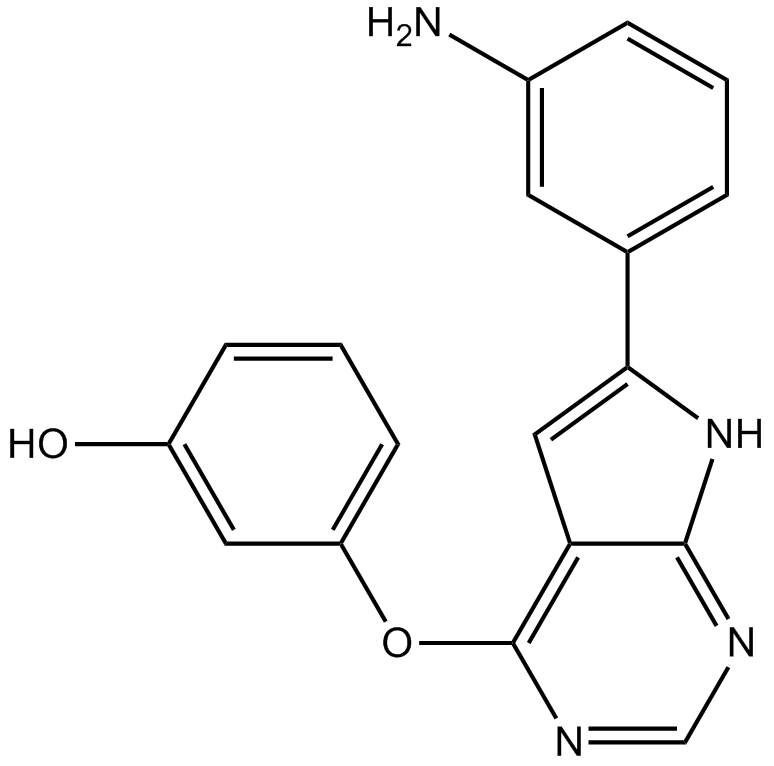 B1540 TWS1191 CitationSummary: GSK-3β inhibitor
B1540 TWS1191 CitationSummary: GSK-3β inhibitor


