Stem Cell
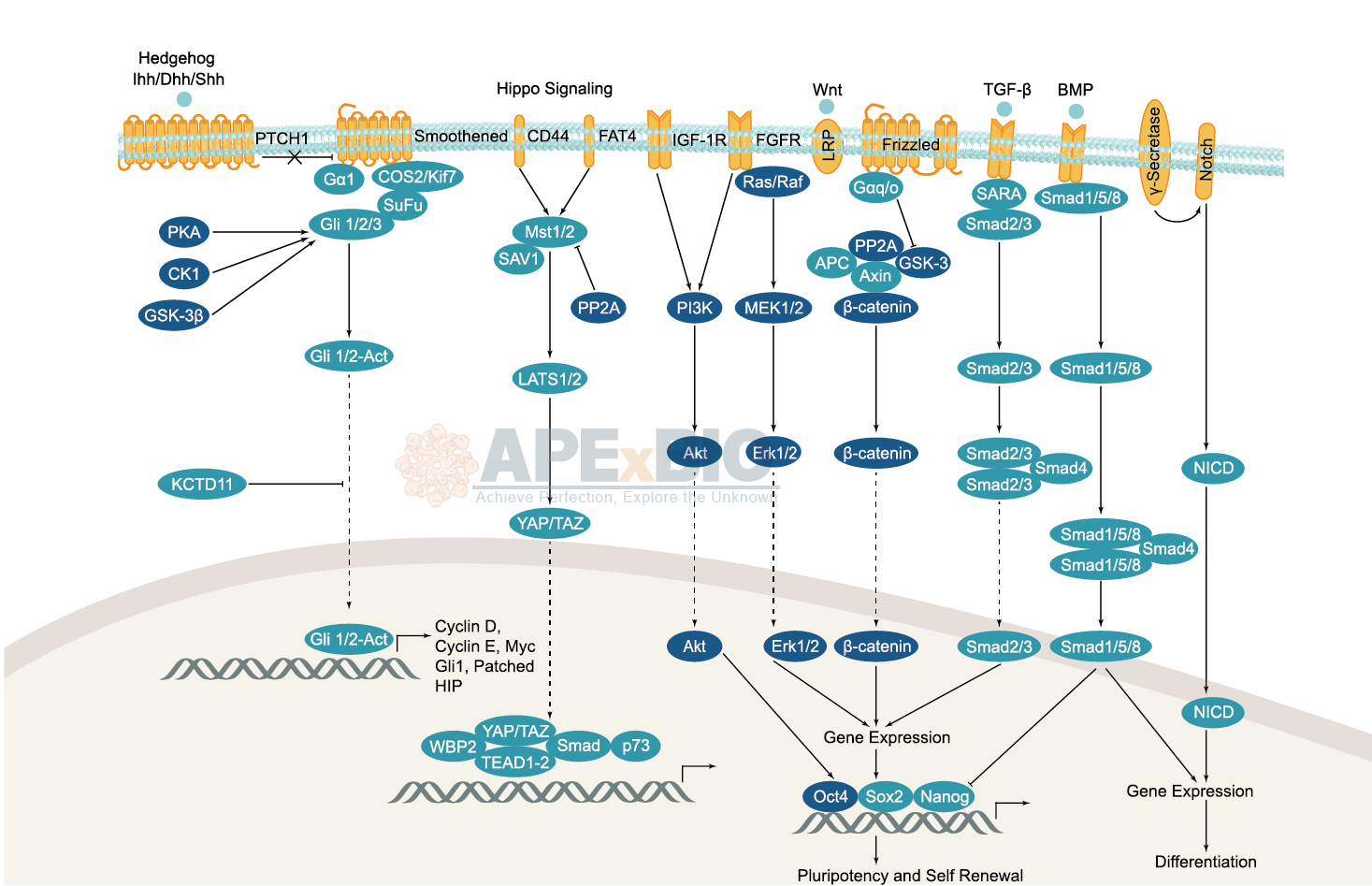

In ESC, BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway plays a key role in maintaining pluripotency and self-renewal. It signals through Smad proteins, and the FGF signaling pathway, which activates the MAPK and Akt pathways. The Wnt signaling pathway also promotes pluripotency. OCT-4, SOX2, and NANOG are three main transcription factors that are expressed and activated by these pathways. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) are pluripotent cells that can be generated from differentiated cells with forced expression of specific reprogramming factors. Both ESC and iPSC can be induced to develop into distinct cell types that associated with three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Signaling pathways that control the development of these cell lineages, including BMP/TGF-β, Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog and Hippo pathways, which regulate cell division, growth and differentiation. Defects in stem cell signaling are related to developmental disorders and cancer.
-
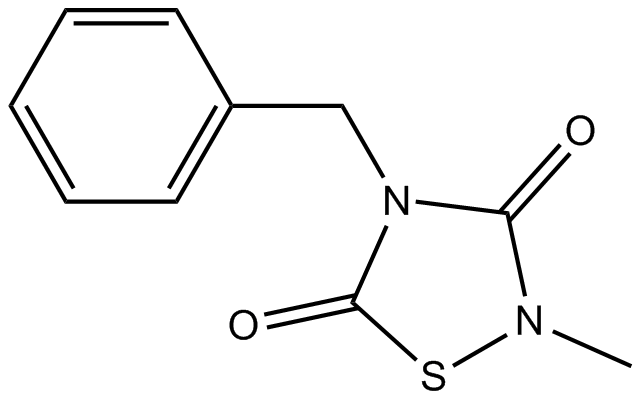 B1249 TDZD-81 CitationSummary: GSK-3β inhibitor
B1249 TDZD-81 CitationSummary: GSK-3β inhibitor -
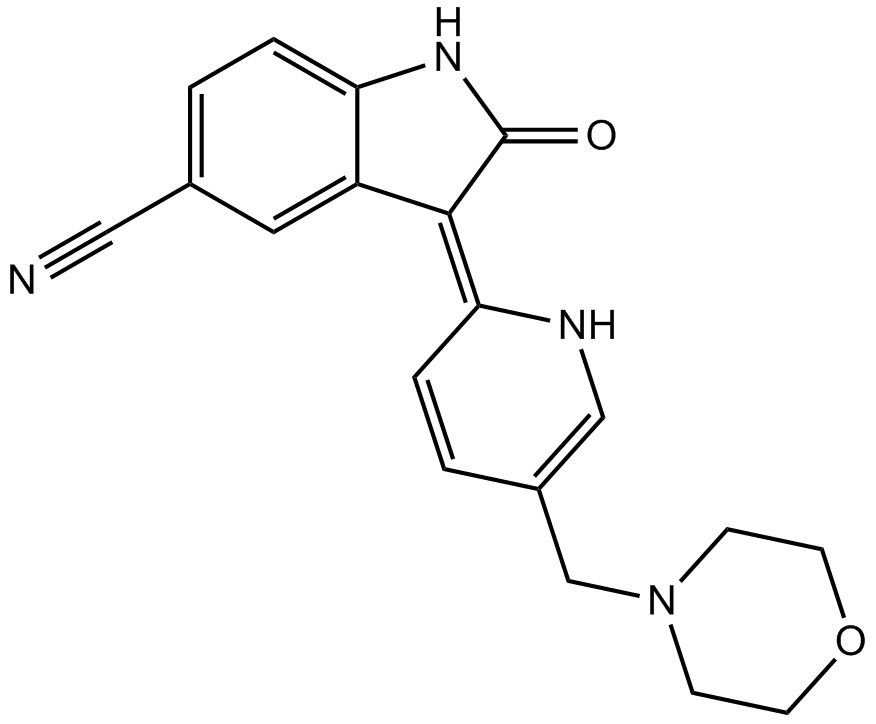 B1536 AZD10801 CitationTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK3βinhibitor
B1536 AZD10801 CitationTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK3βinhibitor -
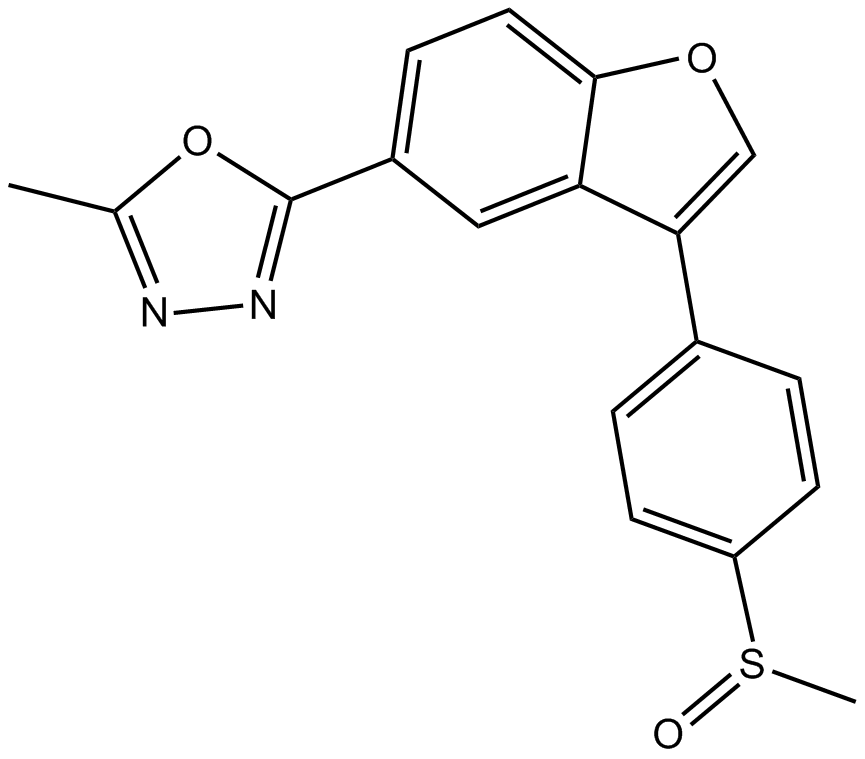 B5486 TCS 2002Summary: GSK -3β inhibitor, potent
B5486 TCS 2002Summary: GSK -3β inhibitor, potent -
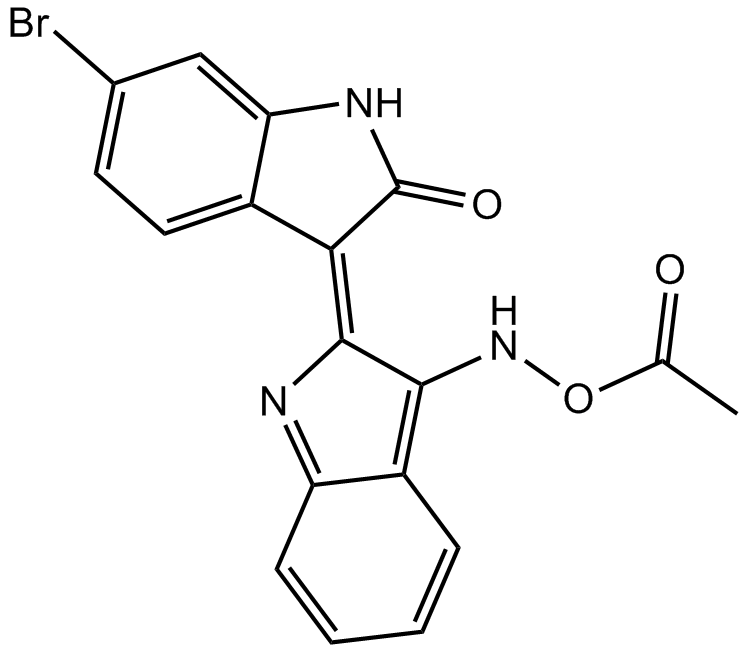 B5488 BIO-acetoximeSummary: GSK-3α/β inhibitor
B5488 BIO-acetoximeSummary: GSK-3α/β inhibitor -
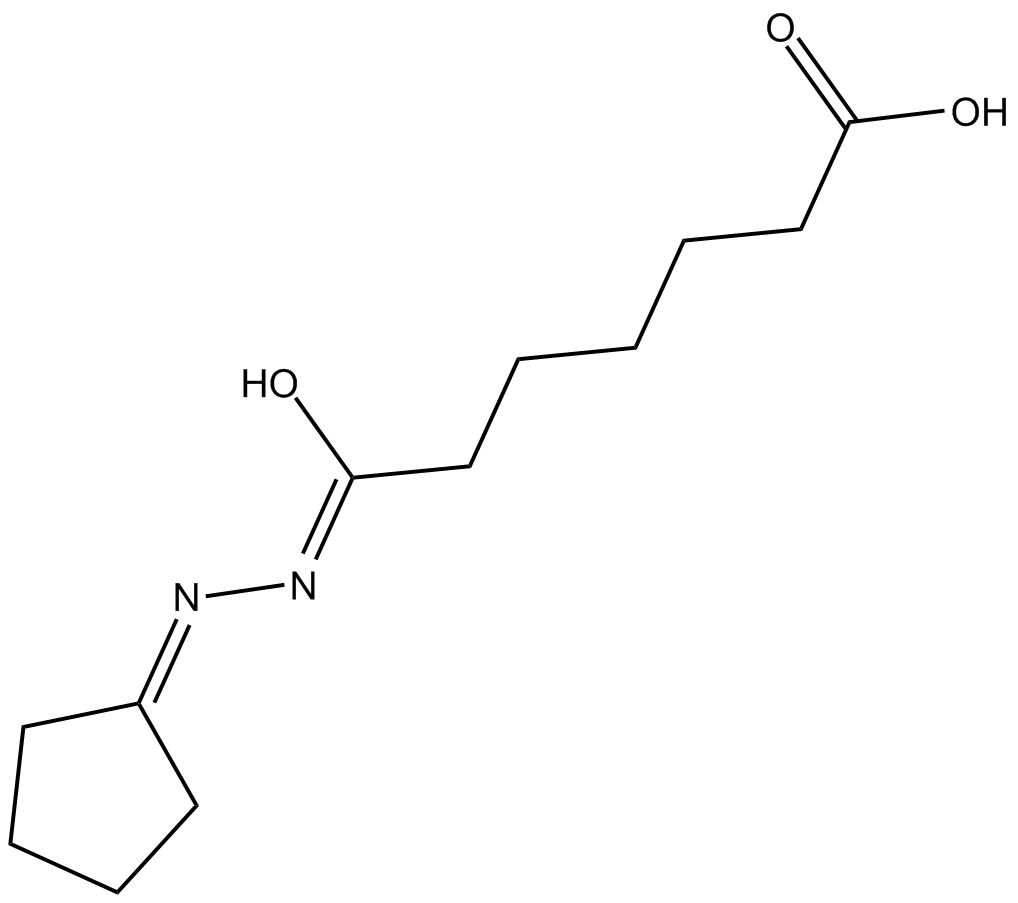 B5511 IDE 2Summary: inducer of definitive endoderm formation
B5511 IDE 2Summary: inducer of definitive endoderm formation -
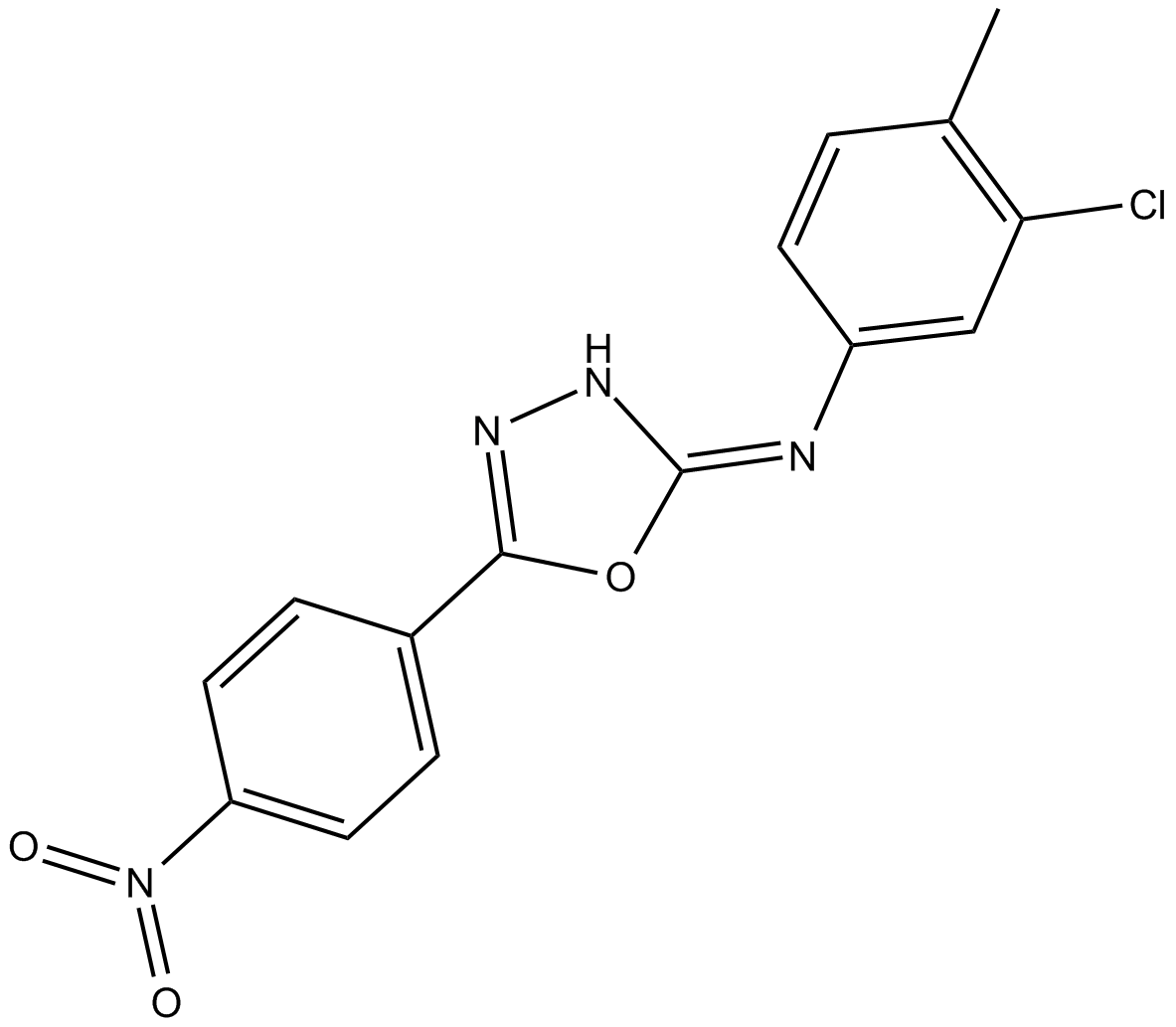 B5561 TC-G 24Summary: GSK-3β inhibitor
B5561 TC-G 24Summary: GSK-3β inhibitor -
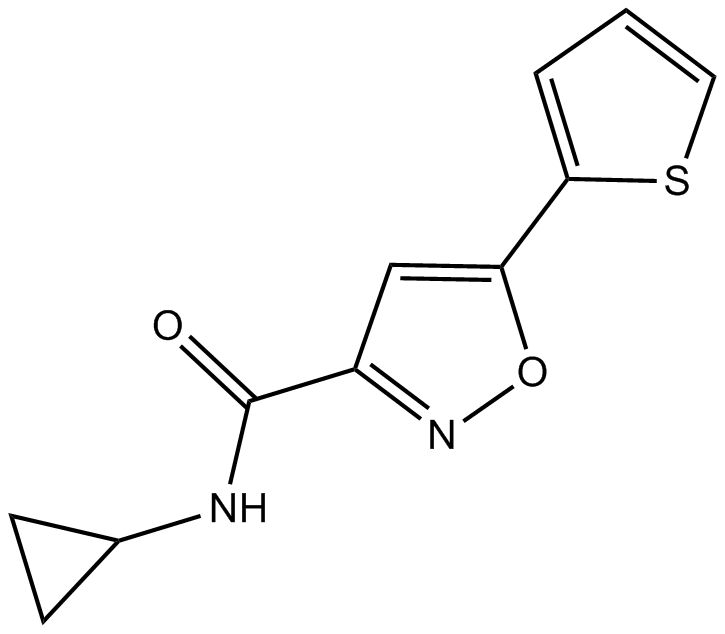 B5596 ISX 9Summary: neurogenic agent
B5596 ISX 9Summary: neurogenic agent -
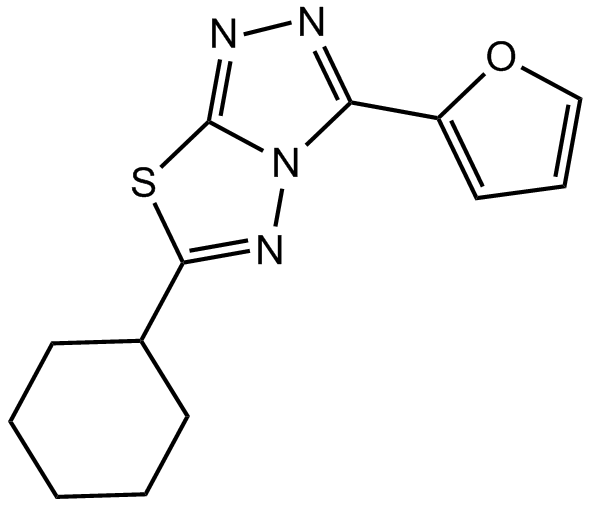 B5614 Cardionogen 1Summary: Wnt signaling modulator
B5614 Cardionogen 1Summary: Wnt signaling modulator -
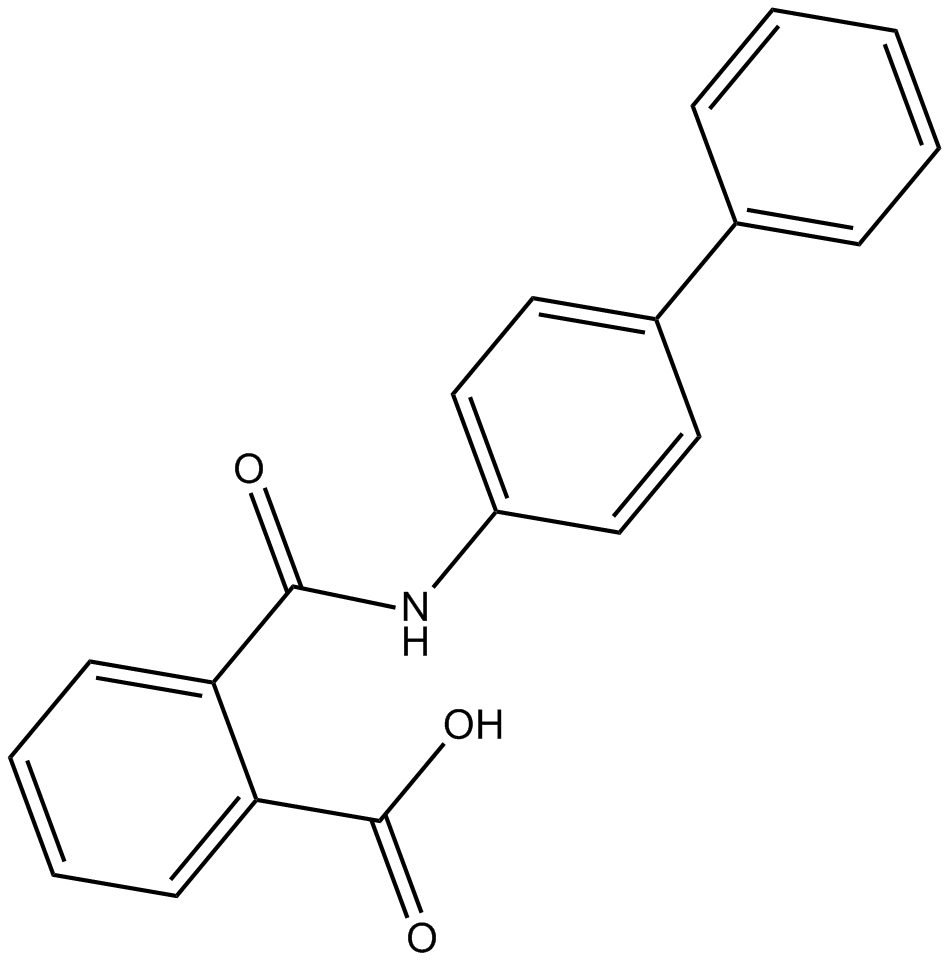 B5626 KartogeninSummary: induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes
B5626 KartogeninSummary: induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes -
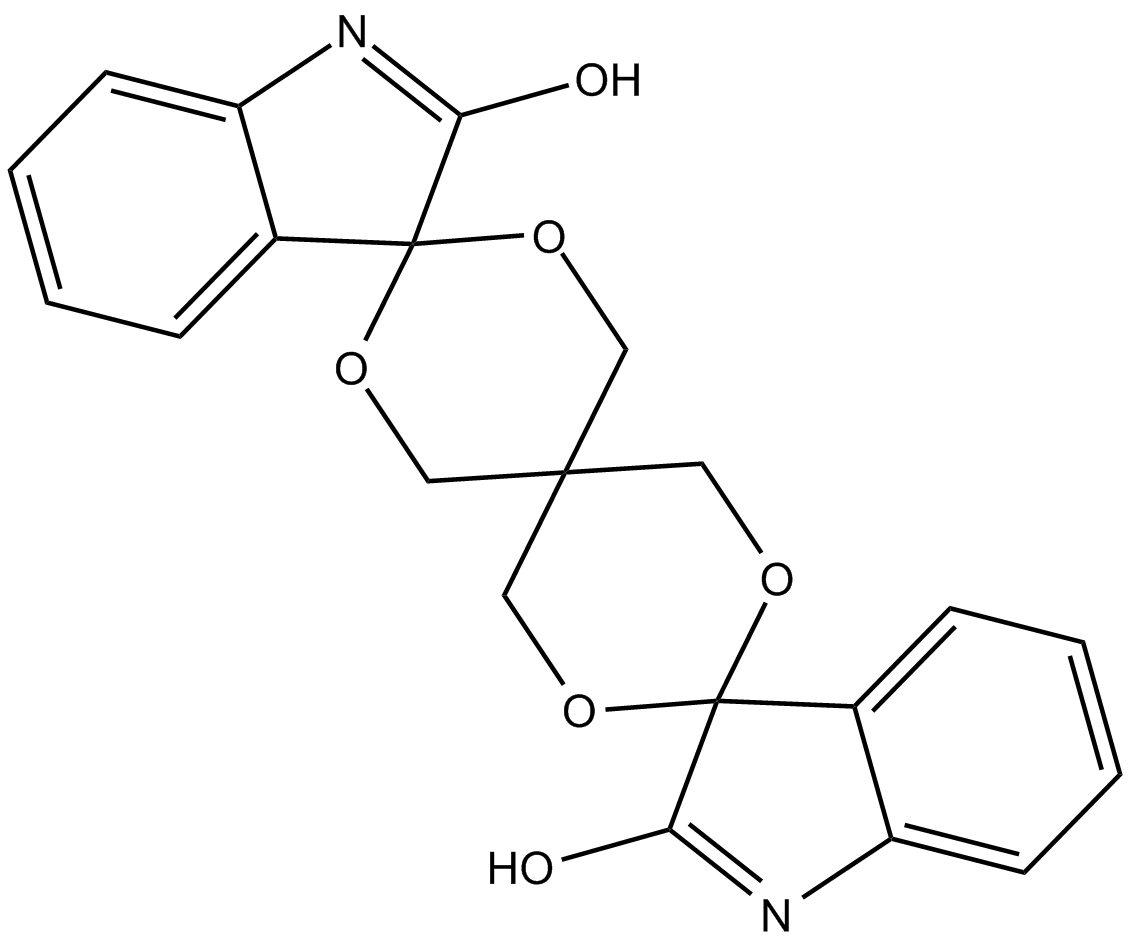 B5671 JW 67Summary: inhibitor of canonical Wnt pathway signaling
B5671 JW 67Summary: inhibitor of canonical Wnt pathway signaling


