Metabolism
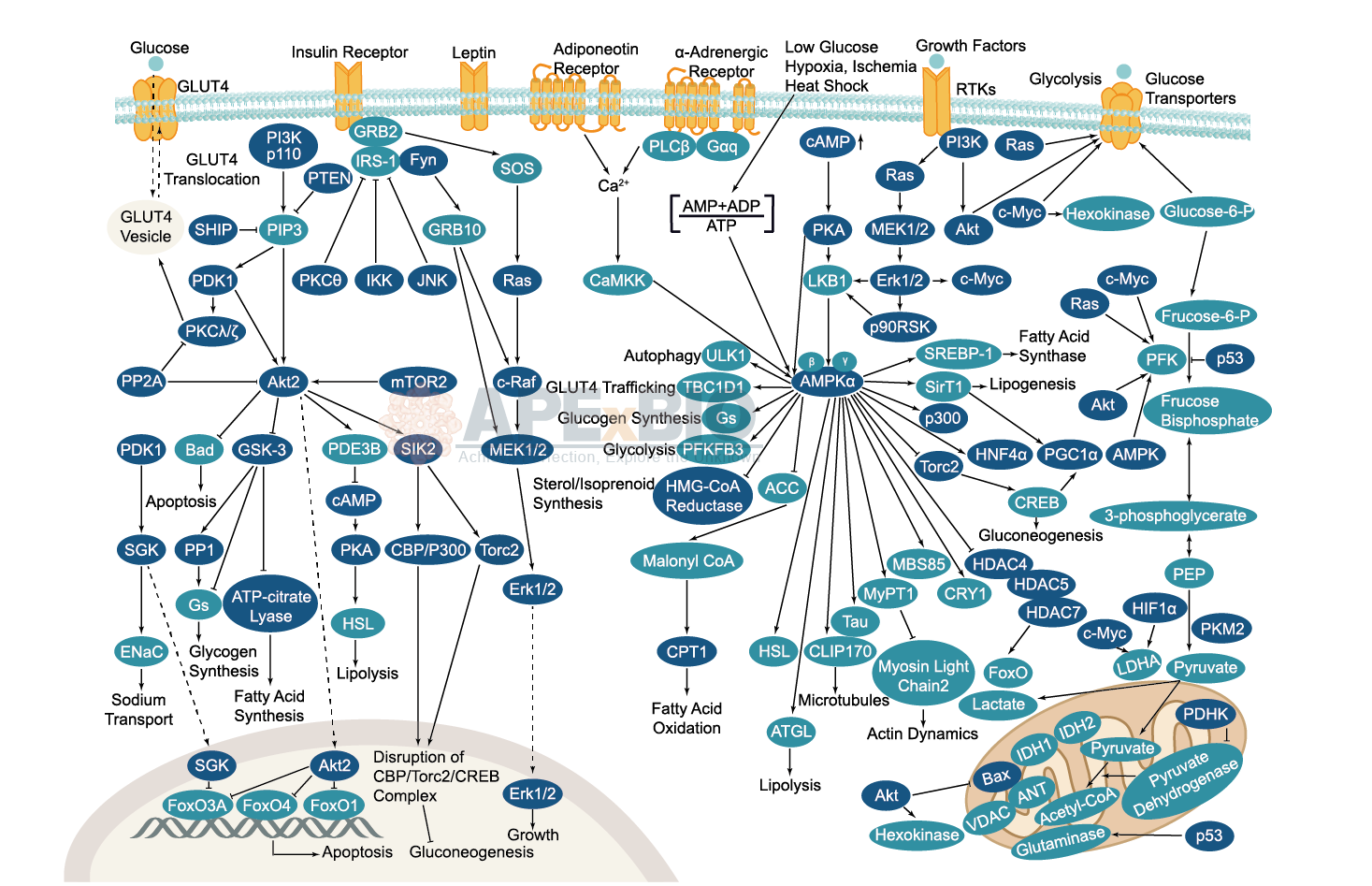

Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
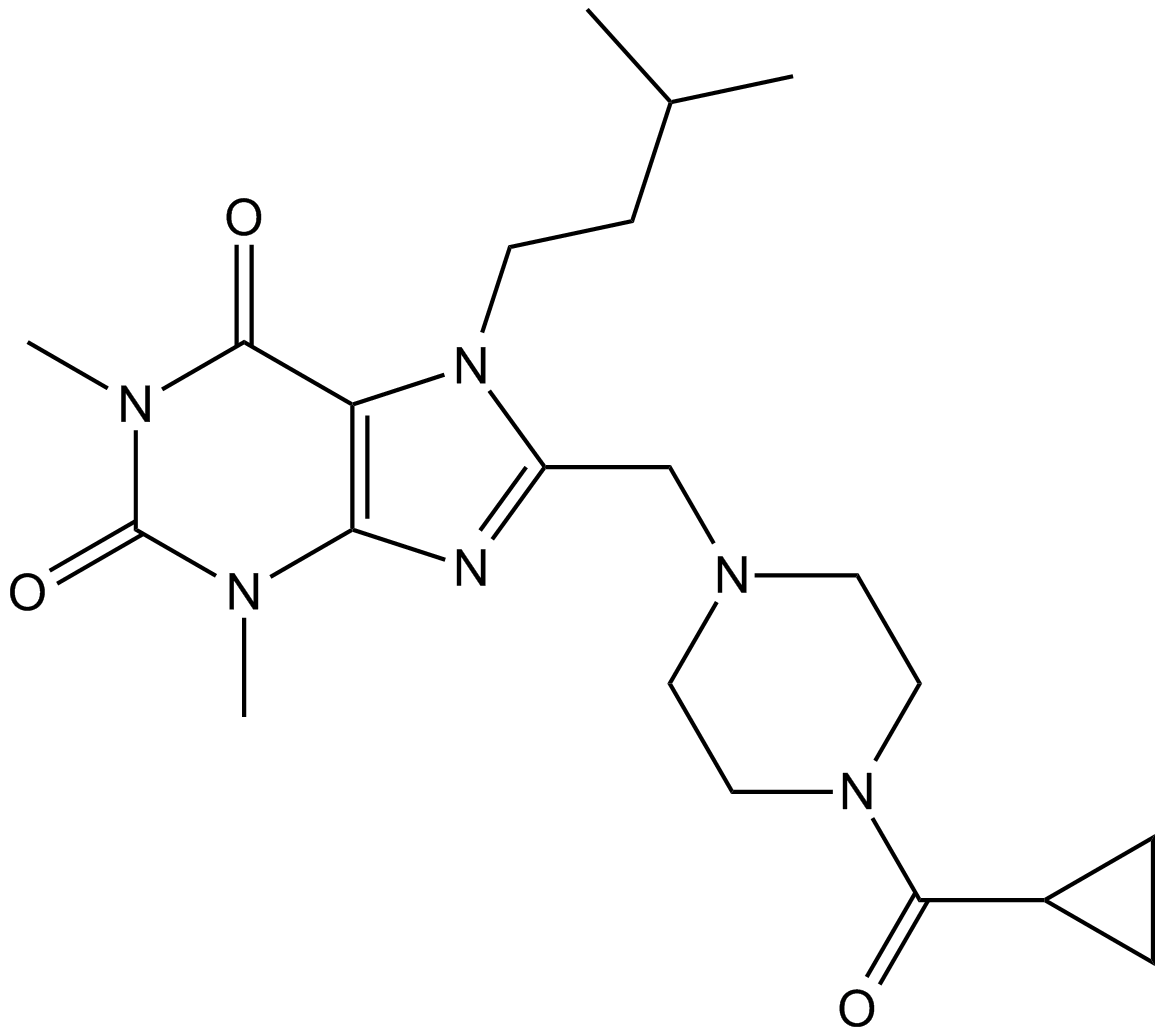 B6044 NCT-501Summary: Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1A1 (ALDH1A1) inhibitor, Potent and Selective
B6044 NCT-501Summary: Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1A1 (ALDH1A1) inhibitor, Potent and Selective -
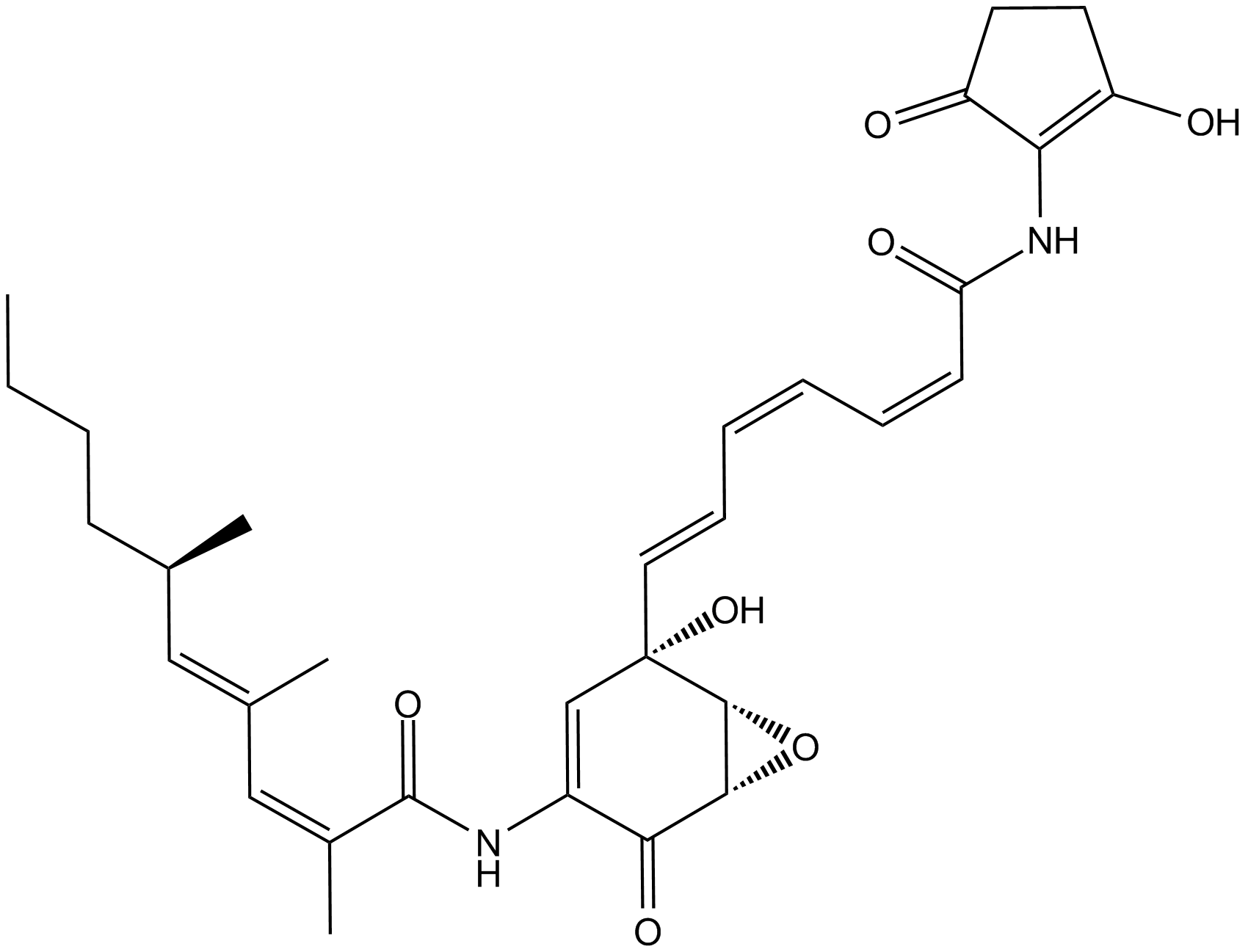 B6062 Manumycin ASummary: farnesyltransferase inhibitor
B6062 Manumycin ASummary: farnesyltransferase inhibitor -
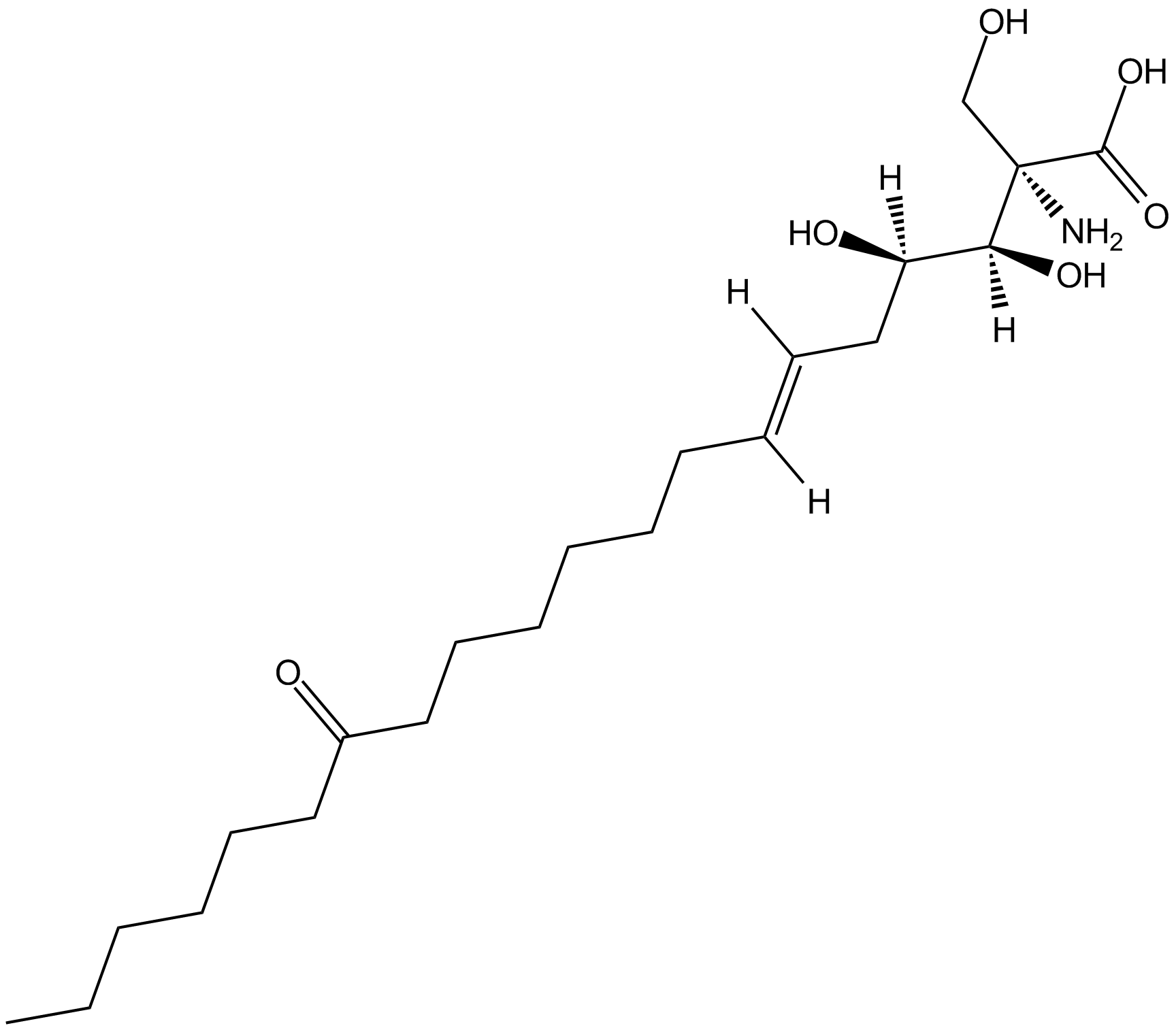 B6064 MyriocinSummary: immunosuppressant and specific serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor
B6064 MyriocinSummary: immunosuppressant and specific serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor -
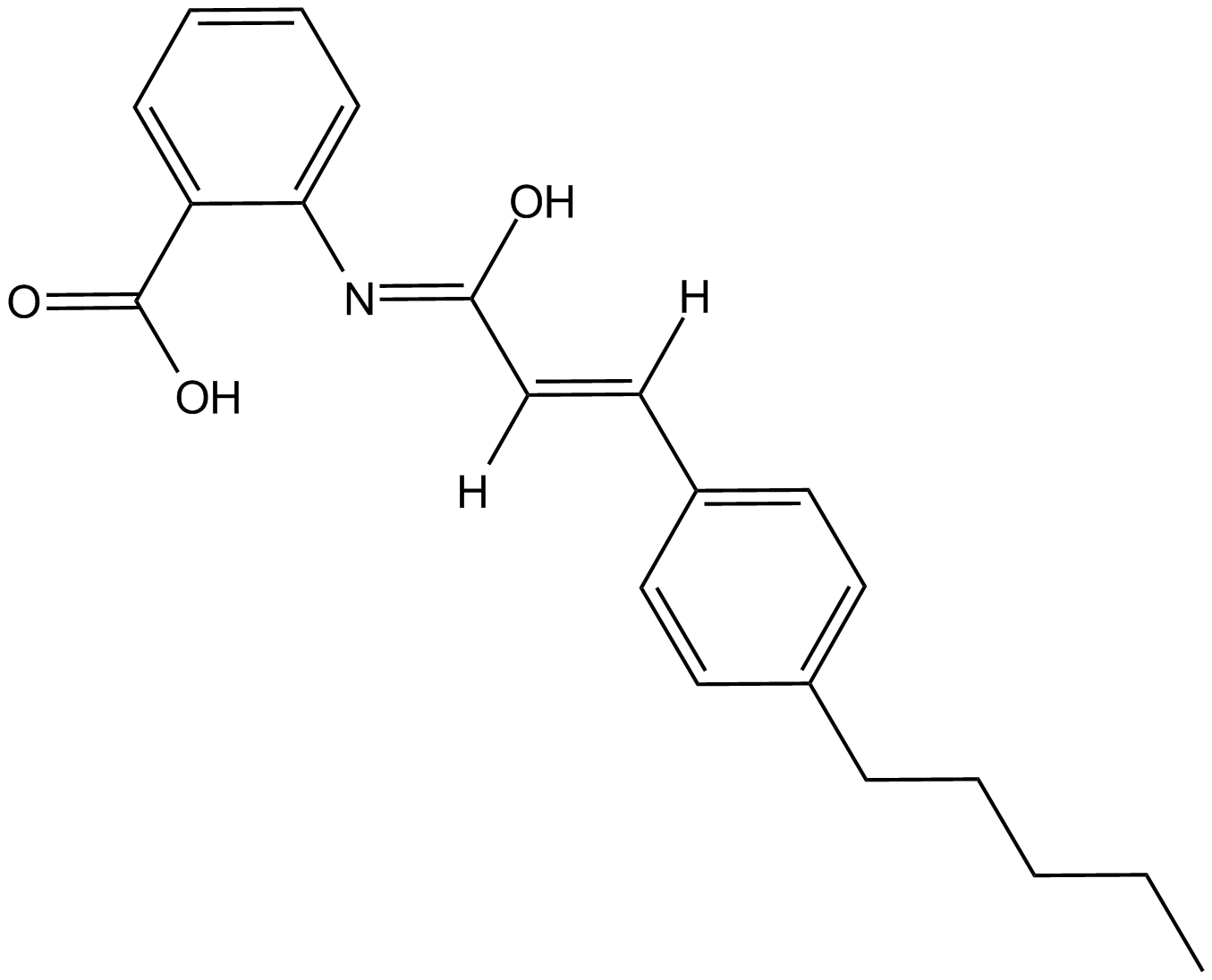 B6067 N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic AcidSummary: phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitor and TRP channel blocker
B6067 N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic AcidSummary: phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitor and TRP channel blocker -
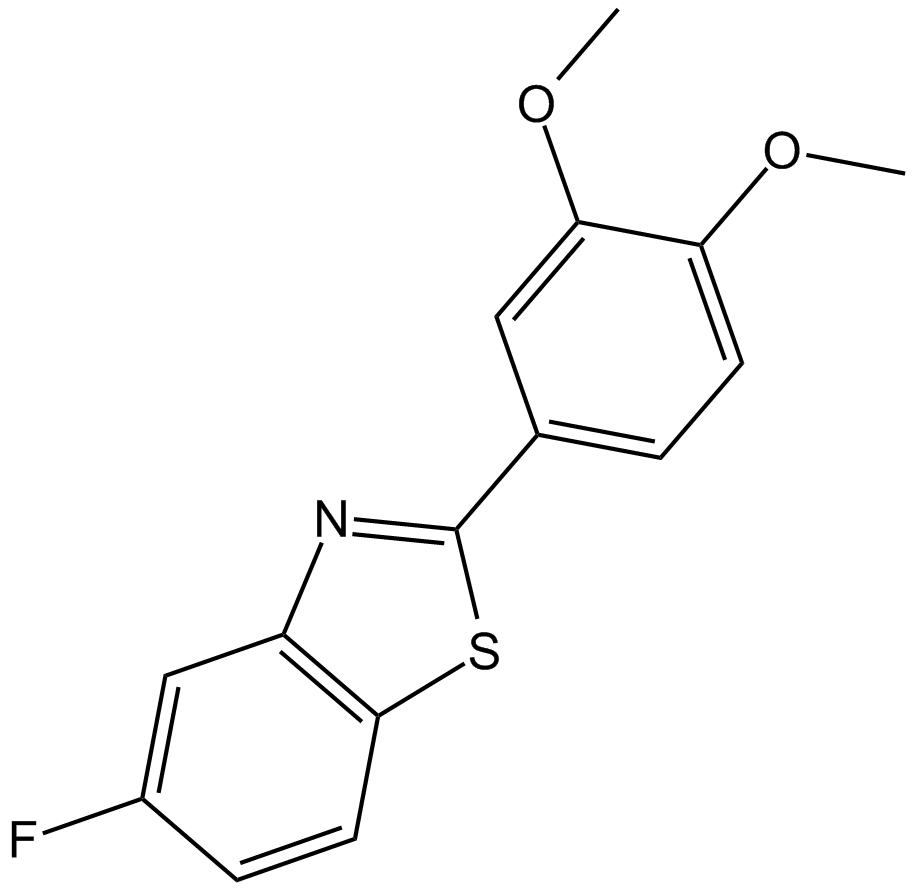 B6072 GW 610Summary: antiproliferative agent
B6072 GW 610Summary: antiproliferative agent -
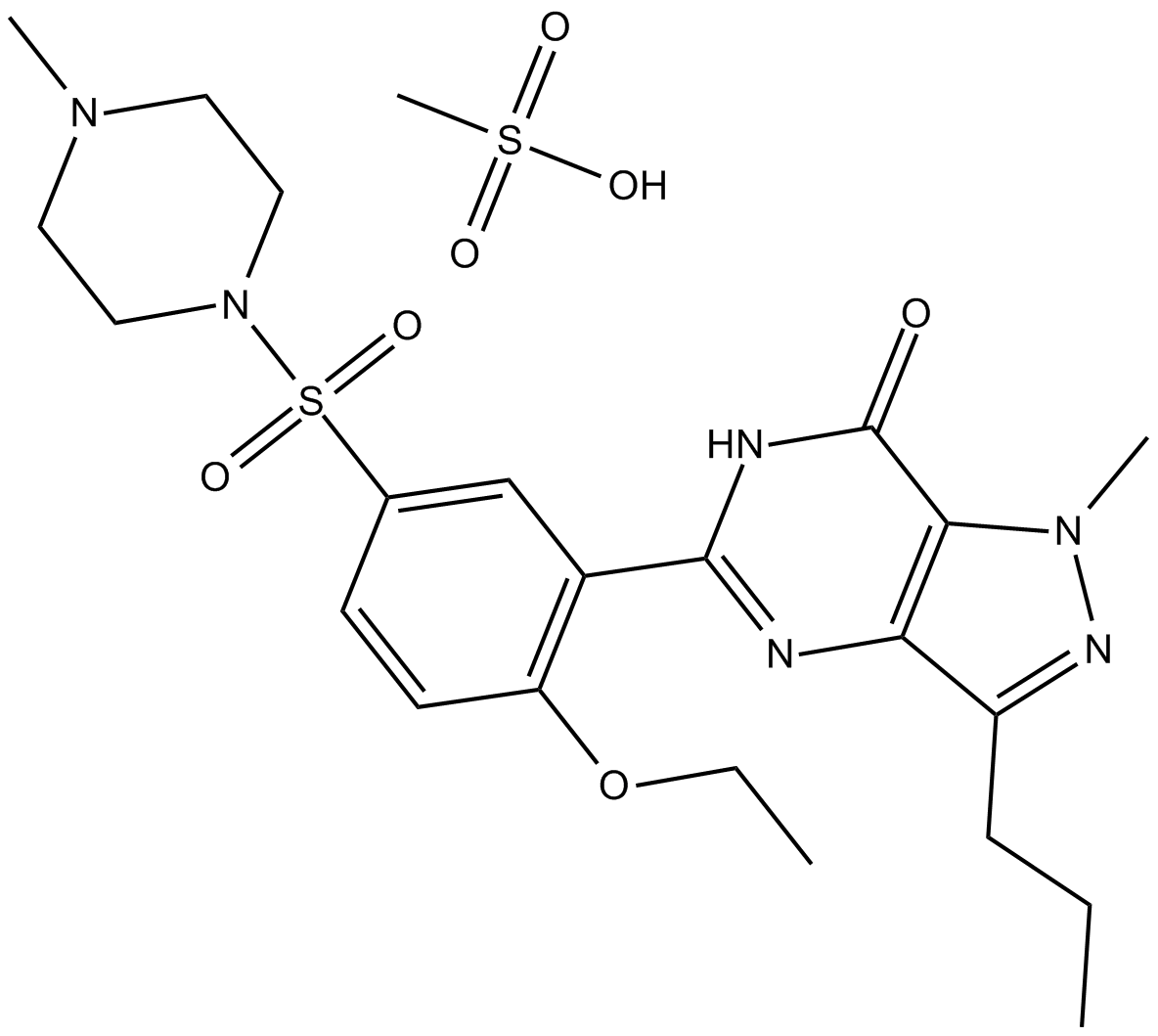 B6073 Sildenafil mesylateSummary: PDE5 inhibitor
B6073 Sildenafil mesylateSummary: PDE5 inhibitor -
 B6083 LiClSummary: used to precipitate RNA
B6083 LiClSummary: used to precipitate RNA -
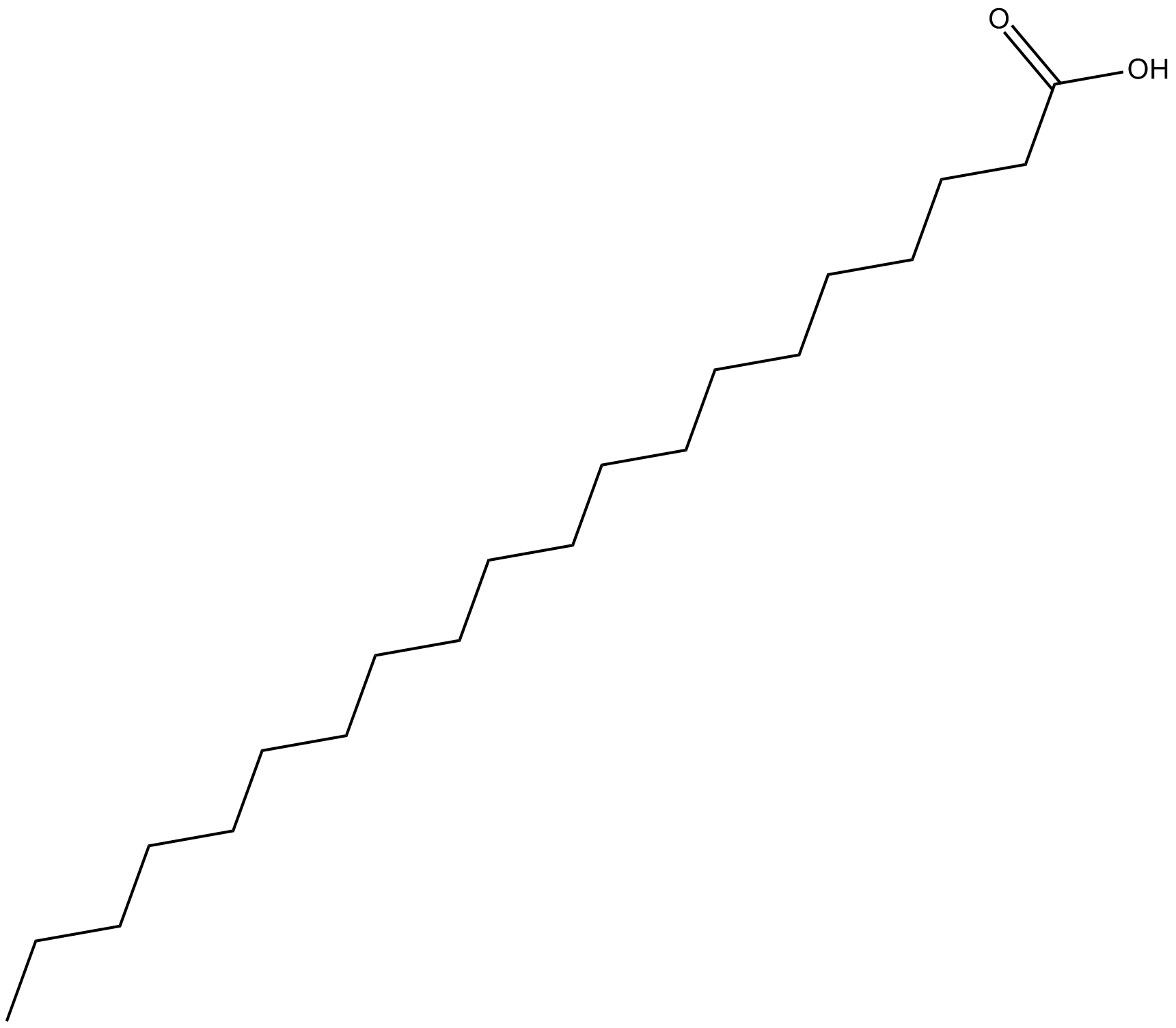 C5811 5,8,11-Eicosatriynoic AcidSummary: nonselective inhibitor of lipoxygenases (12-LO)
C5811 5,8,11-Eicosatriynoic AcidSummary: nonselective inhibitor of lipoxygenases (12-LO) -
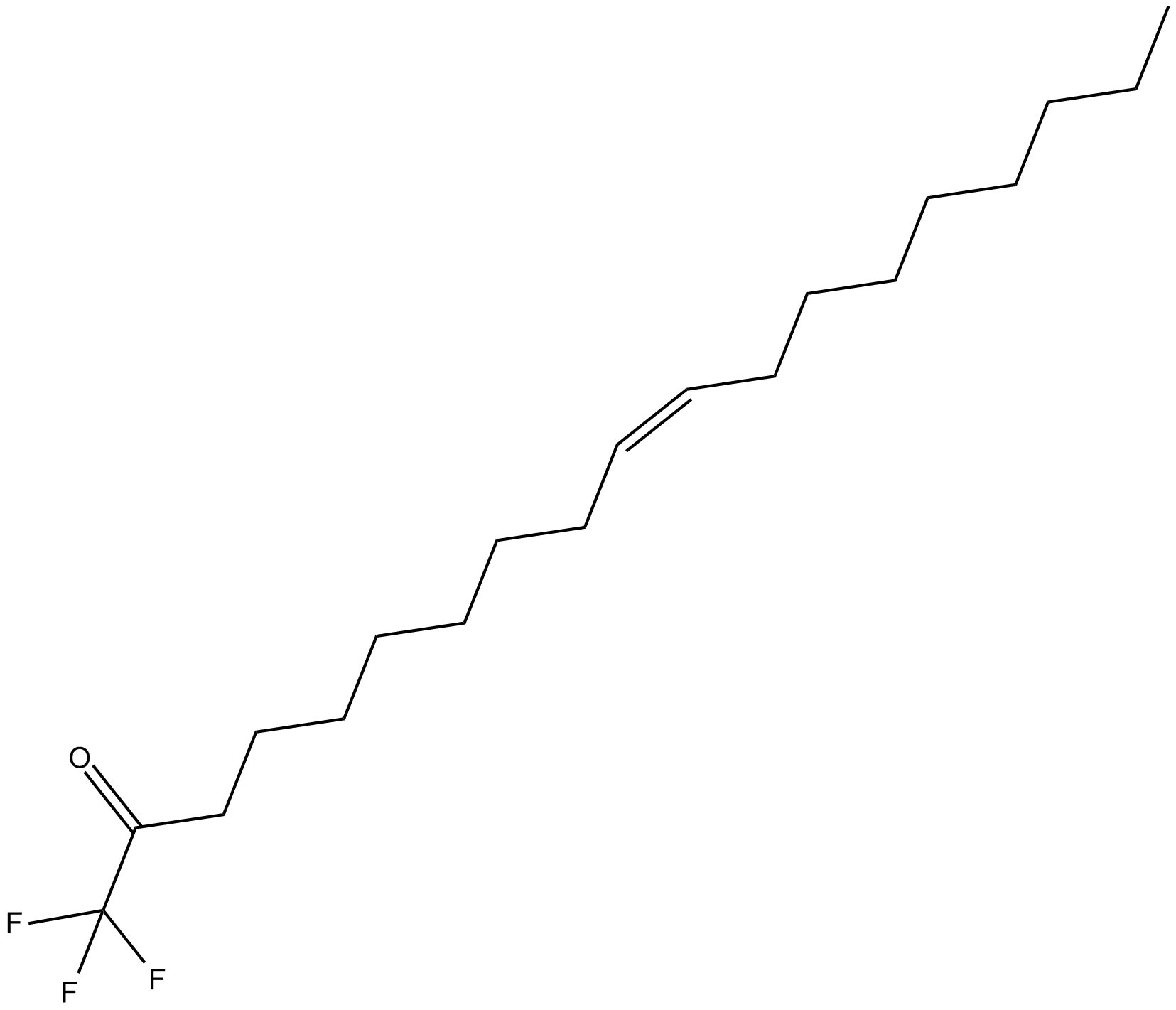 C5719 Oleyl Trifluoromethyl KetoneSummary: potent inhibitor of FAAH
C5719 Oleyl Trifluoromethyl KetoneSummary: potent inhibitor of FAAH -
 B7928 Tienilic Acid
B7928 Tienilic Acid


