GPCR/G protein
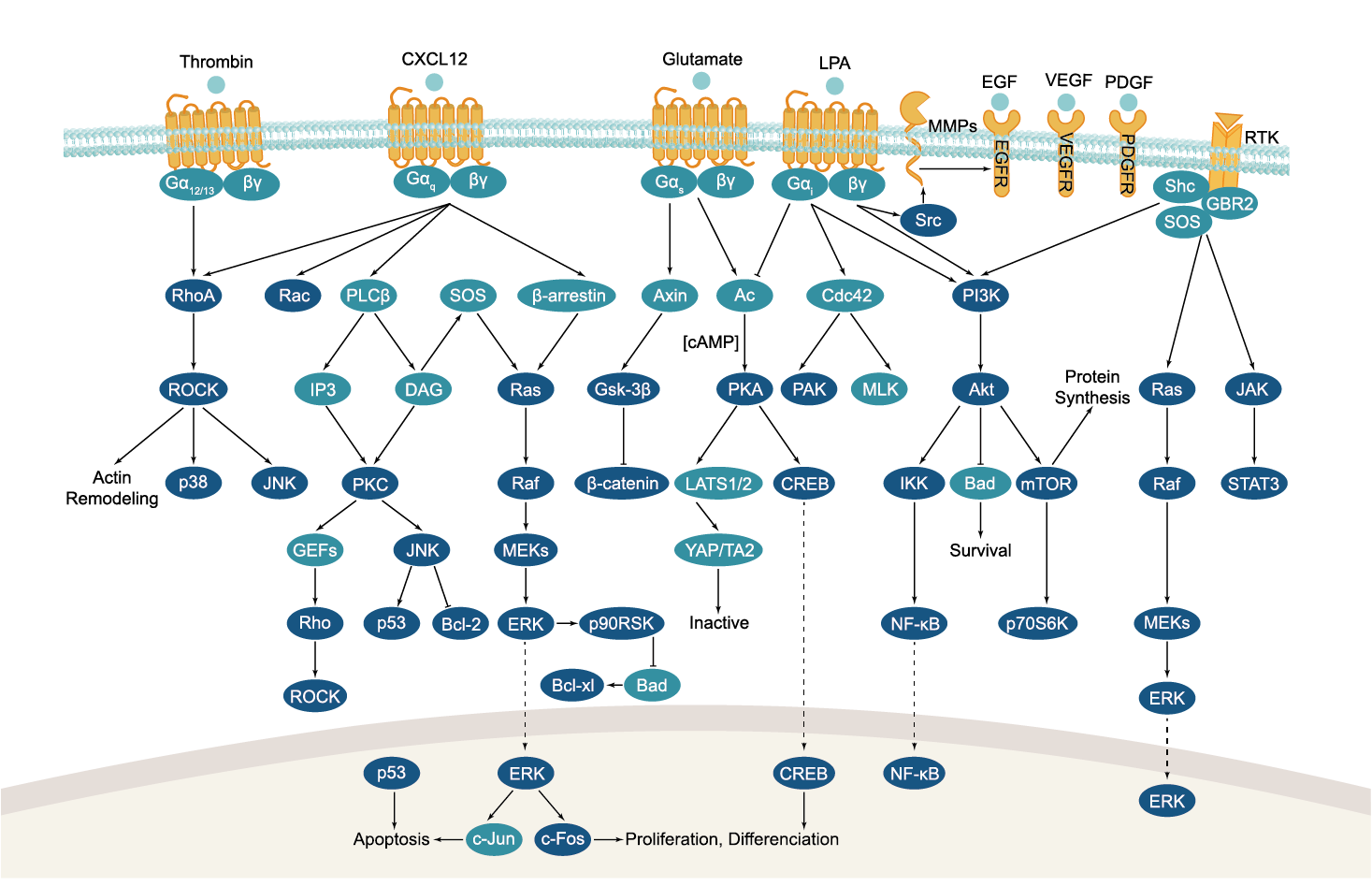

All GPCRs share a common seven trans-membrane structure. GPCRs are associated with heterotrimeric G-proteins which are GTP-binding proteins made of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. When a ligand binds to GPCR, it activates the attached G-protein, the GDP is replaced with GTP. The activated G-protein then dissociates into an alpha and a beta-gamma complex which activates downstream signaling pathways. These intracellular signaling pathways include cAMP/PKA, calcium/NFAT, phospholipase C, protein tyrosine kinases, MAP kinases, PI-3-kinase, nitric oxide/cGMP, Rho, and JAK/STAT.
GPCRs are one of the most important therapeutic targets for various diseases, over 30% of all modern medicinal drugs target this family. Aberrant GPCR functions are involved in pathological conditions such as neurological, immunological and hormonal disorders. A large number of GPCRs have been identified, but whose ligands are not known, are classified as orphan receptors.
-
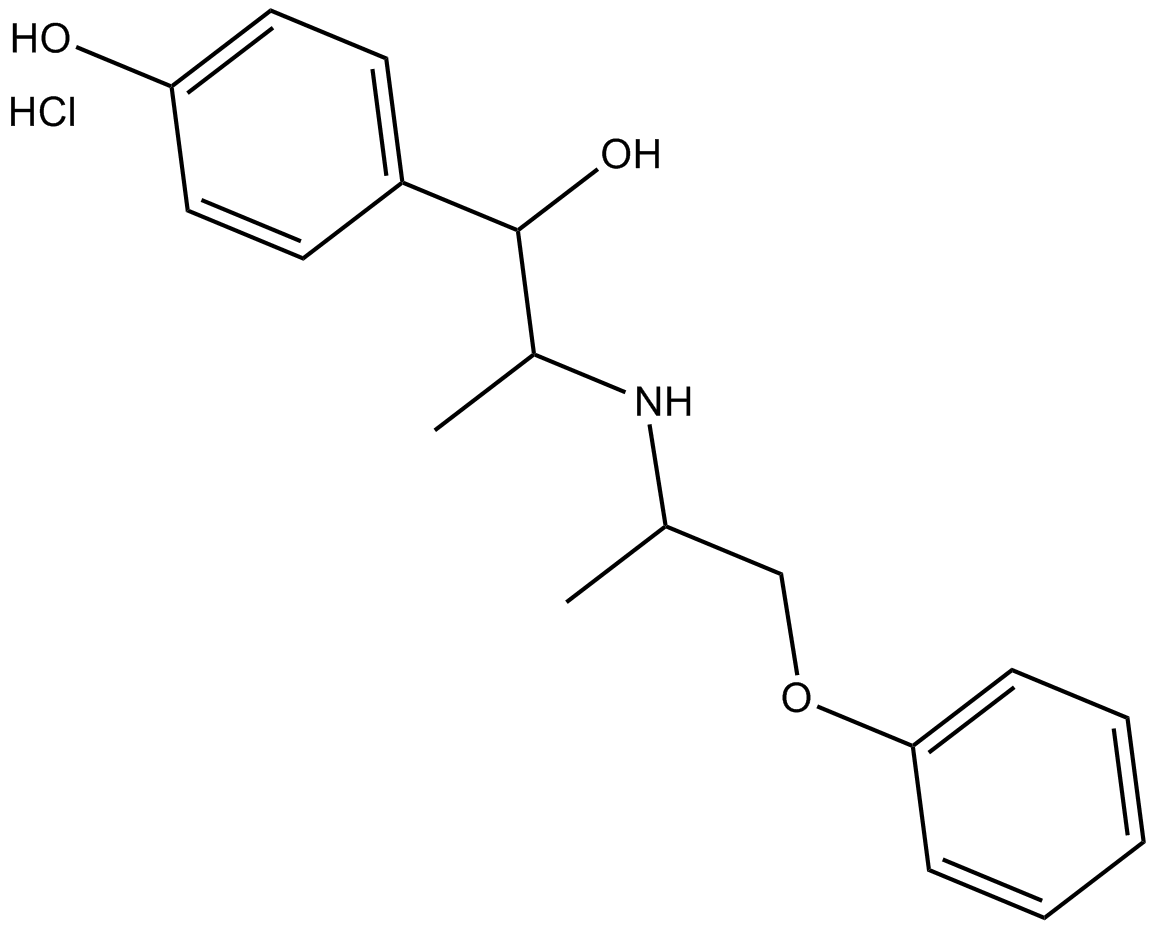 C3347 Isoxsuprine (hydrochloride)Summary: β-adrenergic receptor modulator
C3347 Isoxsuprine (hydrochloride)Summary: β-adrenergic receptor modulator -
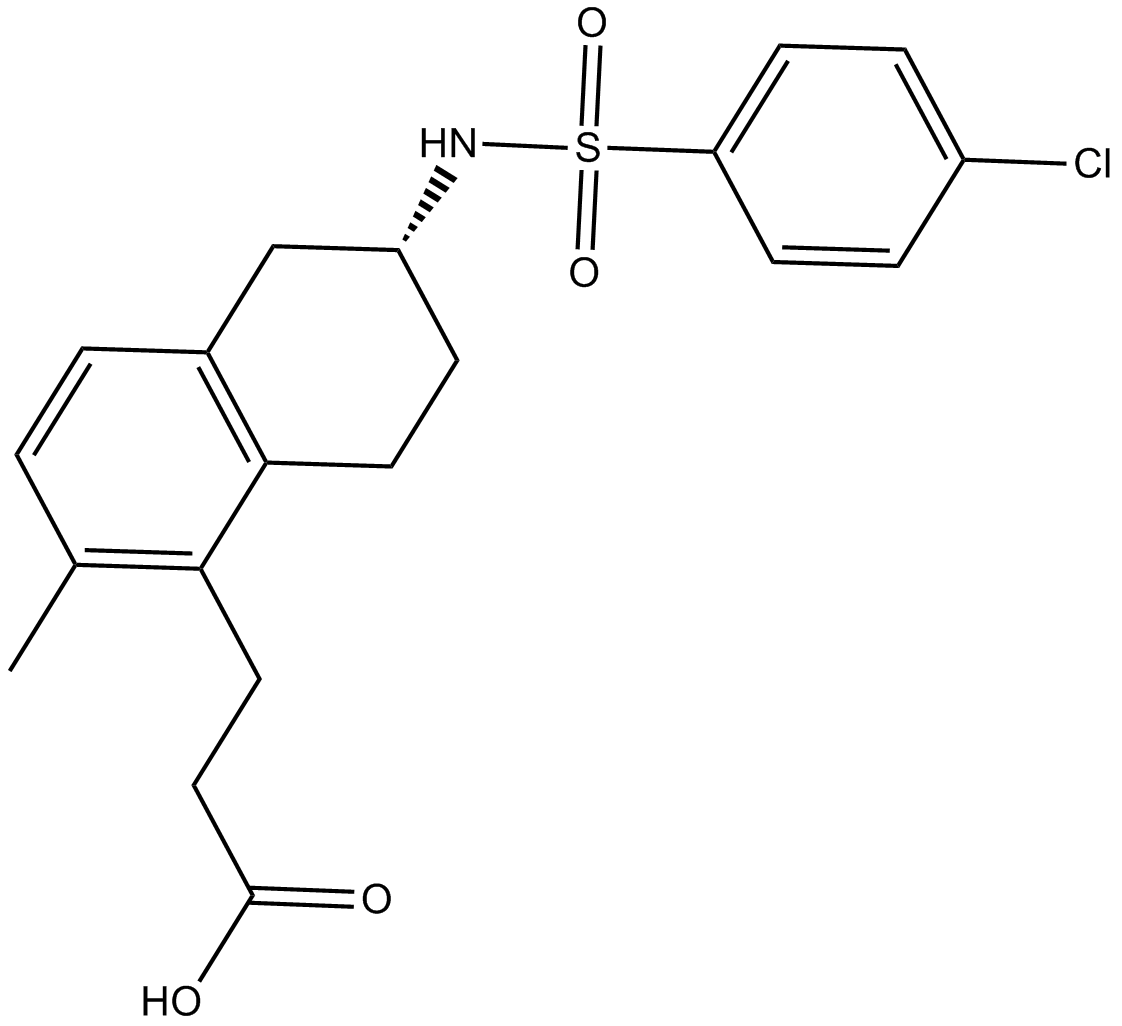 C5387 S18886Summary: Potent thromboxane A2 (TP) inhibitor
C5387 S18886Summary: Potent thromboxane A2 (TP) inhibitor -
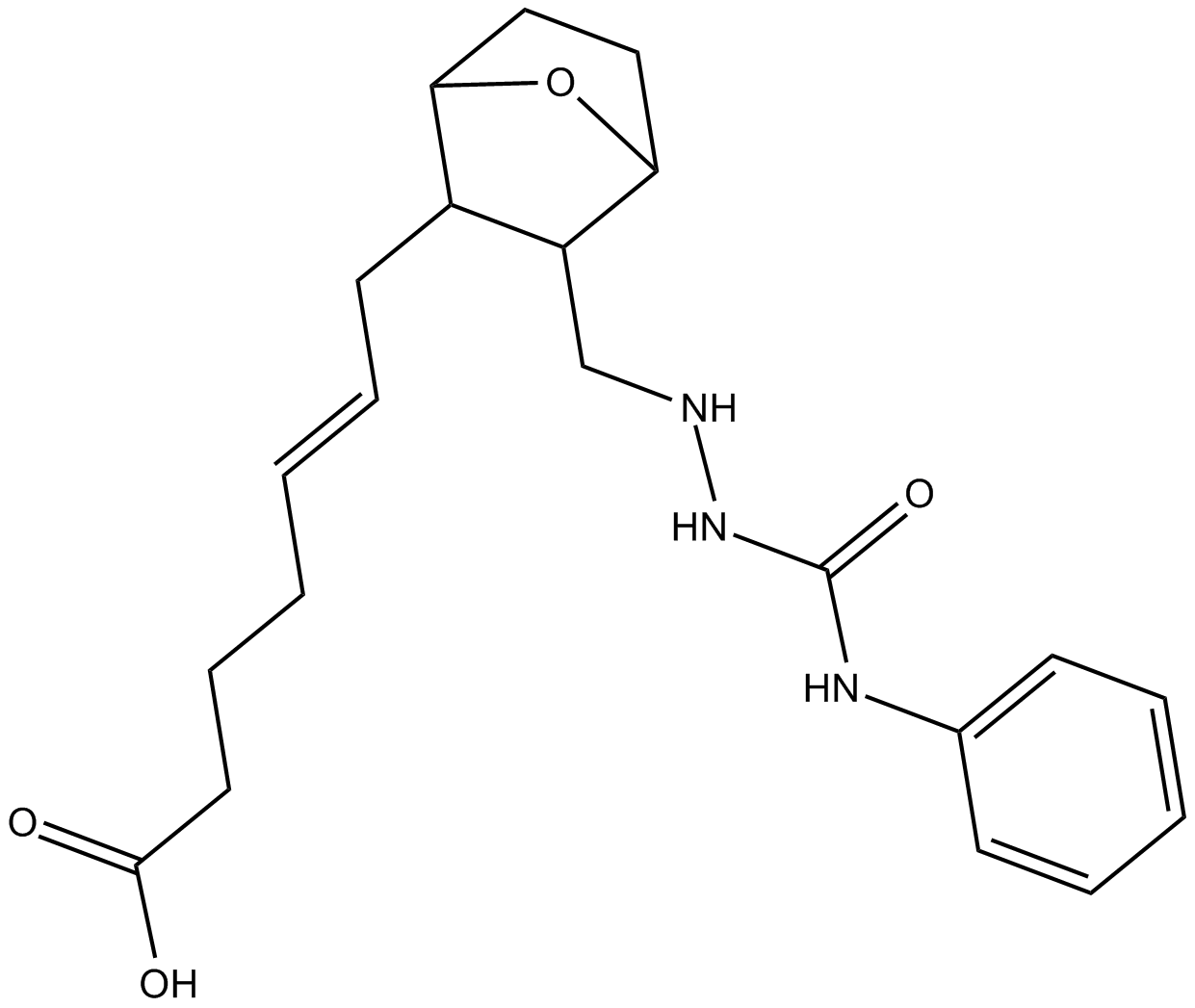 C4237 SQ 29,548Summary: TP receptor antagonist
C4237 SQ 29,548Summary: TP receptor antagonist -
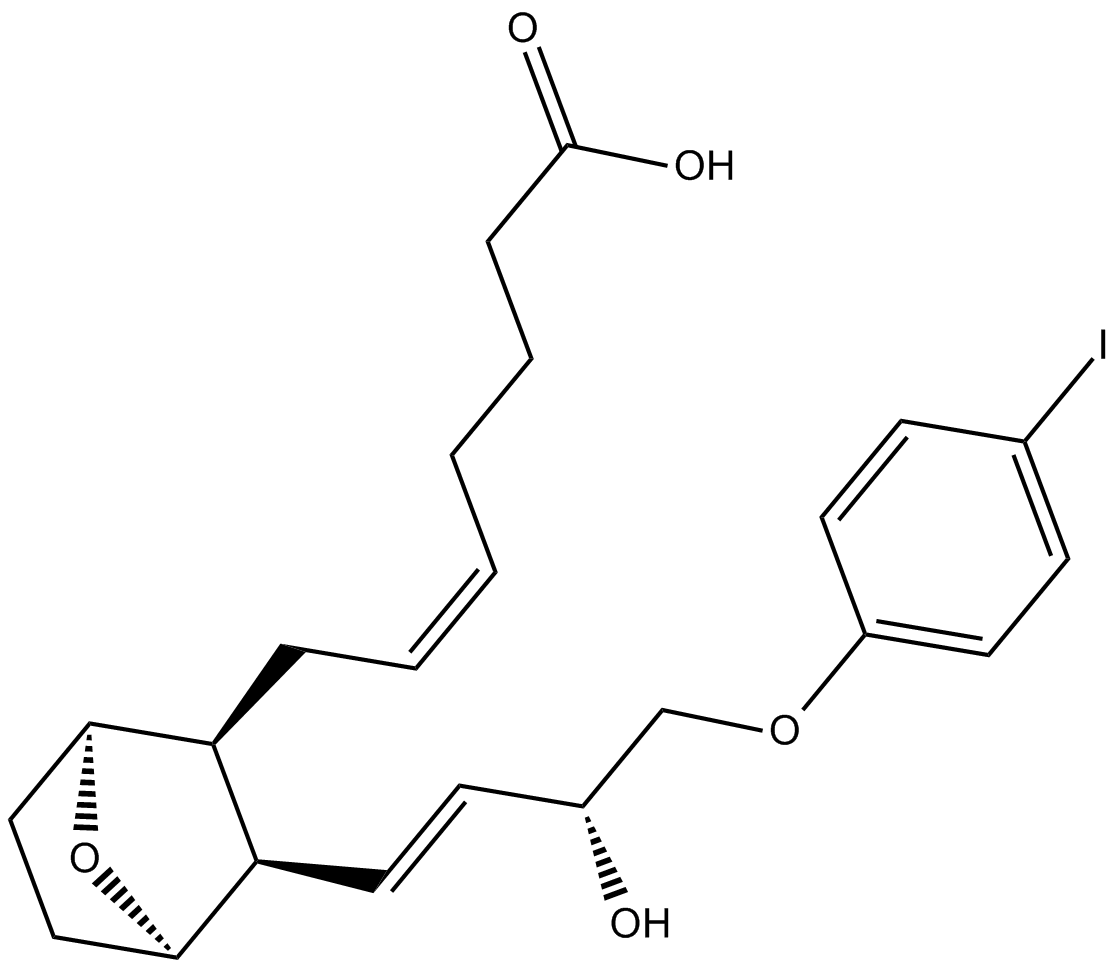 C5805 I-BOPSummary: TP specific agonist
C5805 I-BOPSummary: TP specific agonist -
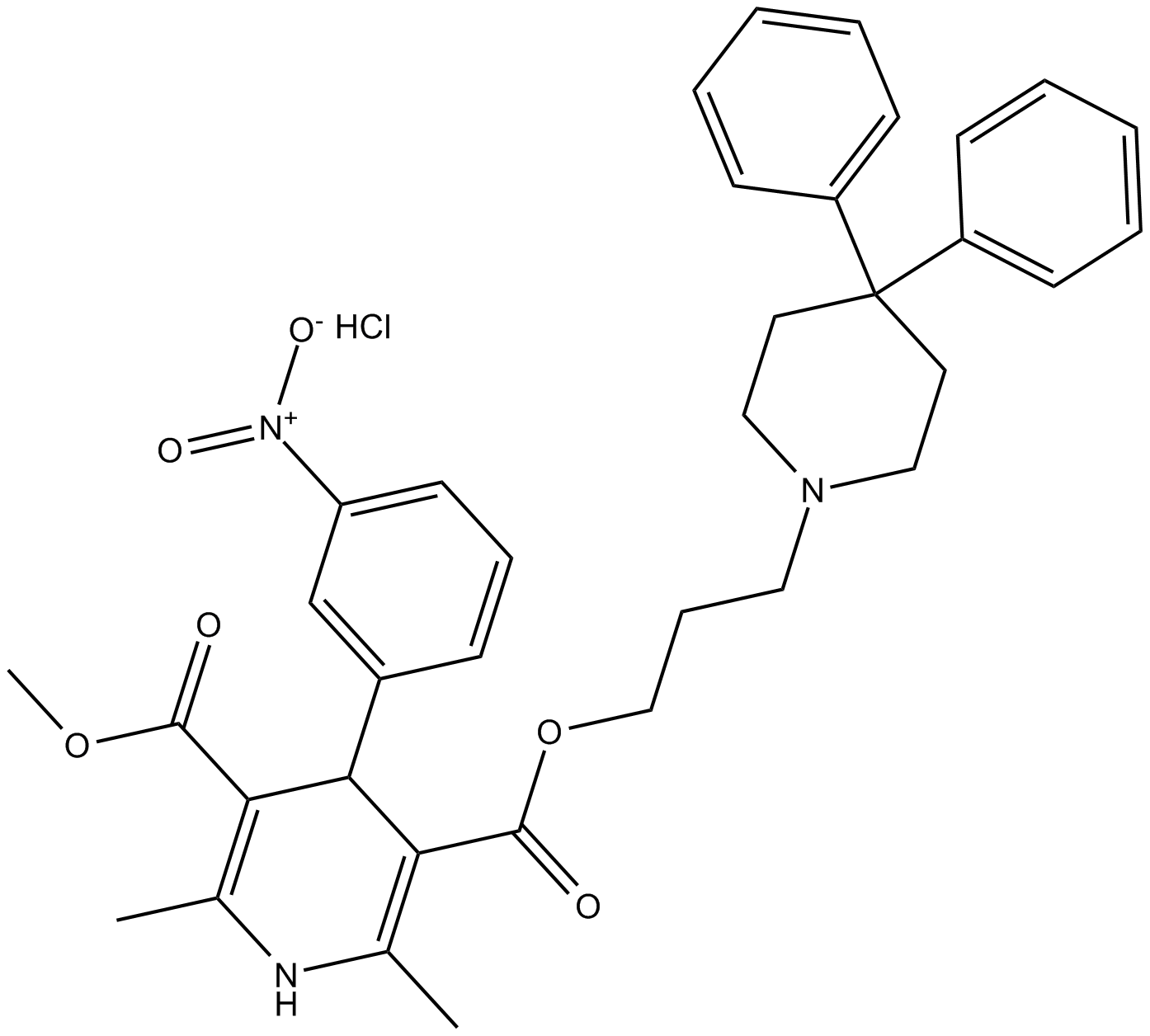 C3067 Niguldipine (hydrochloride)Summary: α1A-adrenoceptor antagonist
C3067 Niguldipine (hydrochloride)Summary: α1A-adrenoceptor antagonist -
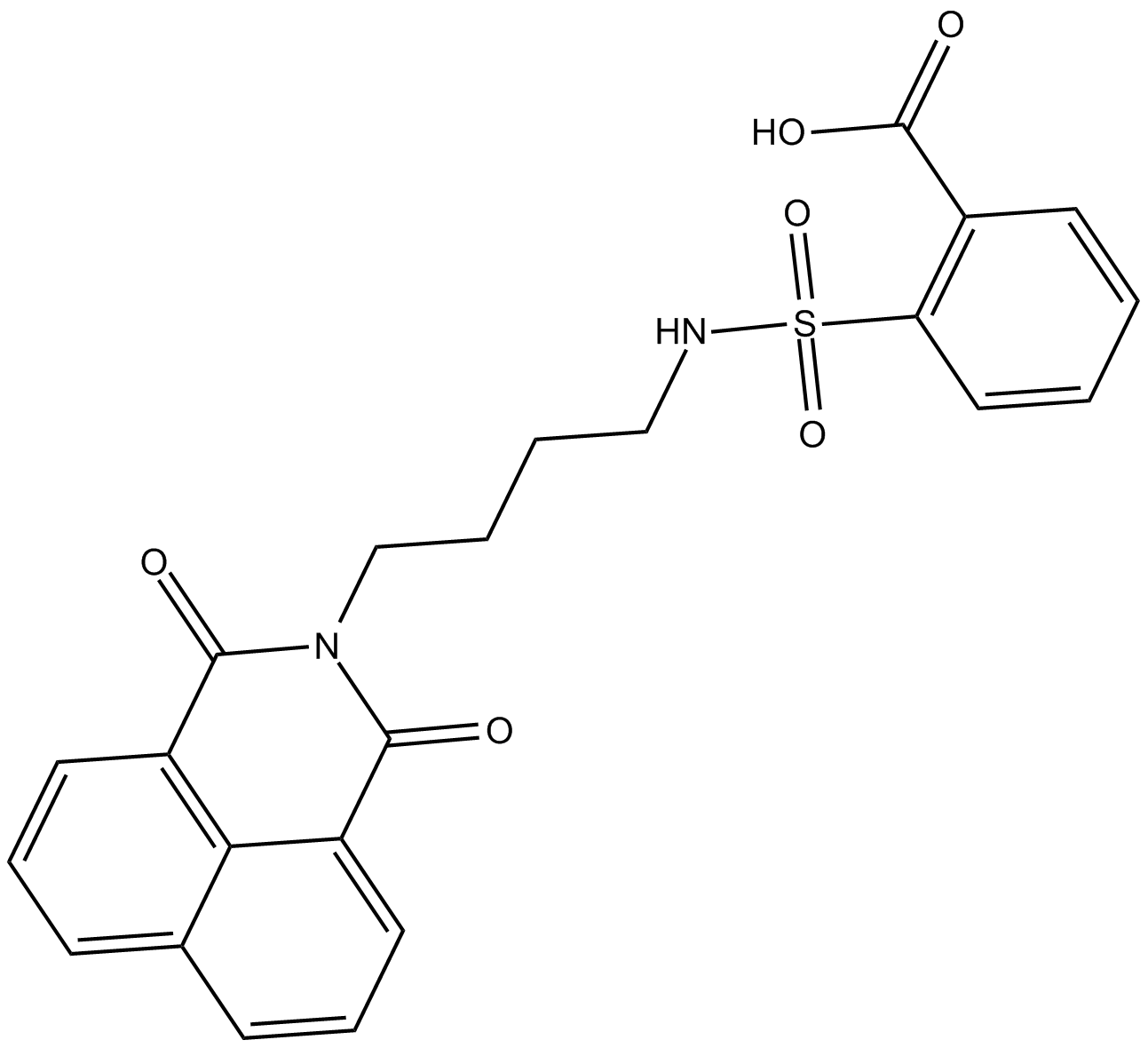 C3497 DBIBBSummary: LPA2 agonist
C3497 DBIBBSummary: LPA2 agonist -
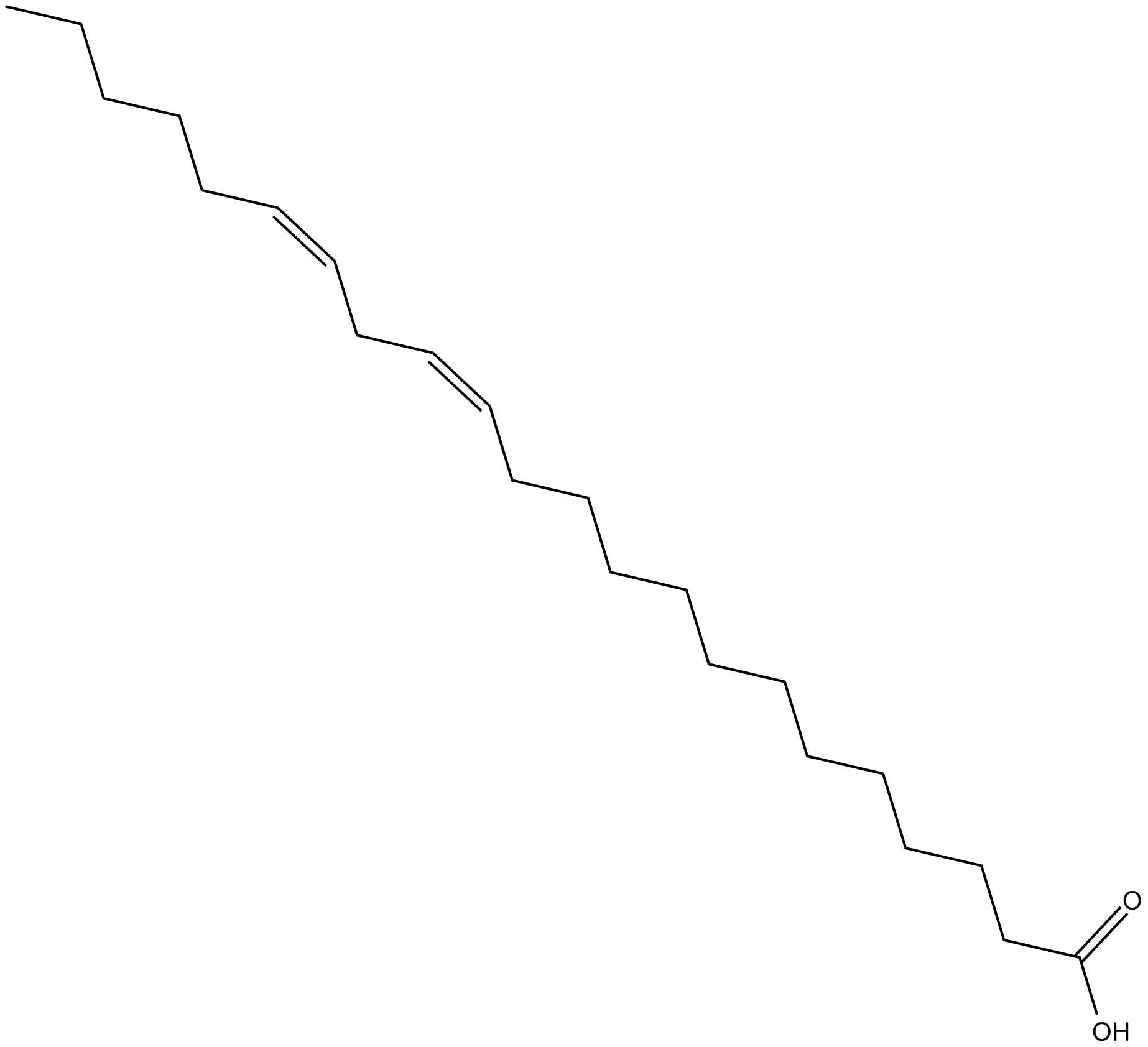 C3385 13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic AcidSummary: FFAR4(GPR120) agonist
C3385 13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic AcidSummary: FFAR4(GPR120) agonist -
 C3343 Tetradecyl PhosphonateSummary: pan-antagonist of lysophosphatidic acid 1 (LPA1), LPA2, and LPA3 receptors
C3343 Tetradecyl PhosphonateSummary: pan-antagonist of lysophosphatidic acid 1 (LPA1), LPA2, and LPA3 receptors -
 C3411 3-chloro-5-hydroxy BASummary: GPR81 agonist
C3411 3-chloro-5-hydroxy BASummary: GPR81 agonist -
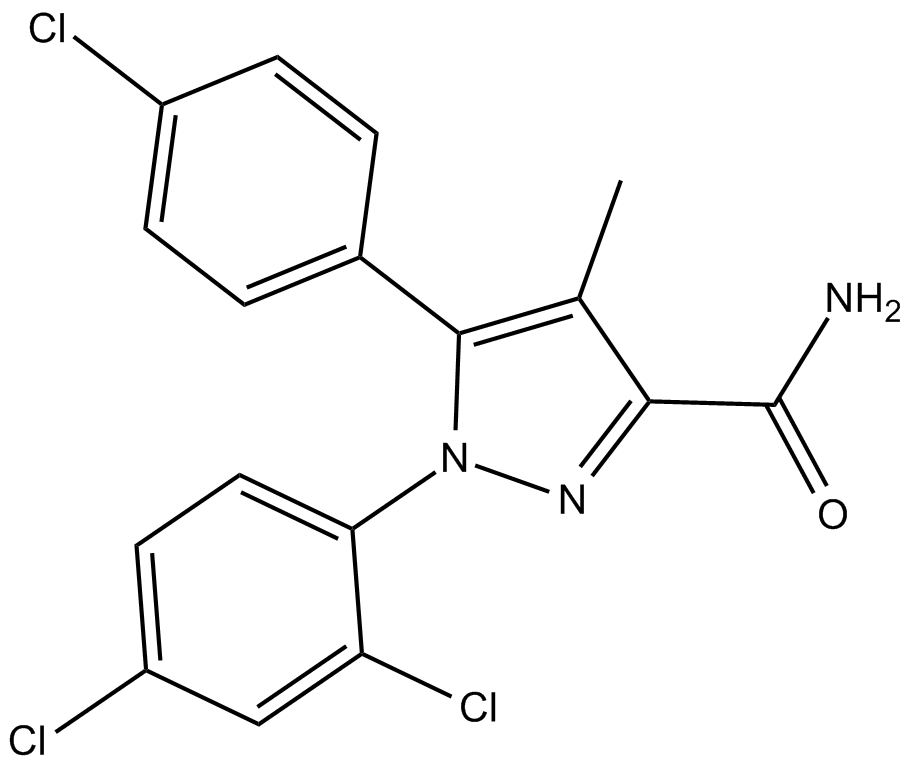 C3493 AM4113Summary: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1)-selective neutral antagonist
C3493 AM4113Summary: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1)-selective neutral antagonist


