Cell Cycle/Checkpoint
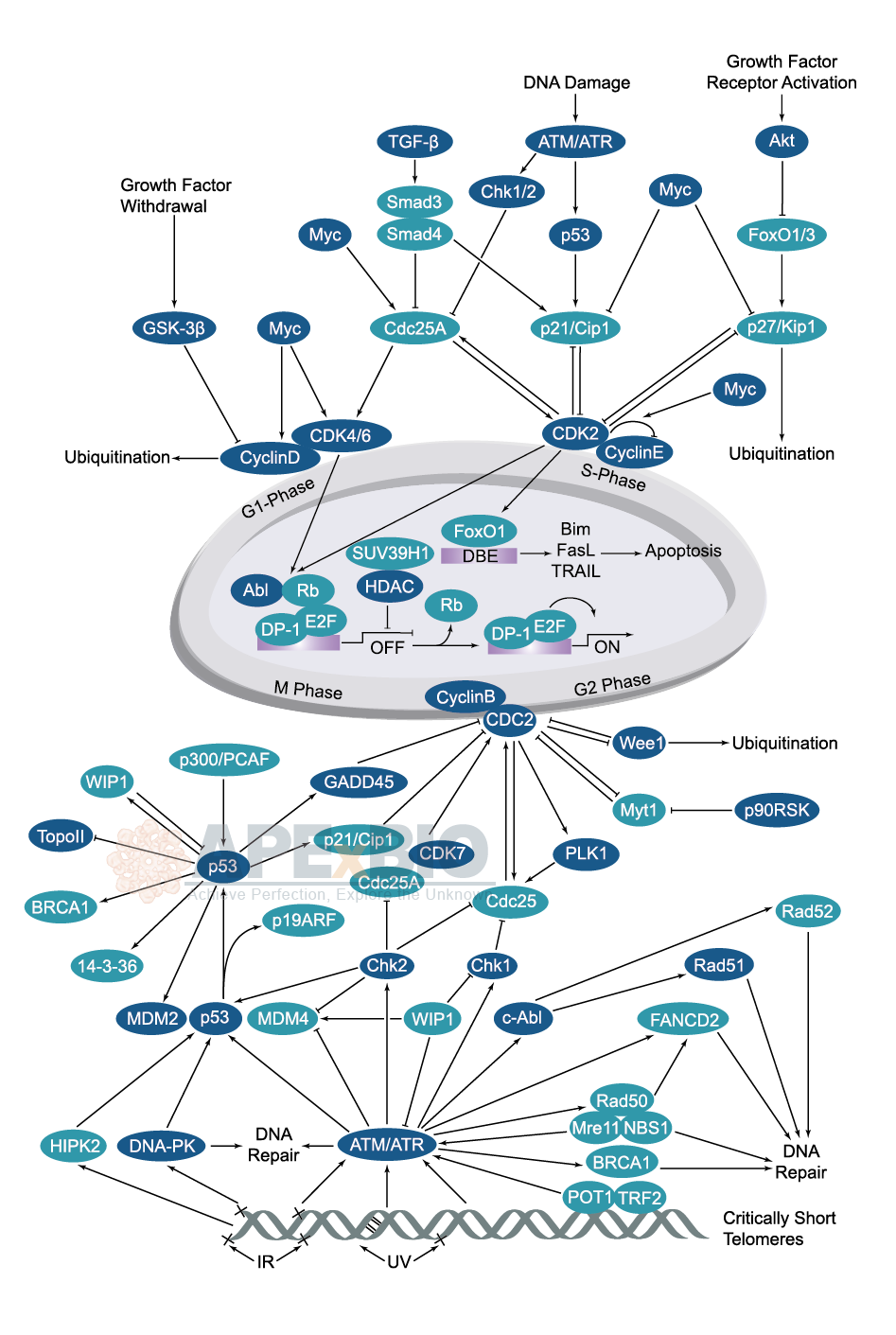

The cell cycle is consisted of 4 main phases: Gap 1 (G1), DNA replication (S), Gap 2 (G2), and mitosis (M). There are “checkpoints” mechanism regulates the transition between these phases, at the G1/S boundary, in the S-phase and during G2/M phases. Cell can only pass through these checkpoints when signaling factors are activated and free of DNA damage. Important proteins that control cell cycle events and checkpoints are cullins, cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), p53 and their inhibitors etc. Cdks family (Cdk2, Cdk3, Cdk4 and Cdk6) are Ser/Thr kinases that regulate cell cycle progression in association with cyclin binding partners (cyclin D, cyclin E and cyclin A) during all four phases. p53 halts the cell cycle if the DNA is damaged and allowing time for DNA repair to progress; it can also initiate apoptosis if DNA damage is too severe to be repaired.
-
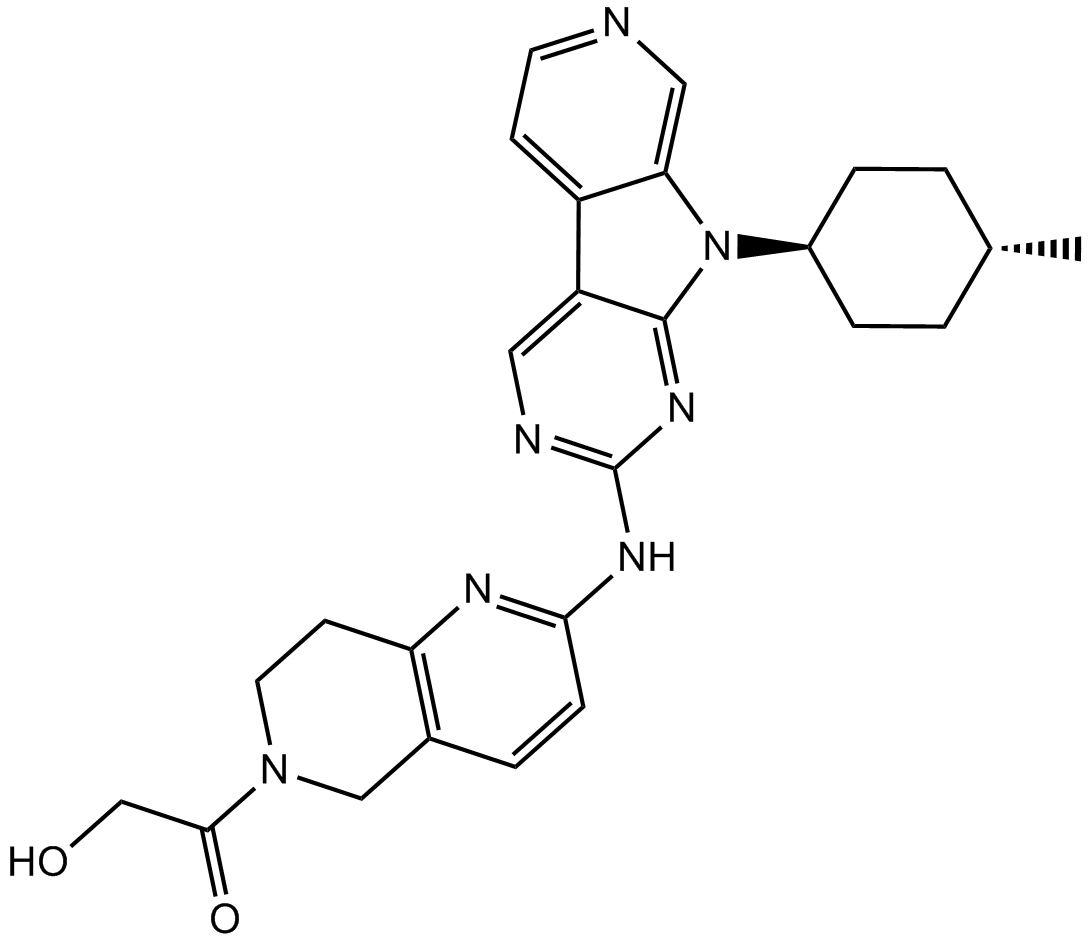 B3277 AMG 925Target: Cyclin-Dependent Kinases|FLT3Summary: FLT3/CDK4 inhibitor,potent and selective
B3277 AMG 925Target: Cyclin-Dependent Kinases|FLT3Summary: FLT3/CDK4 inhibitor,potent and selective -
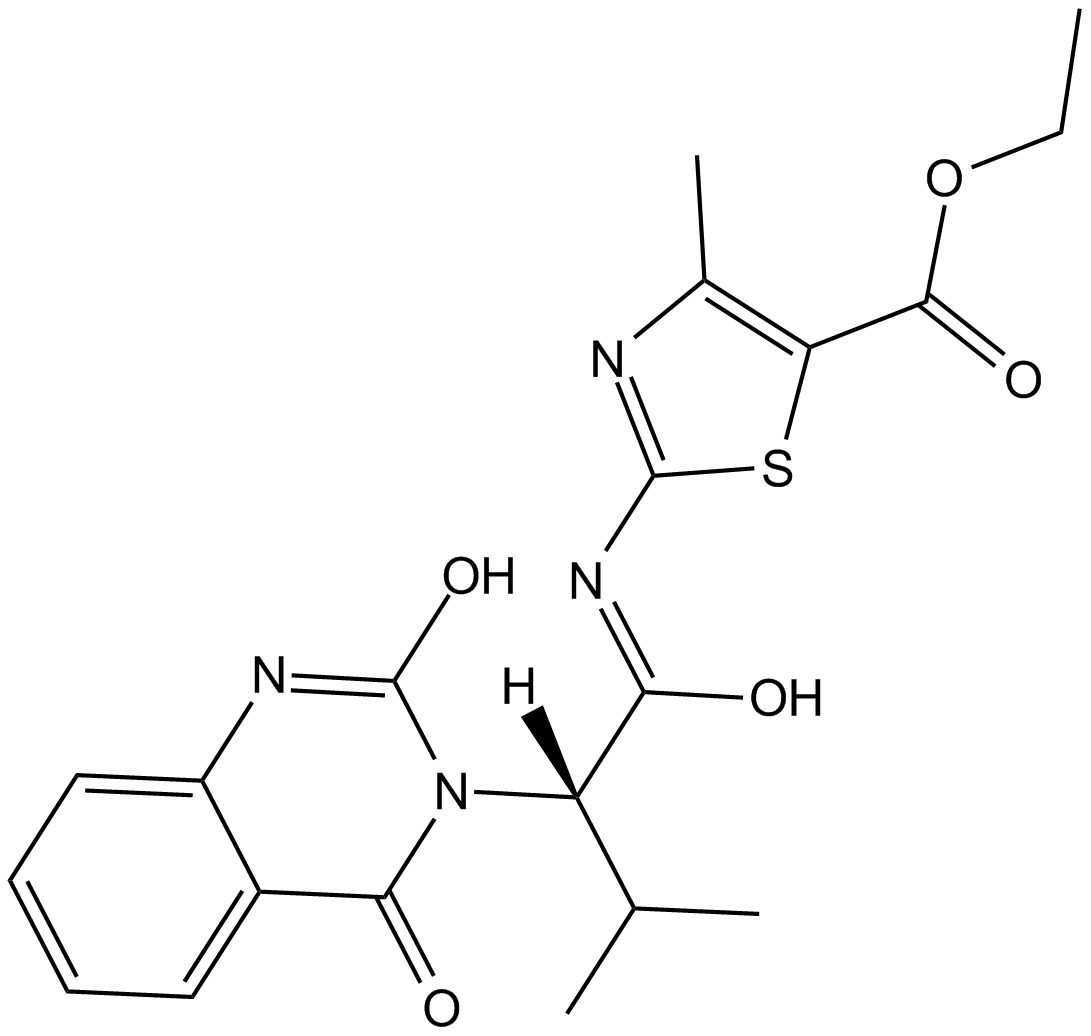 B3280 Kif15-IN-11 CitationSummary: potent Kif15 kinesin inhibitor
B3280 Kif15-IN-11 CitationSummary: potent Kif15 kinesin inhibitor -
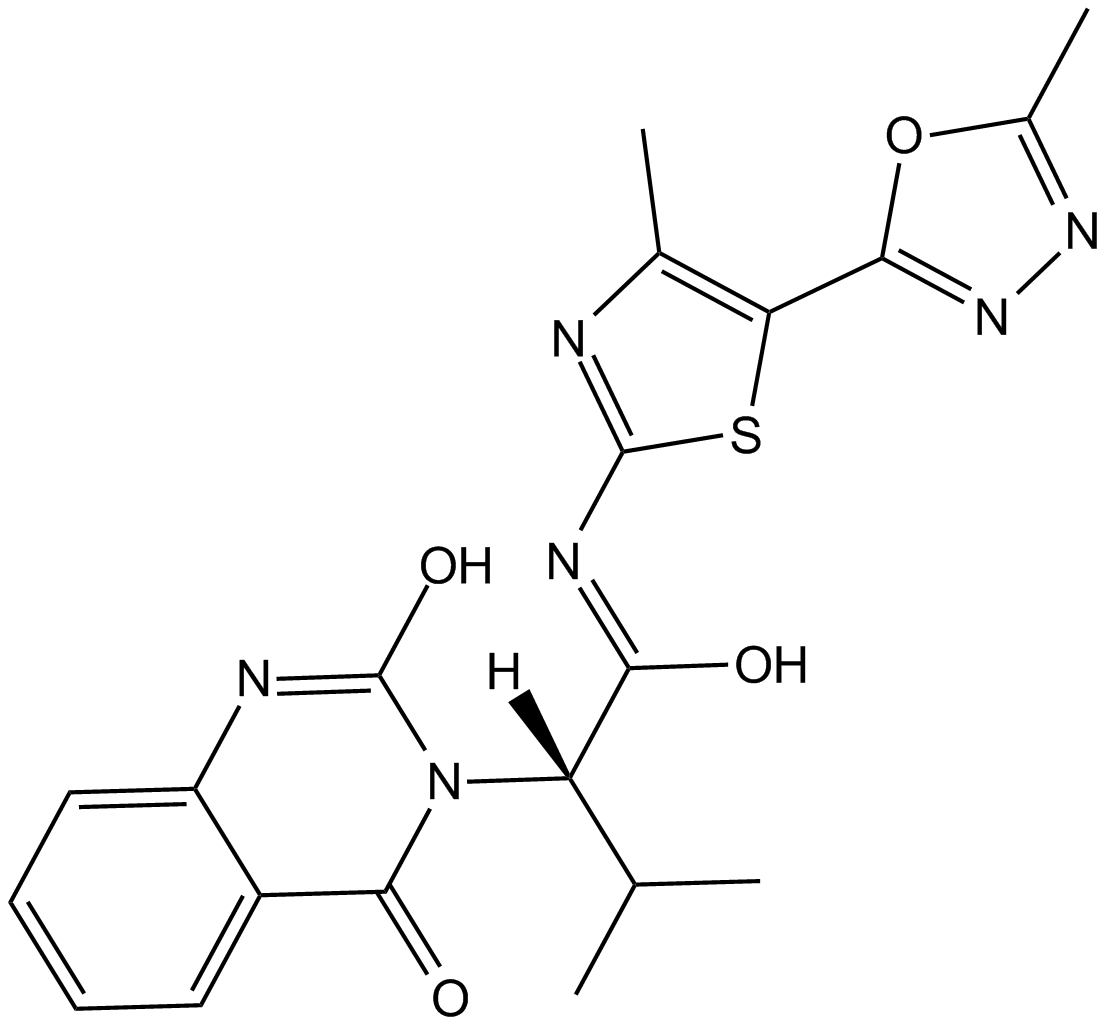 B3281 Kif15-IN-2Summary: potent Kif15 kinesin inhibitor
B3281 Kif15-IN-2Summary: potent Kif15 kinesin inhibitor -
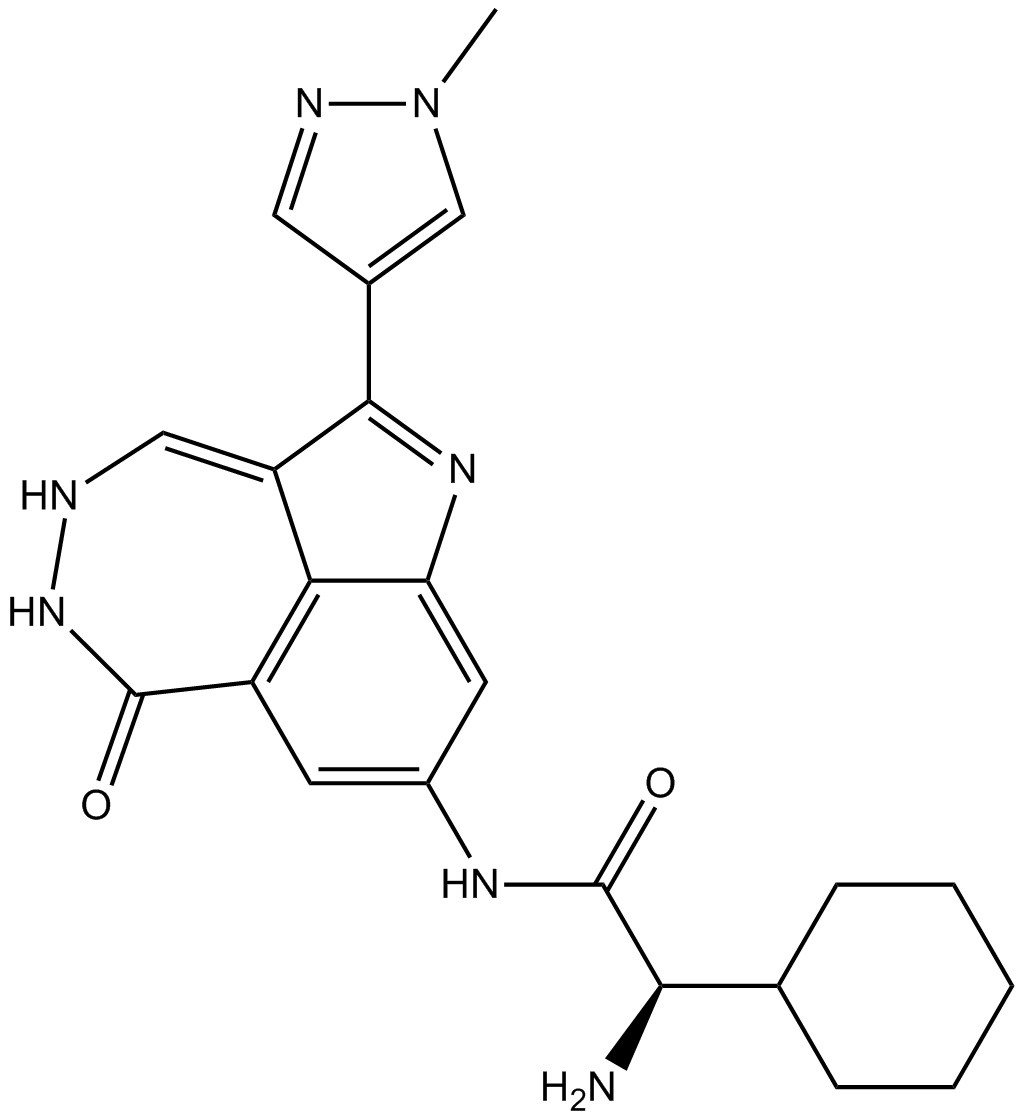 B1437 PF-477736Target: ChkSummary: Chk1 inhibitor
B1437 PF-477736Target: ChkSummary: Chk1 inhibitor -
 B1288 RigosertibTarget: PI3K|PLKSummary: PI3K/PLK1 inhibitor
B1288 RigosertibTarget: PI3K|PLKSummary: PI3K/PLK1 inhibitor -
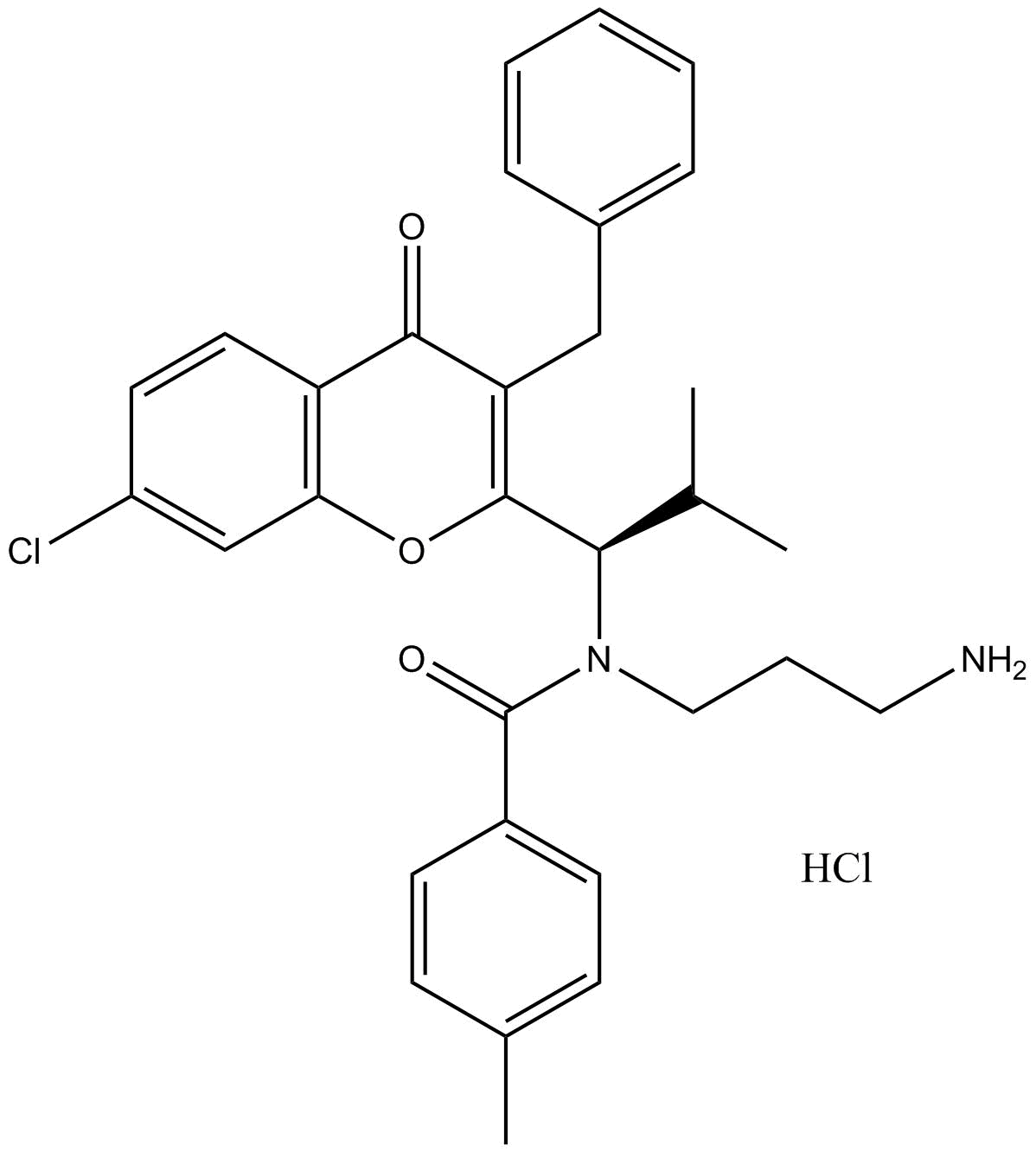 B1590 SB743921Summary: Potent KSP inhibitor
B1590 SB743921Summary: Potent KSP inhibitor -
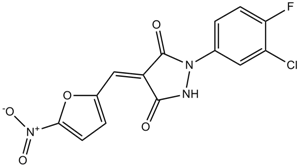 B1244 PYZD-4409Target: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme E1Summary: E1 enzyme inhibitor
B1244 PYZD-4409Target: Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme E1Summary: E1 enzyme inhibitor -
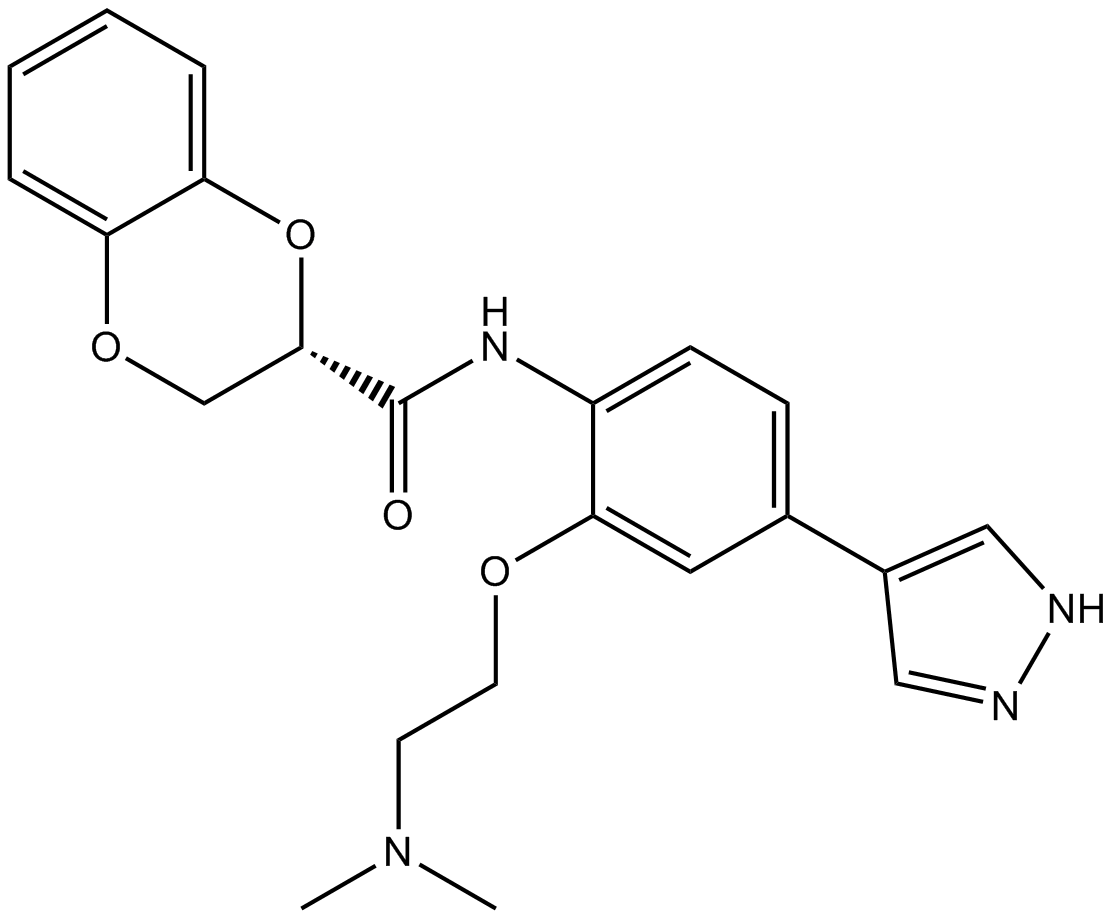 B1294 SR-3677Target: ROCKSummary: Rho Kinase (ROCK-II) inhibitor
B1294 SR-3677Target: ROCKSummary: Rho Kinase (ROCK-II) inhibitor -
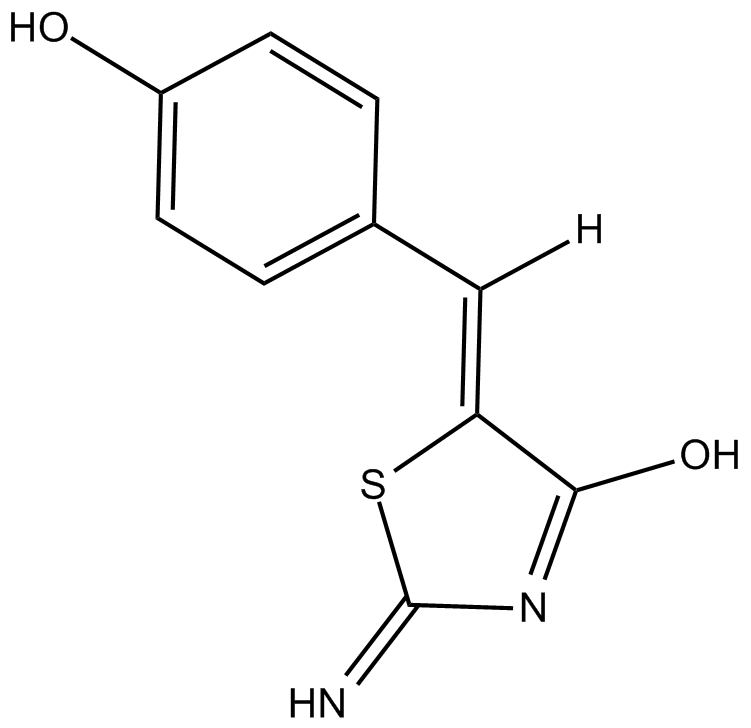 B5389 MirinSummary: A potent inhibitor of the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN)-ATM pathway
B5389 MirinSummary: A potent inhibitor of the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN)-ATM pathway -
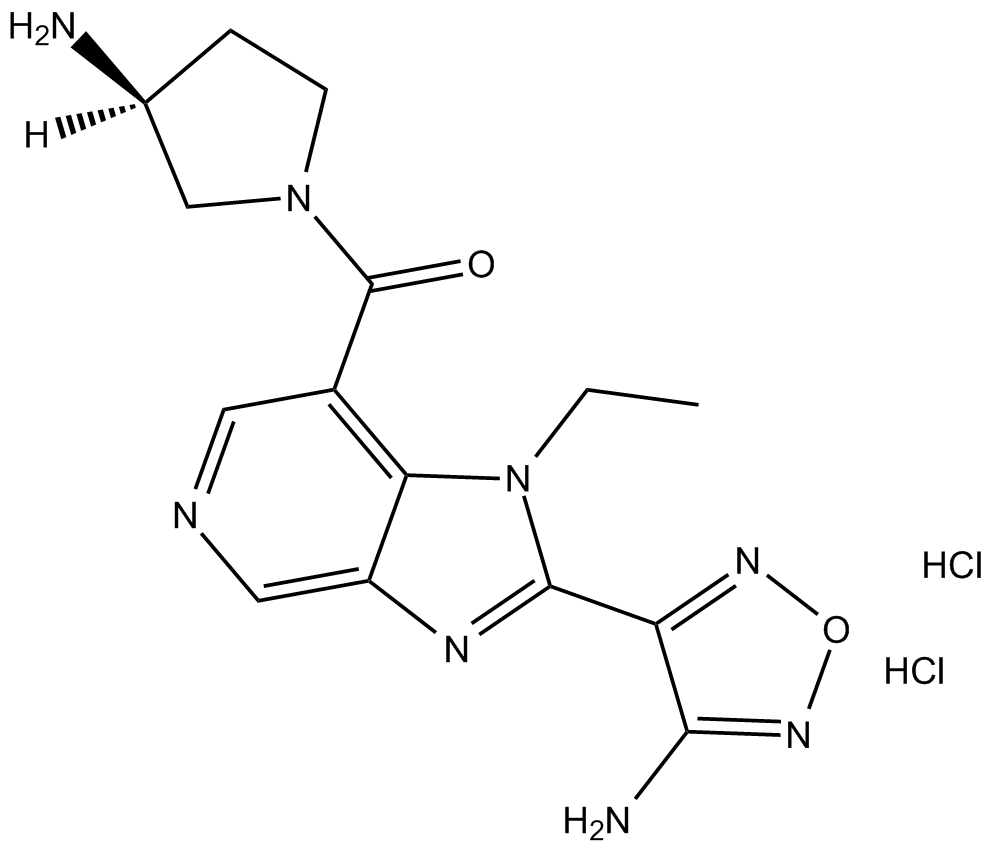 B5529 SB 772077B dihydrochlorideSummary: Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor
B5529 SB 772077B dihydrochlorideSummary: Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor


