Cell Cycle/Checkpoint
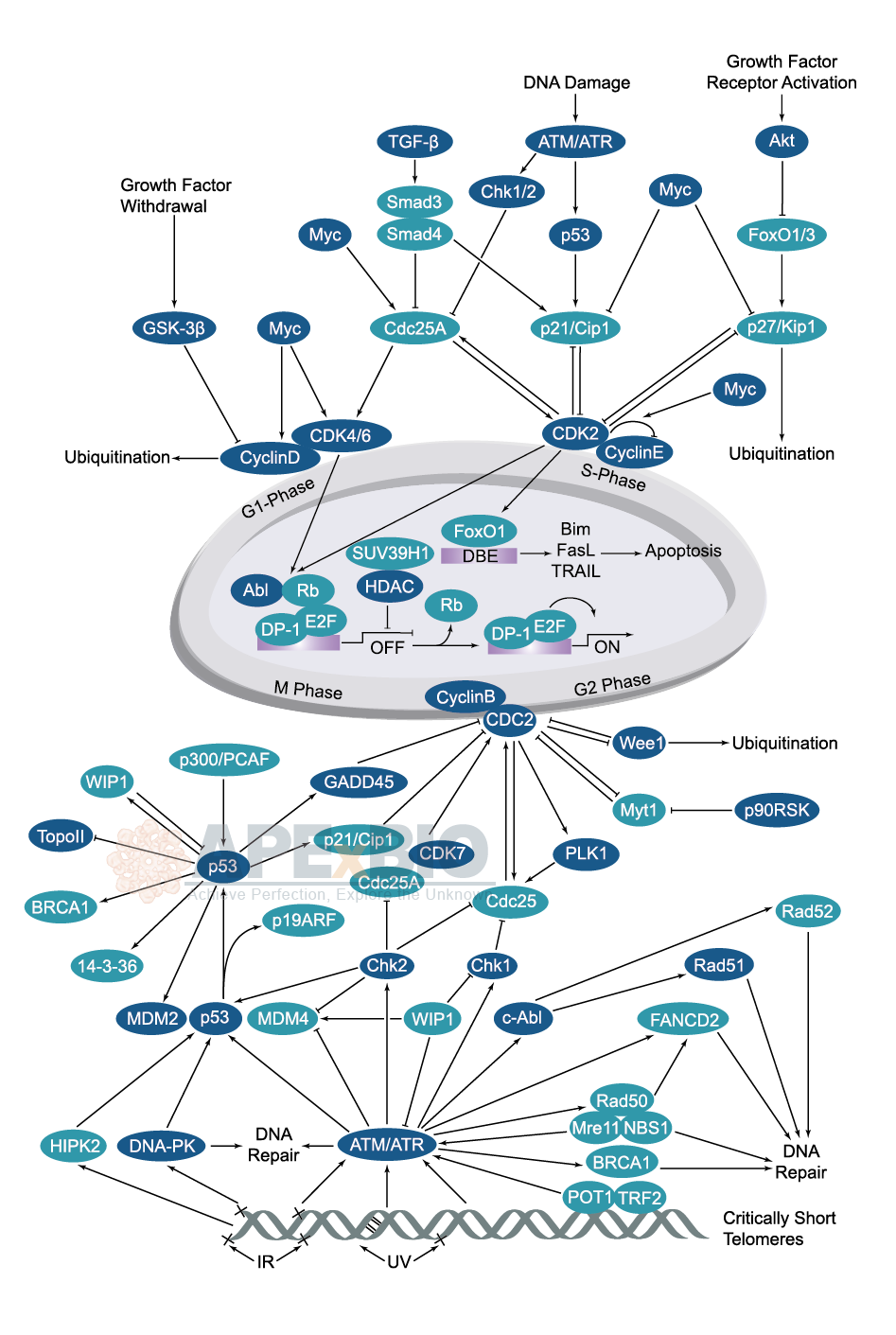

The cell cycle is consisted of 4 main phases: Gap 1 (G1), DNA replication (S), Gap 2 (G2), and mitosis (M). There are “checkpoints” mechanism regulates the transition between these phases, at the G1/S boundary, in the S-phase and during G2/M phases. Cell can only pass through these checkpoints when signaling factors are activated and free of DNA damage. Important proteins that control cell cycle events and checkpoints are cullins, cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), p53 and their inhibitors etc. Cdks family (Cdk2, Cdk3, Cdk4 and Cdk6) are Ser/Thr kinases that regulate cell cycle progression in association with cyclin binding partners (cyclin D, cyclin E and cyclin A) during all four phases. p53 halts the cell cycle if the DNA is damaged and allowing time for DNA repair to progress; it can also initiate apoptosis if DNA damage is too severe to be repaired.
-
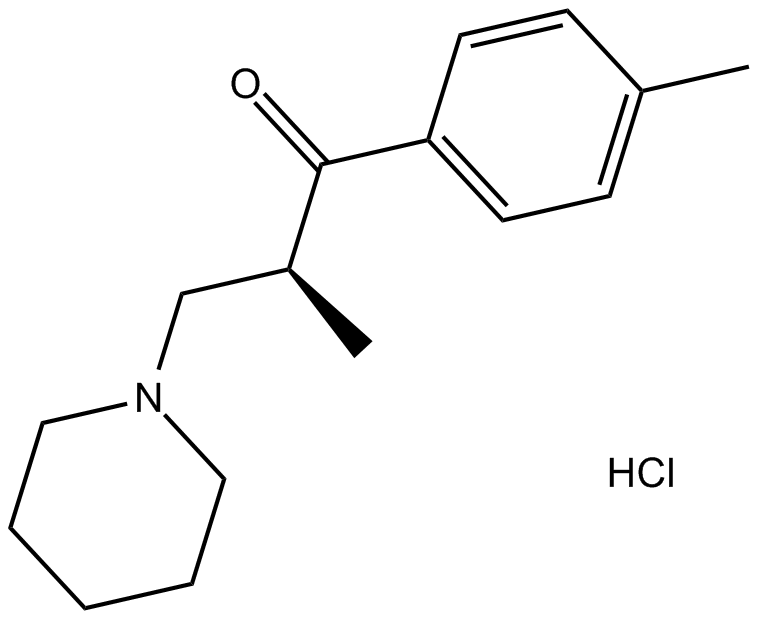 B1857 Tolperisone HClSummary: Sodium channel inhibitor
B1857 Tolperisone HClSummary: Sodium channel inhibitor -
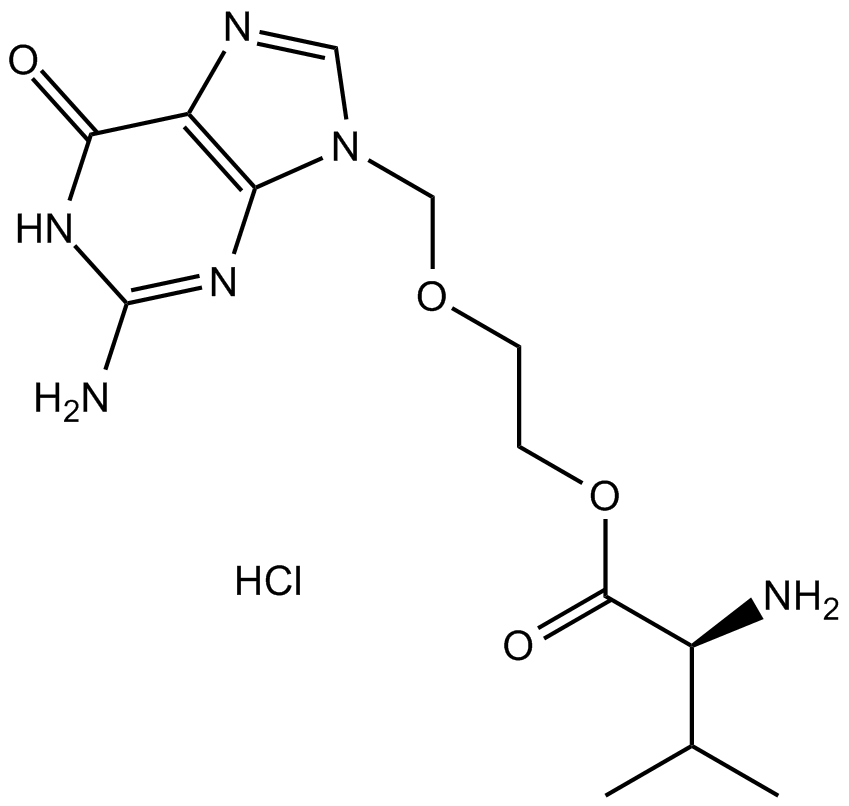 B2061 Valaciclovir HClSummary: antiviral drug for herpes viruses
B2061 Valaciclovir HClSummary: antiviral drug for herpes viruses -
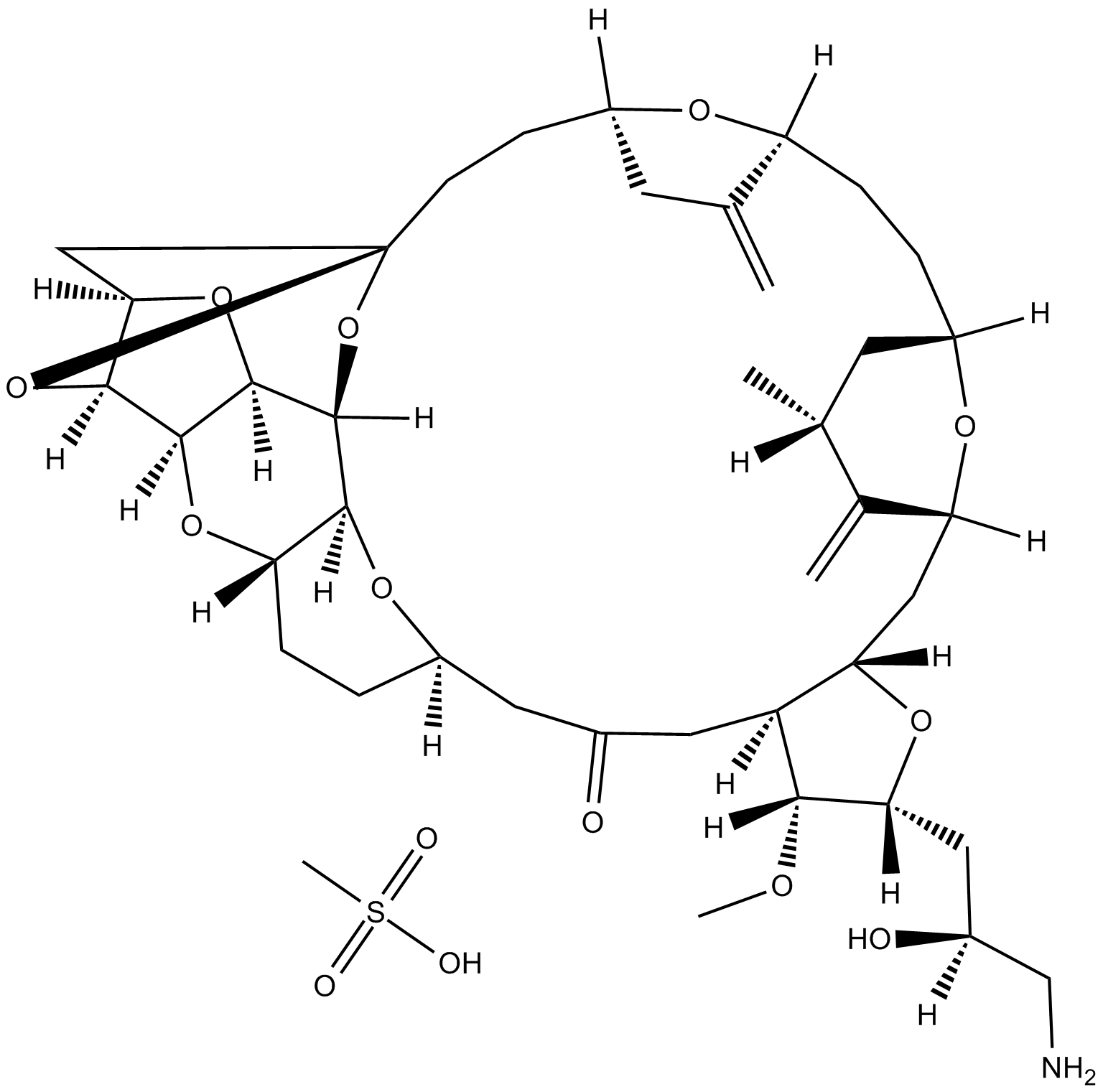 B3386 Eribulin mesylateSummary: synthetic analogue of halichondrin B
B3386 Eribulin mesylateSummary: synthetic analogue of halichondrin B -
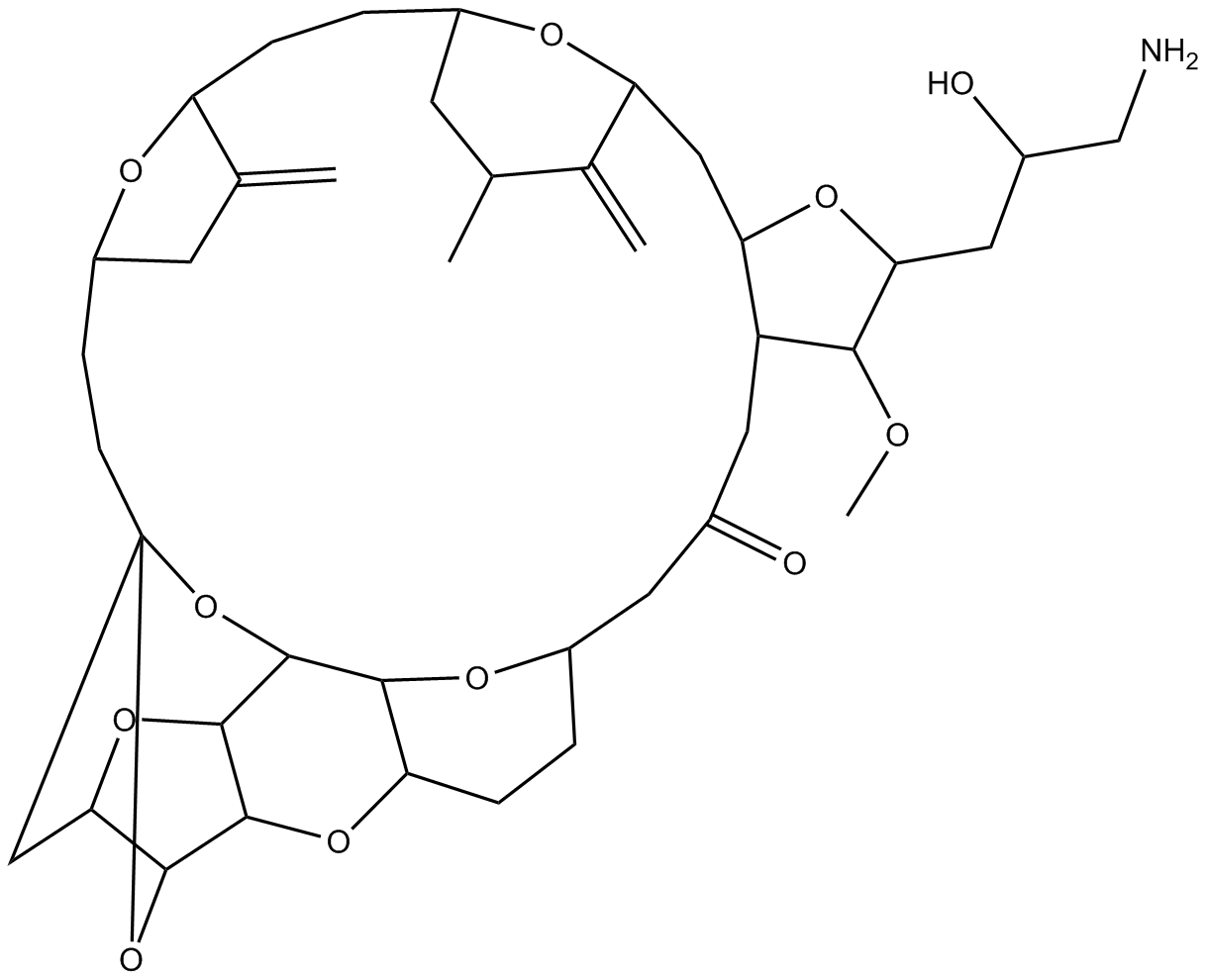 B3387 EribulinSummary: synthetic analogue of halichondrin B
B3387 EribulinSummary: synthetic analogue of halichondrin B -
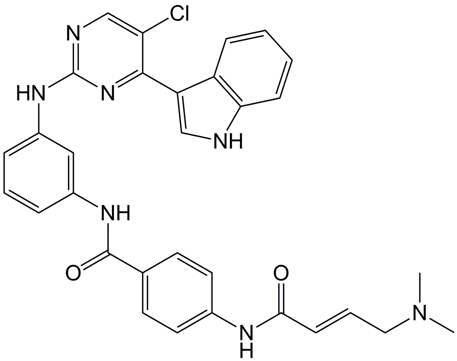 A8882 THZ124 CitationTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: Covalent CDK7 inhibitor,potent and selective
A8882 THZ124 CitationTarget: Cyclin-Dependent KinasesSummary: Covalent CDK7 inhibitor,potent and selective -
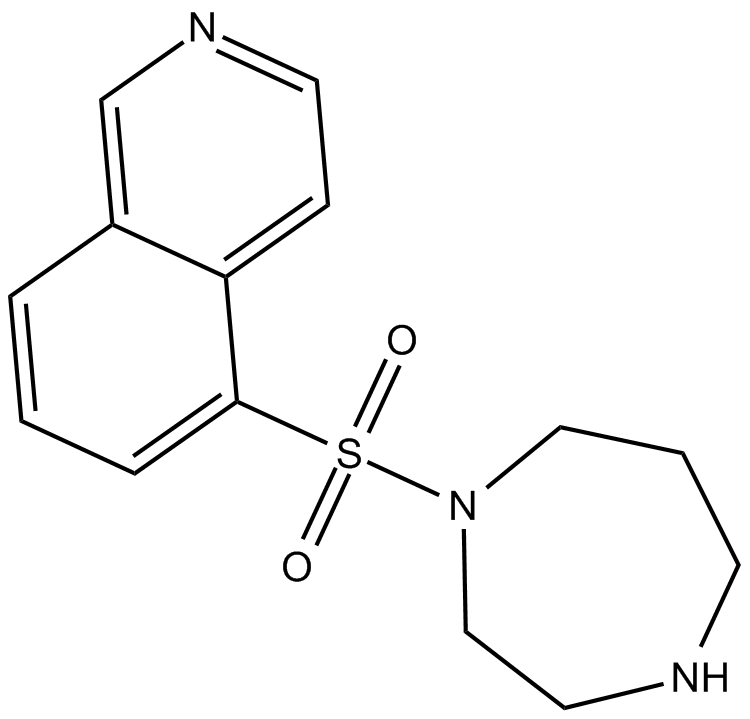 B3523 FasudilTarget: ROCK|PKC|PKG|PKA|Myosin light chain kinases (MLCKs)Summary: calcium antagonist
B3523 FasudilTarget: ROCK|PKC|PKG|PKA|Myosin light chain kinases (MLCKs)Summary: calcium antagonist -
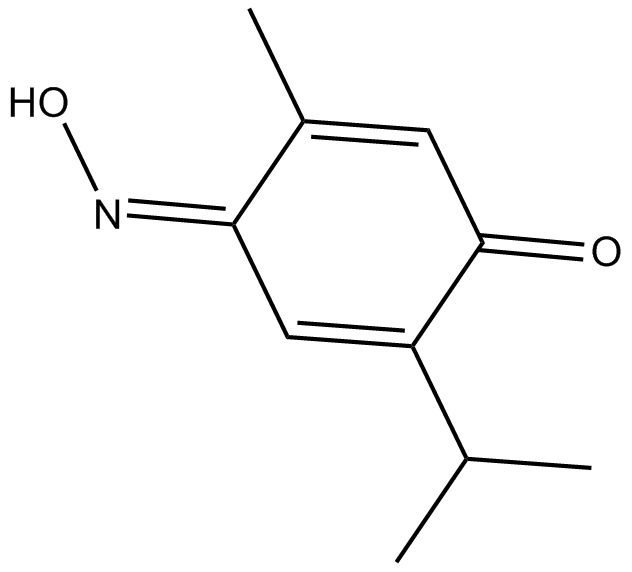 B3609 PoloximeSummary: polo-like kinase 1 (PLK) analogue
B3609 PoloximeSummary: polo-like kinase 1 (PLK) analogue -
 B9014 ML 141Summary: Cdc42 GTPase inhibitor
B9014 ML 141Summary: Cdc42 GTPase inhibitor -
 B3680 GriseofulvinSummary: Microtubule associated inhibitor
B3680 GriseofulvinSummary: Microtubule associated inhibitor -
 B3694 K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 6Target: KRAS G12CSummary: K-Ras (G12C) inhibitor
B3694 K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 6Target: KRAS G12CSummary: K-Ras (G12C) inhibitor


