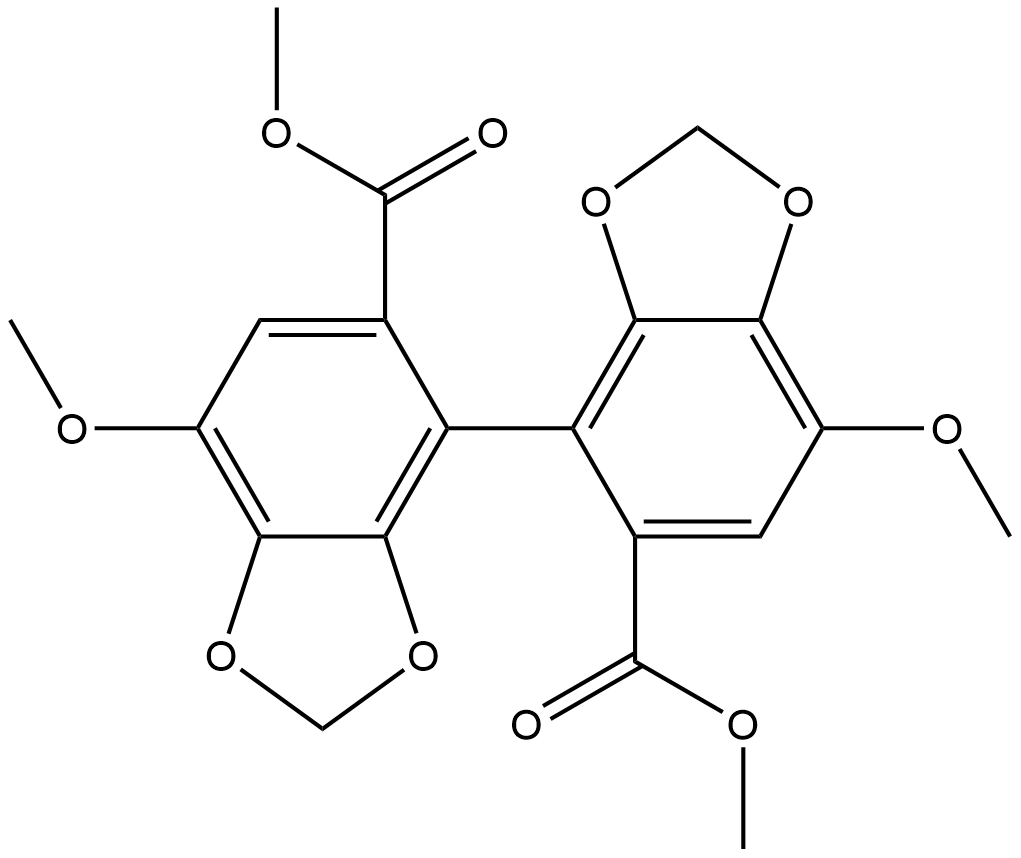
Bifendate
Bifendate (CAS No. 73536-69-3) is a synthetic derivative of Schisandrin C, with core biological activities focused on hepatoprotection, regulation of lipid metabolism, and inhibition of autophagy. Its targets include the autophagy pathway (inhibition of autophagosome-lysosome fusion, lysosomal acidification, and autolysosome reformation), CYP3A4 enzyme, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), as well as ncRNAs (SNORD43, RNU11) and immune/inflammation-related proteins (Rac2, Fermt3, Plg). In vitro cell experiments (Hela, HepG2, etc.) mostly use 50 μM (12 h treatment). In animal experiments, mice are administered 0.03~1.0 g/kg by gavage (for 4~14 consecutive days), with high doses up to 1 g/kg, and there is also a dosing regimen of 0.25% (w/w) added to the diet. Effective therapeutic concentrations correspond to clinical settings: for adult chronic hepatitis, the oral dose is 75~150 mg/day (1.5~3 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/tablet). In animal experiments, 30 mg/kg by gavage can improve acute liver injury, and doses of 0.03~1.0 g/kg can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation induced by high-fat/high-cholesterol diets. Attention should be paid to its interaction with cyclosporine (CYP3A4 genotype-dependent reduction of cyclosporine plasma concentration).
References:
[1] Pan SY, Yang R, Han YF, Dong H, Feng XD, Li N, Geng W, Ko KM. High doses of bifendate elevate serum and hepatic triglyceride levels in rabbits and mice: animal models of acute hypertriglyceridemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006 Jun;27(6):673-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00332.x. PMID: 16723084.
[2] Pan SY, Yang R, Dong H, Yu ZL, Ko KM. Bifendate treatment attenuates hepatic steatosis in cholesterol/bile salt- and high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Dec 15;552(1-3):170-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.09.011. Epub 2006 Sep 16. PMID: 17046746.
[3] Zeng Y, He YJ, He FY, Fan L, Zhou HH. Effect of bifendate on the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in relation to the CYP3A4*18B genotype in healthy subjects. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009 Apr;30(4):478-84. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.27. PMID: 19343062; PMCID: PMC4002280.
[4] Talifu A, Saimaiti R, Maitinuer Y, Liu G, Abudureyimu M, Xin X. Multiomics analysis profile acute liver injury module clusters to compare the therapeutic efficacy of bifendate and muaddil sapra. Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 13;9(1):4335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40356-5. PMID: 30867448; PMCID: PMC6416310.
[5] Yuan W, Jian F, Rong Y. Bifendate inhibits autophagy at multiple steps and attenuates oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Nov 26;631:115-123. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.09.067. Epub 2022 Sep 20. PMID: 36183552.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | 4°C, protect from light |
| M.Wt | 418.35 |
| Cas No. | 73536-69-3 |
| Formula | C20H18O10 |
| Synonyms | DDB |
| Chemical Name | dimethyl 7,7'-dimethoxy-[4,4'-bibenzo[d][1,3]dioxole]-5,5'-dicarboxylate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(OC)C=1C=C(OC)C=2OCOC2C1C3=C4OCOC4=C(OC)C=C3C(=O)OC |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |