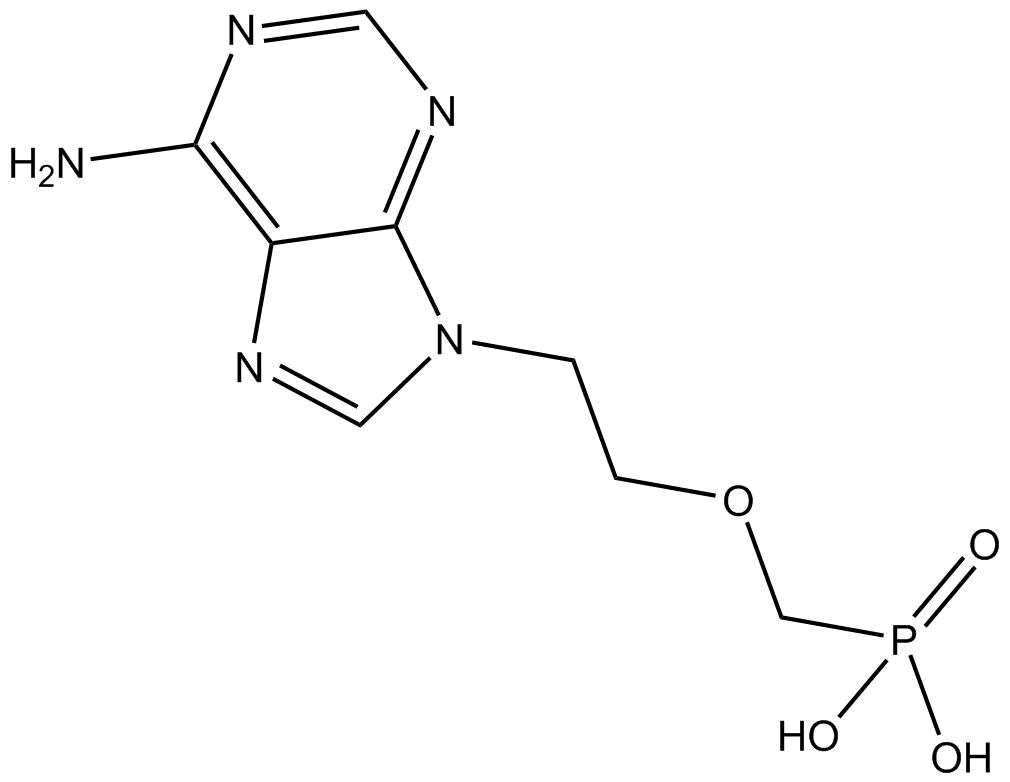
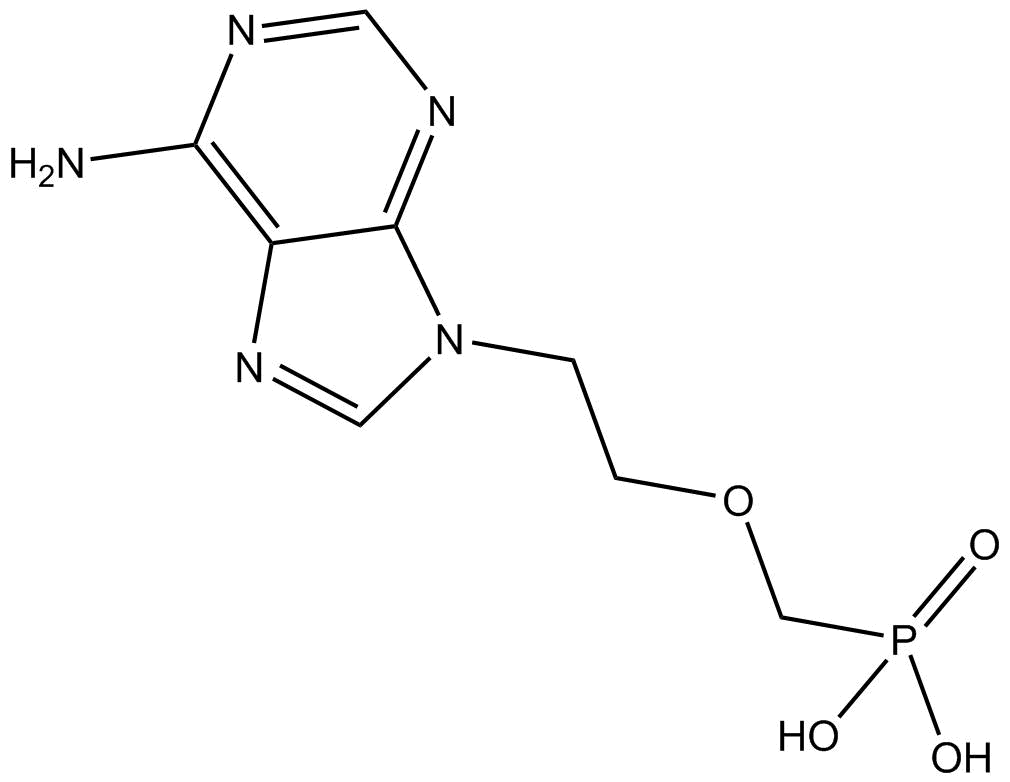
Adefovir
Adefovir (CAS No. 106941-25-7) is an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate antiviral drug. Its core target is hepatitis B virus (HBV) polymerase (the active pharmaceutical form is adefovir diphosphate, CAS No. 129556-87-2), which competitively binds to deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) and terminates HBV DNA chain elongation. It also serves as a specific probe substrate for renal organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1). It has clear concentrations related to biological activity: the IC₅₀ for HBV polymerase is 0.1 µmol/L, the IC₅₀ for human DNA polymerase α is >100 µmol/L, the IC₅₀ range in HBV-producing hepatocyte lines is 0.2~2.5 µmol/L, and the Michaelis-Menten constant (Kₘ) for nonlinear renal elimination is 170 nmol/L with a maximum rate (Vₘₐₓ) of 2.40 µmol/h (corresponding to a median estimated glomerular filtration rate of 105 mL/min). Commonly used application concentrations: clinically relevant plasma concentrations (5.56~91.0 nmol/L) are adopted in transporter phenotyping studies, and 0.2~2.5 µmol/L is commonly used in in vitro antiviral experiments. The clinically effective therapeutic concentration corresponds to an oral dose of 10 mg/day (once daily) of the prodrug adefovir dipivoxil, with a peak plasma concentration of approximately 64~75 nmol/L (17.5~20.4 ng/ml). It is indicated for chronic hepatitis B (including HBeAg-positive/negative and lamivudine-resistant strains), and the dosing interval needs to be extended in patients with renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance < 50 ml/min). Its biological activity is reflected in highly effective inhibition of HBV replication, being effective against both wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV with a 3-year resistance rate of only 5.9%. It is mainly excreted via the kidneys (approximately 60% through OAT1-mediated tubular secretion), and long-term use may cause hypophosphatemia and bone disease, requiring monitoring of renal function and serum phosphorus levels.
References:
[1] Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV. Adefovir dipivoxil in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2004 Aug;2(4):475-83. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2.4.475. PMID: 15482214.
[2] Zhang J, Shi X, Wang J, Qi J, Li Y, Jiang H, Sun Q, Gu Q, Li C, Ying Z. Adefovir-induced hypophosphatemic osteochondrosis mimicks ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024 Jan;27(1):e15040. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15040. PMID: 38287538.
[3] Dong Q, Chen C, Taubert M, Bilal M, Kinzig M, Sörgel F, Scherf-Clavel O, Fuhr U, Dokos C. Understanding adefovir pharmacokinetics as a component of a transporter phenotyping cocktail. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;80(7):1069-1078. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03673-x. Epub 2024 Mar 28. PMID: 38546841; PMCID: PMC11156719.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 273.19 |
| Cas No. | 106941-25-7 |
| Formula | C8H12N5O4P |
| Synonyms | GS-0393; PMEA |
| Solubility | Insoluble in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥2.7 mg/mL in H2O (Need ultrasonic and warming) |
| Chemical Name | ((2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)ethoxy)methyl)phosphonic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Nc1c2nc[n](CCOCP(O)(O)=O)c2ncn1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure