AAF
Catalog No.
C8739
Mainly used to induce animal models for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and multiple primary tumors
Featured Products
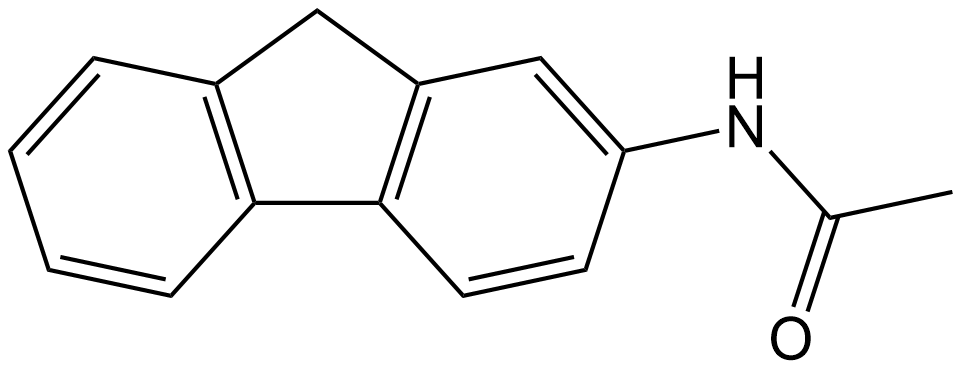
2-Acetamidofluorene (2-Acetamidofluorene, CAS No.: 53-96-3) is a carcinogenic substance widely used in biomedical research, mainly for establishing animal models to induce hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and multiple primary tumors. Its carcinogenic mechanism involves covalent binding to DNA after metabolic activation, leading to gene mutations and abnormal cell proliferation. In in vitro studies, the active levels of 2-acetamidofluorene are typically in the low micromolar to micromolar range, depending on experimental conditions and cell type. In cell models, researchers often add it to the culture medium to observe its effects on cell proliferation and apoptosis; in animal models, it is usually administered orally or via intraperitoneal injection to induce liver tumor development. The dose or concentration used in experiments typically depends on the experimental design and research objectives. Due to its strong carcinogenicity, strict safety operating procedures must be followed during experiments.
| Storage | Store at 4°C, protect from light |
| M.Wt | 223.28 |
| Cas No. | 53-96-3 |
| Formula | C15H13NO |
| Synonyms | 2-Acetamidofluorene; FAA; NSC 12279; N-9H-Fluoren-2-ylacetamide |
| Chemical Name | N-(9H-fluoren-2-yl)acetamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(NC1=CC=C2C=3C=CC=CC3CC2=C1)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |