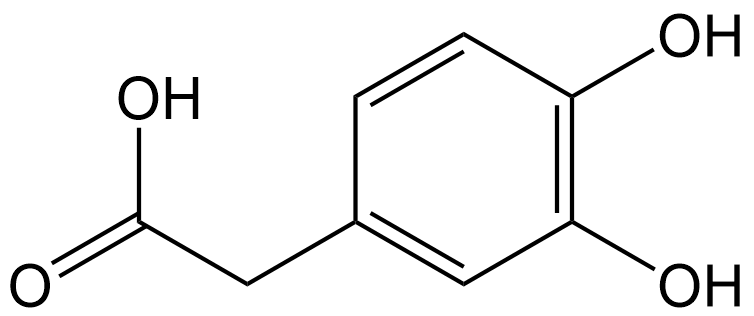
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic Acid
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC, CAS 102-32-9) is an important metabolite of dopamine, and changes in its levels are closely associated with the functional status of dopaminergic neurons. In MPTP- (Cat. No.: A3634) induced Parkinson’s disease (PD) mouse models and 6-OHDA-induced PD rat models, DOPAC levels in the striatum and other brain regions decrease markedly in parallel with dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Intervention with puerarin (Cat. No.: N1114), administered via intragastric or intraperitoneal routes at doses typically ranging from 15–120 mg/kg/day for 7–30 days, significantly elevates brain DOPAC levels in these models, accompanied by increased contents of dopamine (DA) and homovanillic acid (HVA). This effect is associated with the neuroprotective actions of puerarin on dopaminergic neurons and the amelioration of motor symptoms in PD, potentially involving anti-apoptotic mechanisms (regulation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK pathways), attenuation of oxidative stress (activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway), inhibition of neuroinflammation, and modulation of the ubiquitin–proteasome system.
References:
[1] Zhang N, Guo P, Zhao Y, Qiu X, Shao S, Liu Z, Gao Z. Pharmacological mechanisms of puerarin in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: An overview. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Aug;177:117101. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117101. Epub 2024 Jul 14. PMID: 39002442.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 168.15 |
| Cas No. | 102-32-9 |
| Formula | C8H8O4 |
| Synonyms | DOPAC, DHAA |
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acetic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC1=C(O)C=CC(CC(O)=O)=C1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure