Search results for: 'signaling pathways gpcr g protein'
-
 K1304 Protein G Magnetic BeadsSummary: Protein G Magnetic beads
K1304 Protein G Magnetic BeadsSummary: Protein G Magnetic beads -
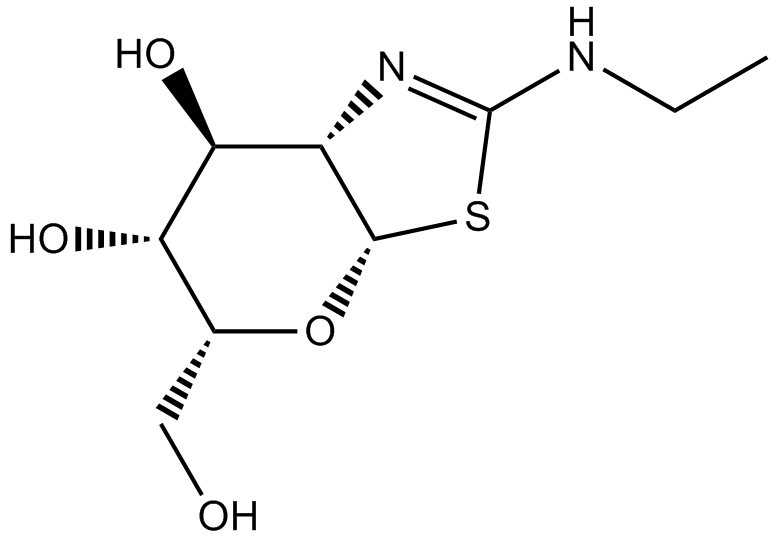 B2048 Thiamet G1 CitationTarget: O-GlcNAcaseSummary: O-GlcNAcase inhibitor, potent and selective
B2048 Thiamet G1 CitationTarget: O-GlcNAcaseSummary: O-GlcNAcase inhibitor, potent and selective -
 N2128 Tenacissoside G
N2128 Tenacissoside G -
 B5243 Antagonist GSummary: broad spectrum neuropeptide antagonist and antiproliferative agent
B5243 Antagonist GSummary: broad spectrum neuropeptide antagonist and antiproliferative agent -
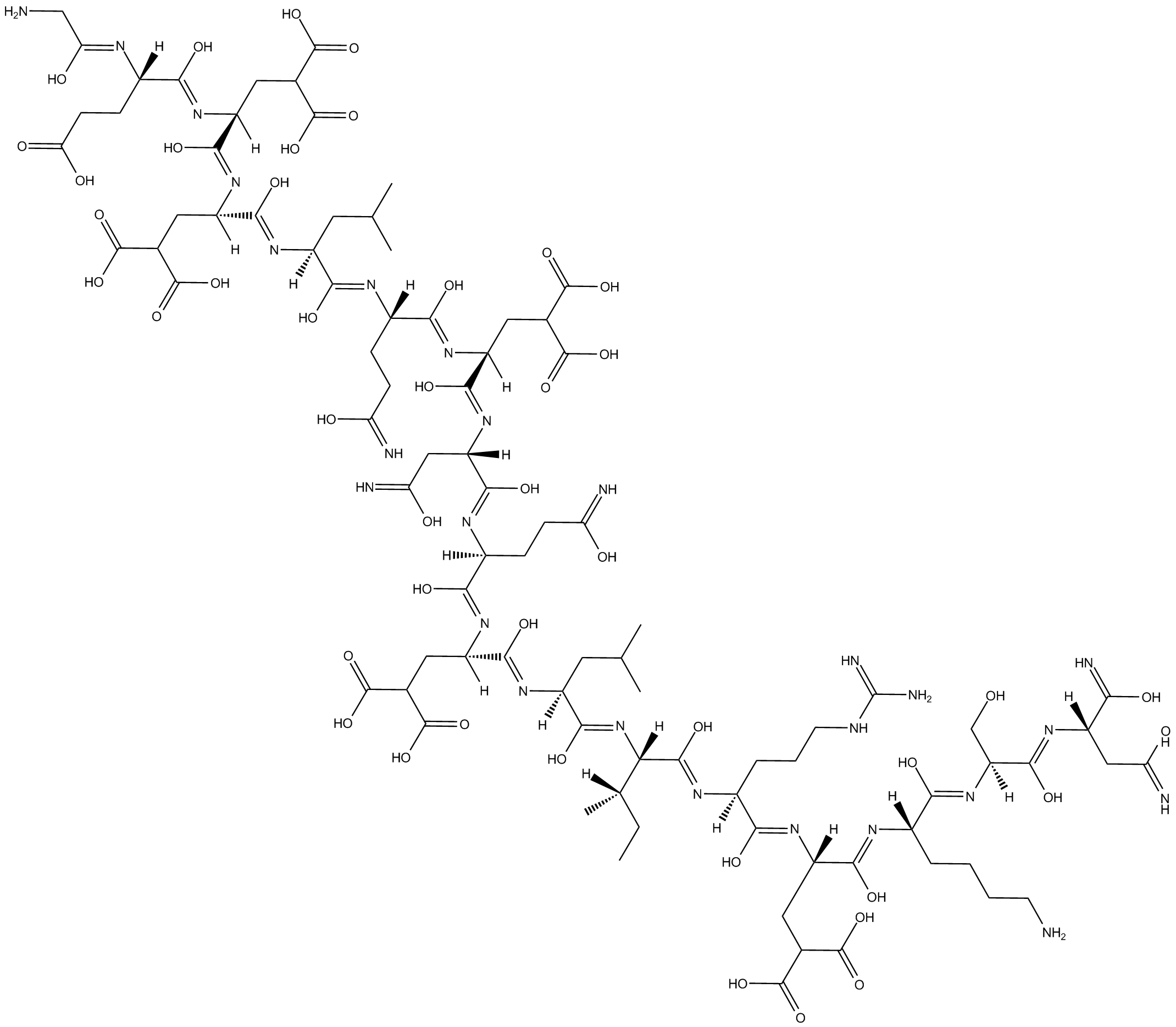 B5533 Conantokin GSummary: NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist
B5533 Conantokin GSummary: NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist -
 PC2006 HyperChrom Protein G 4FF AgaroseSummary: Protein G Agarose Affinity Chromatography Media
PC2006 HyperChrom Protein G 4FF AgaroseSummary: Protein G Agarose Affinity Chromatography Media -
 PC1006 HyperTrap Protein G 4FF ColumnSummary: Protein G affinity chromatography preloaded column with high flow rates, resistance to organic solvents and chemical stability.
PC1006 HyperTrap Protein G 4FF ColumnSummary: Protein G affinity chromatography preloaded column with high flow rates, resistance to organic solvents and chemical stability. -
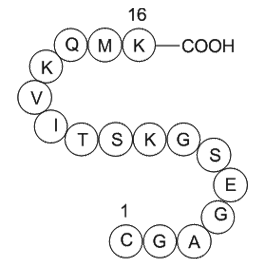 A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP
A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP -
 K4622 Immunoprecipitation Kit (Protein G Agarose Gel)Summary: Universal IP Toolkit (Protein G Agarose Gel) mainly used for IP/Co-IP and Protein-molecule interactions, etc.
K4622 Immunoprecipitation Kit (Protein G Agarose Gel)Summary: Universal IP Toolkit (Protein G Agarose Gel) mainly used for IP/Co-IP and Protein-molecule interactions, etc. -
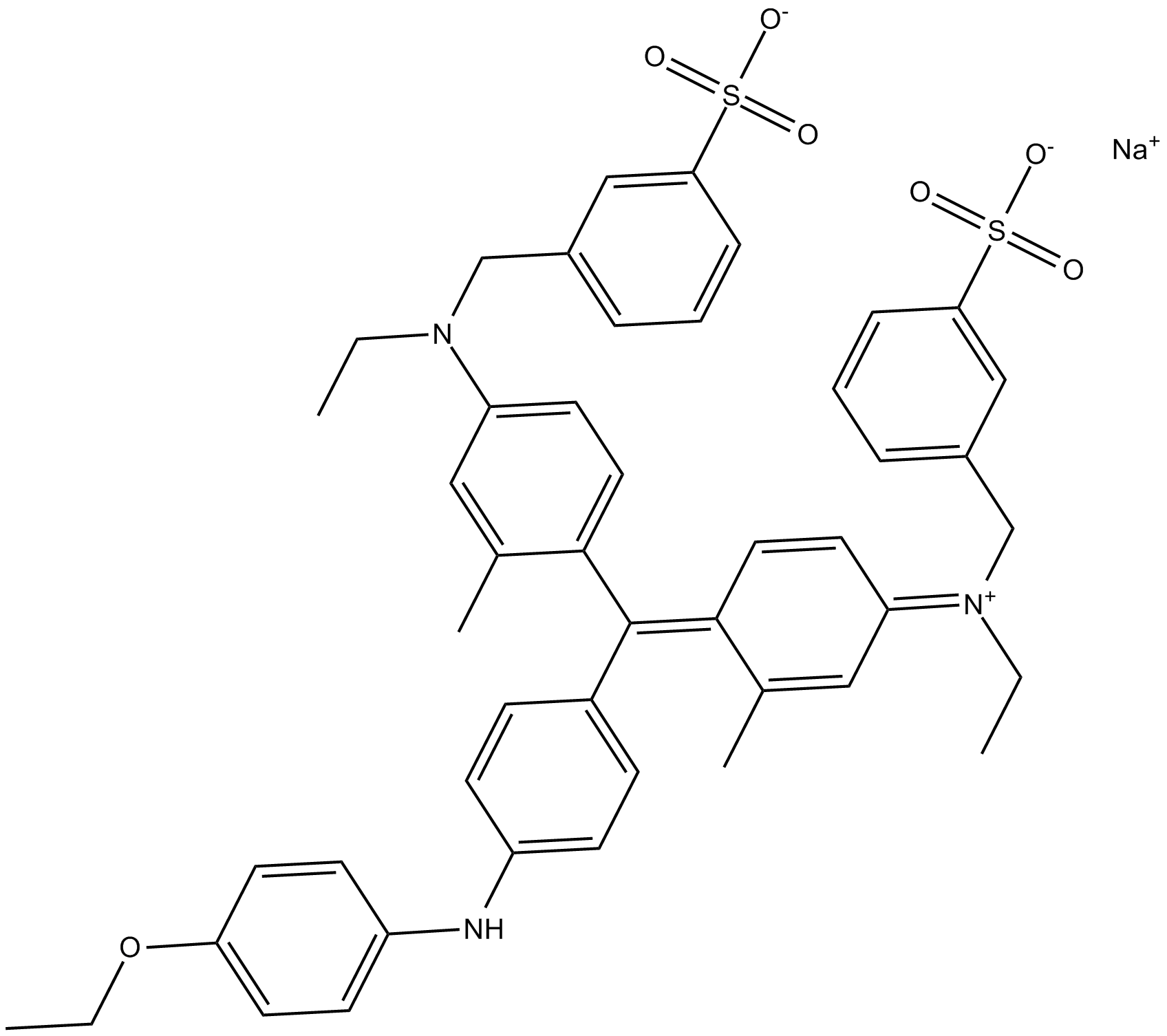 C5579 Brilliant Blue GSummary: used for protein staining in SDS-PAGE, Blue Native PAGE, and the Bradford Method; selective inhibitor of the P2X purinoceptor channel P2X7
C5579 Brilliant Blue GSummary: used for protein staining in SDS-PAGE, Blue Native PAGE, and the Bradford Method; selective inhibitor of the P2X purinoceptor channel P2X7


