Signaling Pathways
Signal transduction pathways constitute a precisely regulated network through which cells perceive external stimuli and initiate intracellular responses. Core research in this field focuses on the mechanisms of molecular signal transmission and regulation within cells and typically encompasses three fundamental stages: signal initiation, signal propagation through cascades, and downstream effector responses. Key molecules—including proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules—interact with high specificity and are subject to tight regulation (e.g., protein phosphorylation, molecular activation/inhibition). These processes underpin the full spectrum of cellular activities, including proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, apoptosis, and immune responses. While accurate regulation of these pathways is essential for maintaining organismal homeostasis, their dysregulation is a major driver of the onset and progression of diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
APExBIO is strongly committed to advancing life science research by providing a comprehensive portfolio of small-molecule tools designed to support the elucidation of signaling mechanisms and the identification of key regulatory targets—critical steps for deciphering disease etiology and developing innovative therapies. Our offerings span all major signal transduction pathways, including classical pathways (e.g., PI3K/Akt, MAPK, NF-κB), emerging modalities (e.g., ferroptosis, cuproptosis, pyroptosis), and research on pathway crosstalk. With tens of thousands of products—including inhibitors, activators, and modulators—we robustly support research in oncology, immunology, neuroscience, epigenetics, and other key fields.
Every APExBIO product undergoes rigorous functional validation and purity testing, ensuring suitability for diverse research applications such as pathway mechanism studies, target identification and validation, drug activity evaluation, cell-based assays, and animal model development. We complement our high-quality tools with comprehensive support: each product is supplied with detailed chemical property reports, biological activity data, standardized usage guidelines, and extensive literature citations in high-impact journals. In addition, we provide end-to-end assistance—from product selection and experimental protocol optimization to technical troubleshooting—enabling researchers to rely on tool quality, focus on core scientific questions, and accelerate progress in signal transduction research and translational medicine.
-
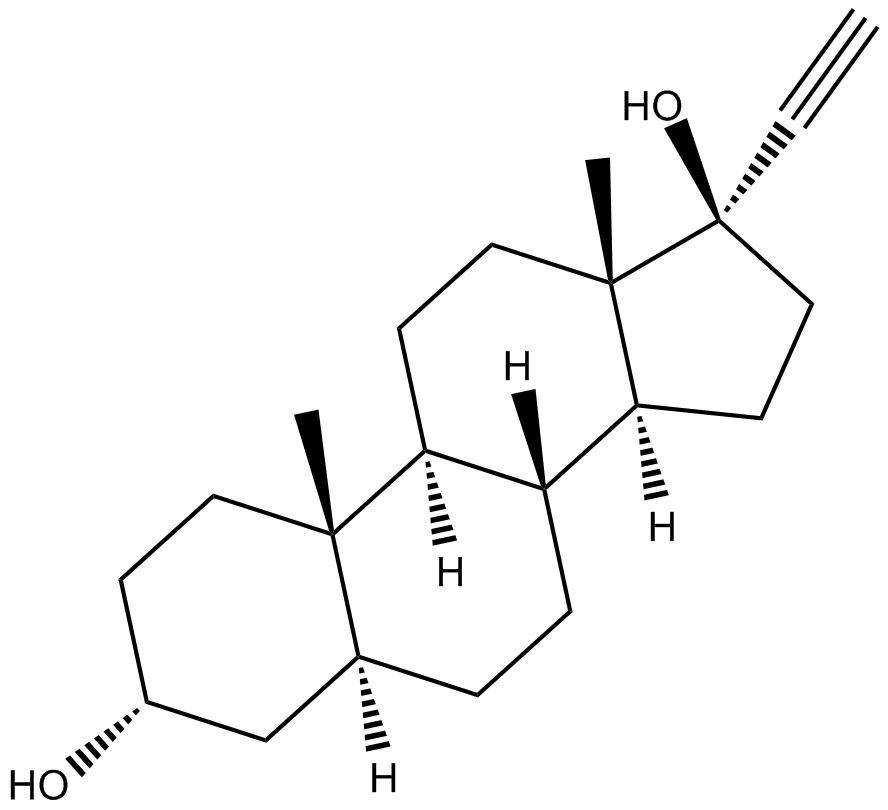 C3546 HE-3235Summary: androgen receptor antagonist
C3546 HE-3235Summary: androgen receptor antagonist -
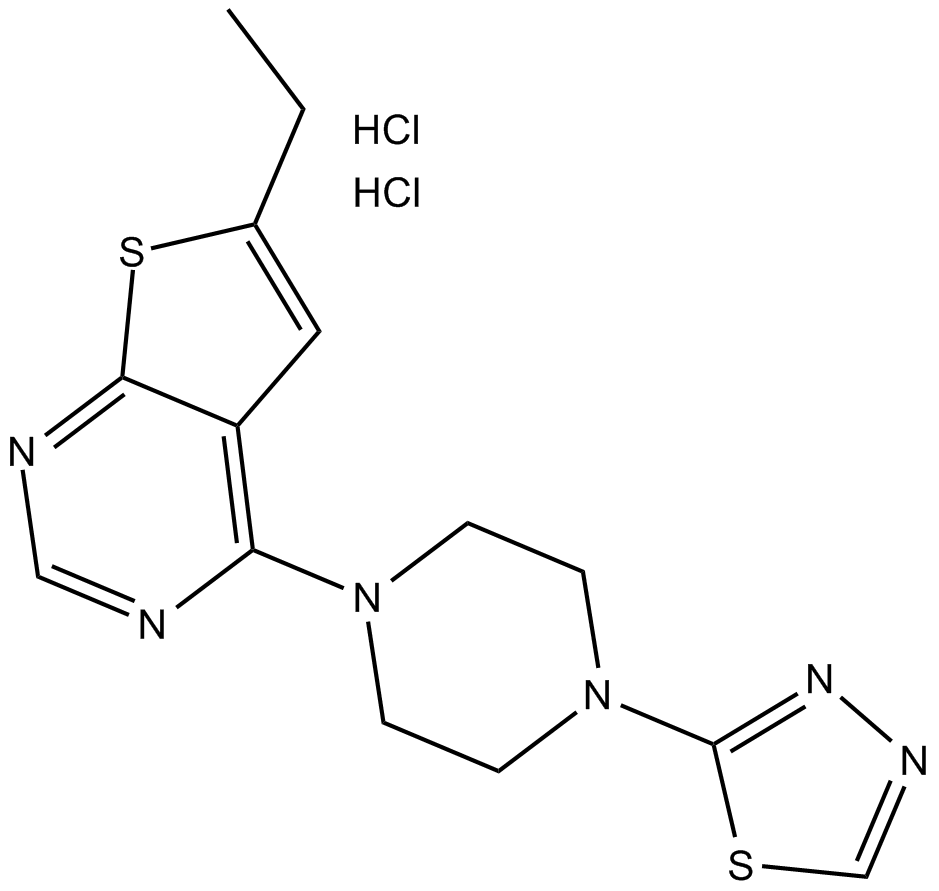 C3379 MI-nc (hydrochloride)Summary: weak inhibitor of menin-MLL interaction
C3379 MI-nc (hydrochloride)Summary: weak inhibitor of menin-MLL interaction -
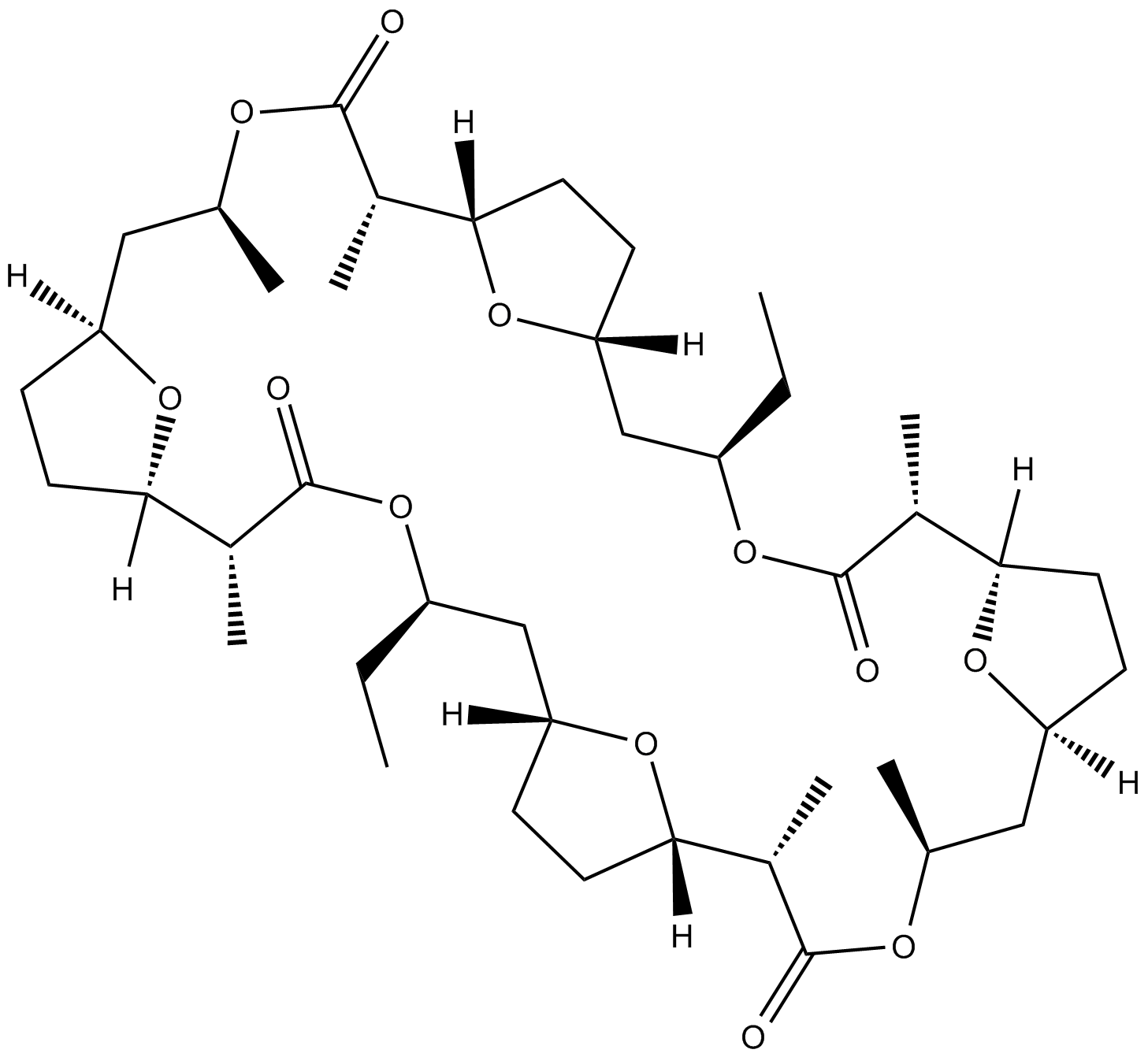 C3454 DinactinSummary: macrotetrolide antibiotic that acts as an ionophore for monovalent cations.
C3454 DinactinSummary: macrotetrolide antibiotic that acts as an ionophore for monovalent cations. -
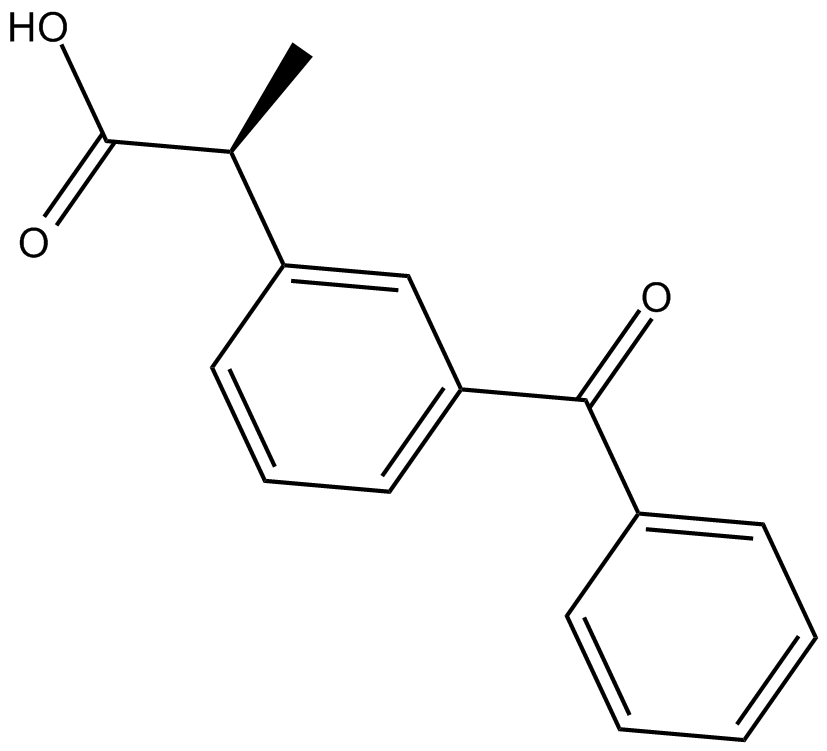 C3334 (S)-KetoprofenSummary: COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitor
C3334 (S)-KetoprofenSummary: COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitor -
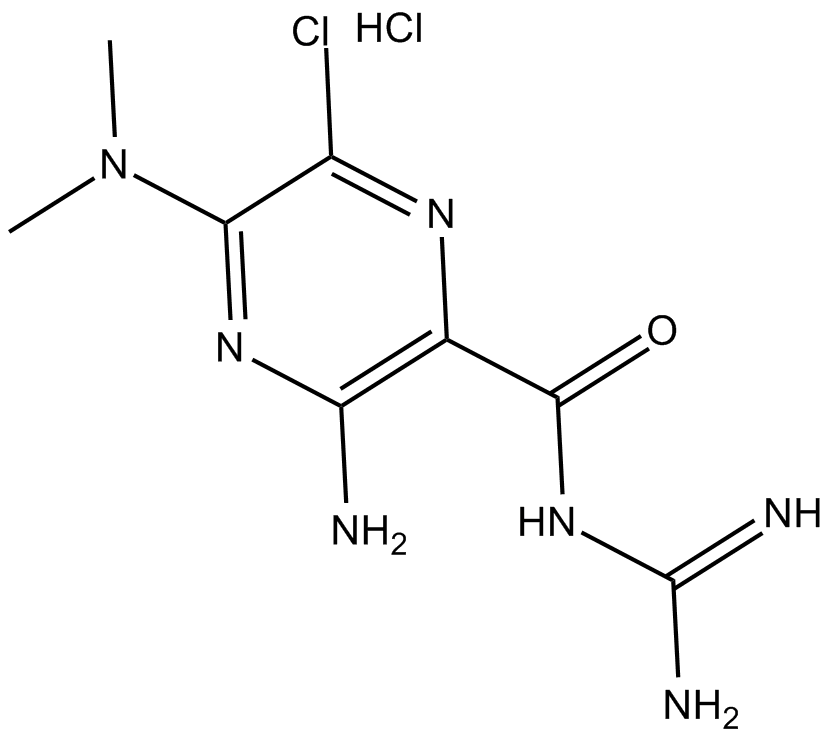 C3505 5-(N,N-dimethyl)-Amiloride (hydrochloride)Summary: NHE1, NHE2, and NHE3 inhibitor
C3505 5-(N,N-dimethyl)-Amiloride (hydrochloride)Summary: NHE1, NHE2, and NHE3 inhibitor -
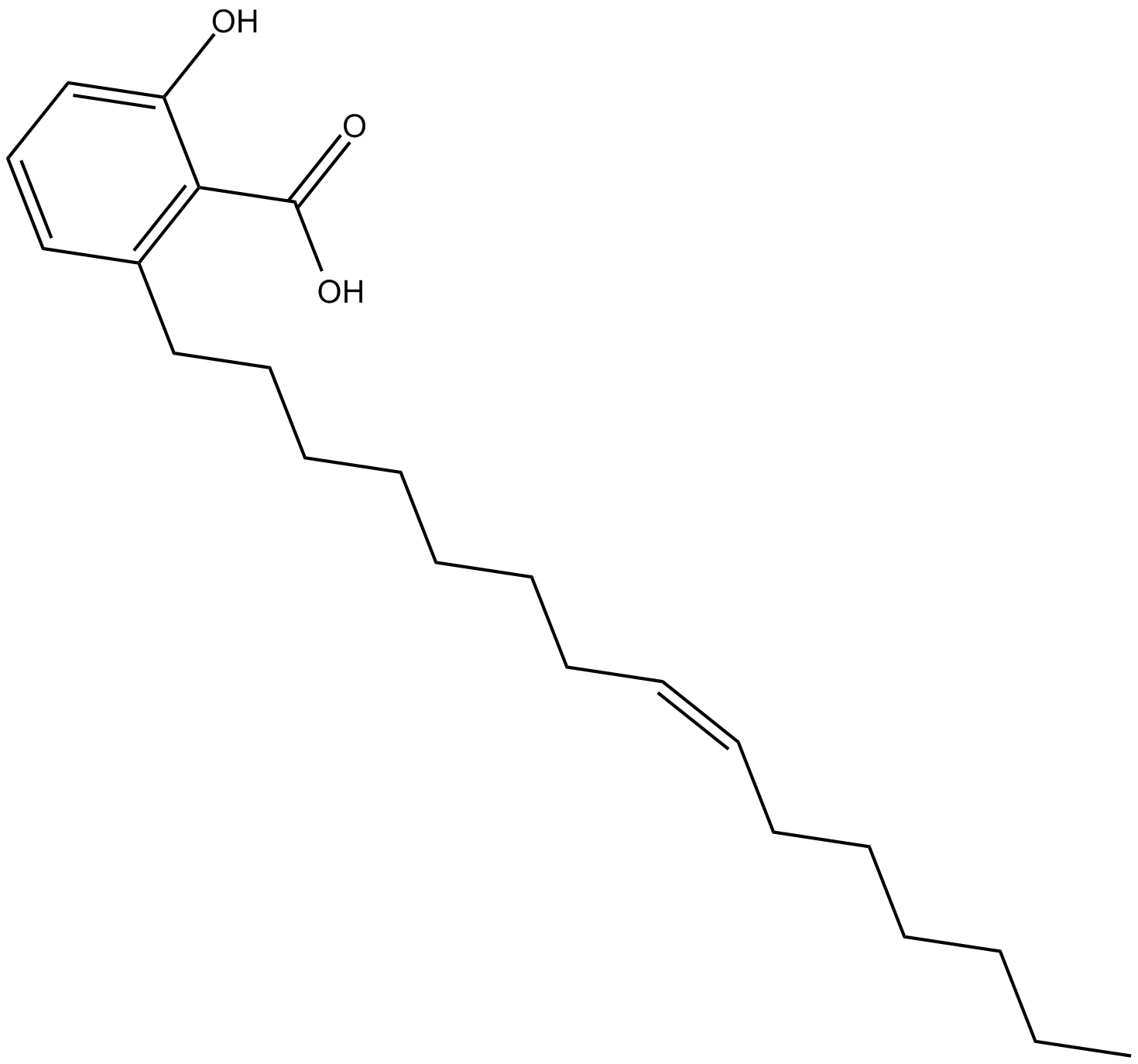 C3421 Ginkgolic Acid C15:1Summary: inhibits SUMOylation
C3421 Ginkgolic Acid C15:1Summary: inhibits SUMOylation -
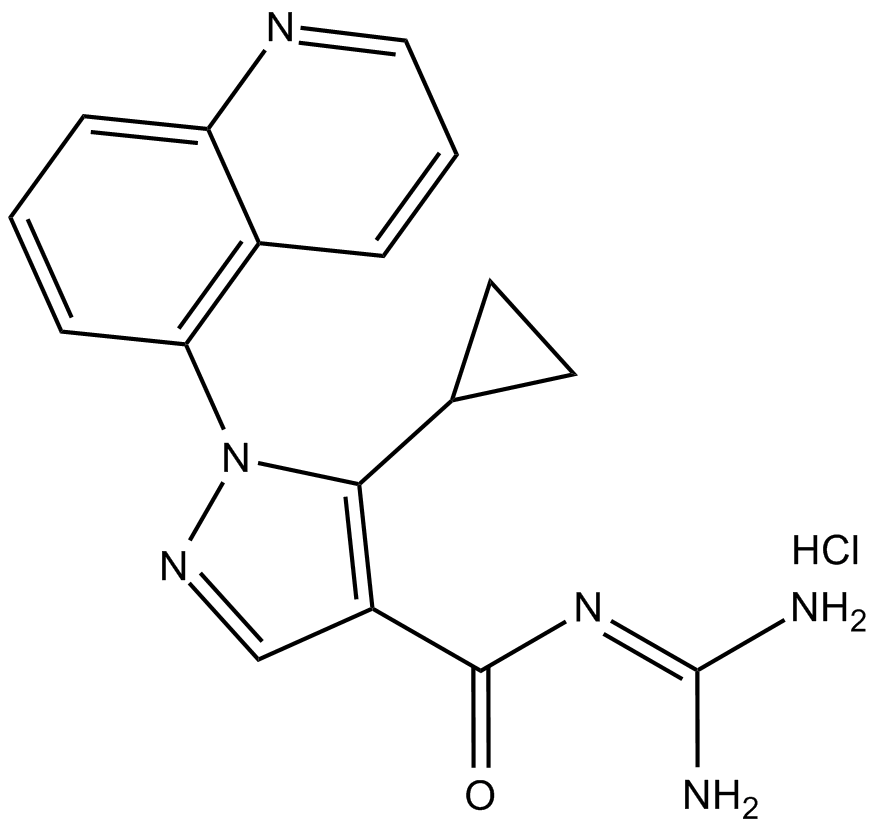 C3480 Zoniporide (hydrochloride)Summary: sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform-1 (NHE-1) inhibitor
C3480 Zoniporide (hydrochloride)Summary: sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform-1 (NHE-1) inhibitor -
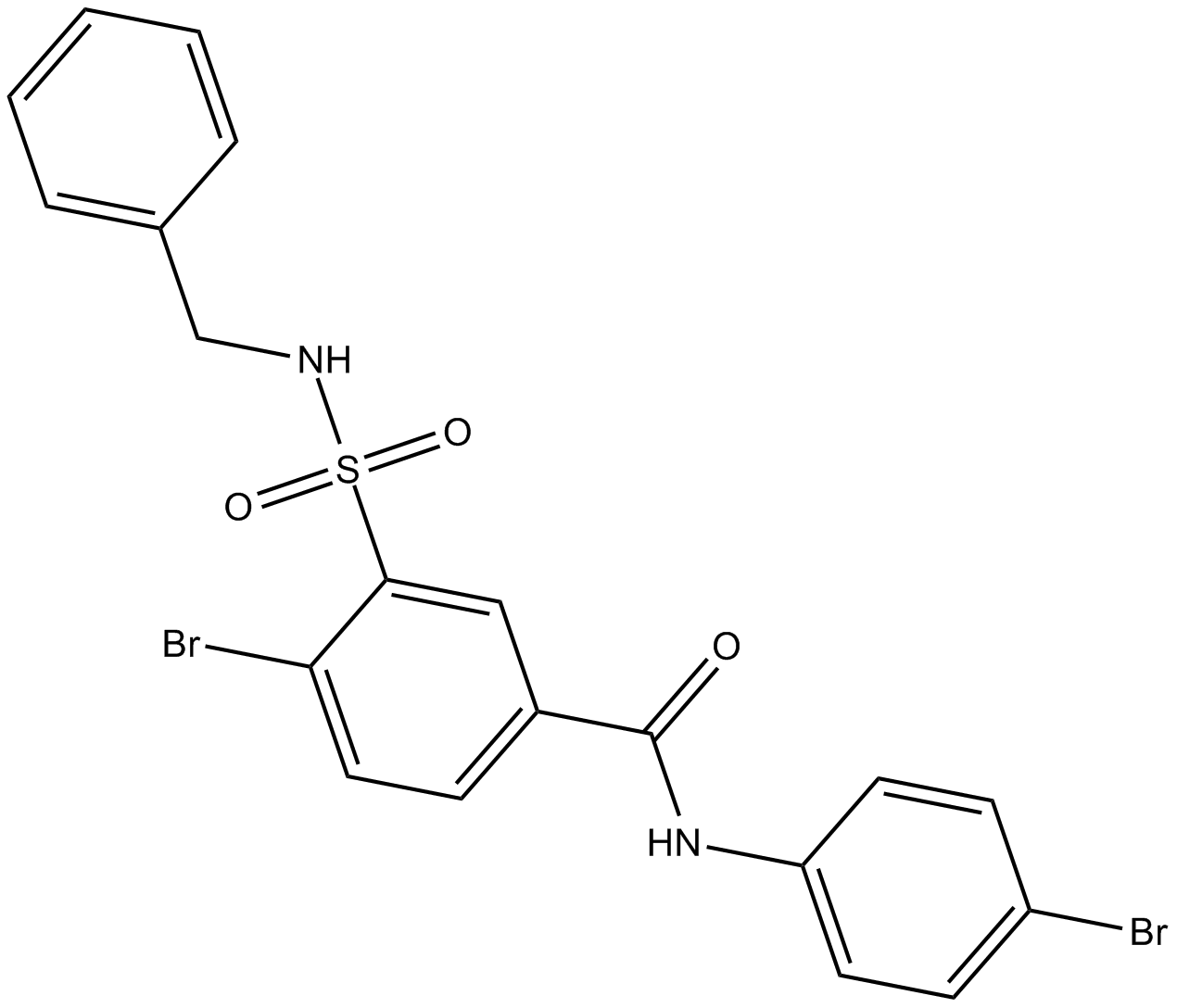 C3357 RS-13 CitationSummary: RAD51 activator
C3357 RS-13 CitationSummary: RAD51 activator -
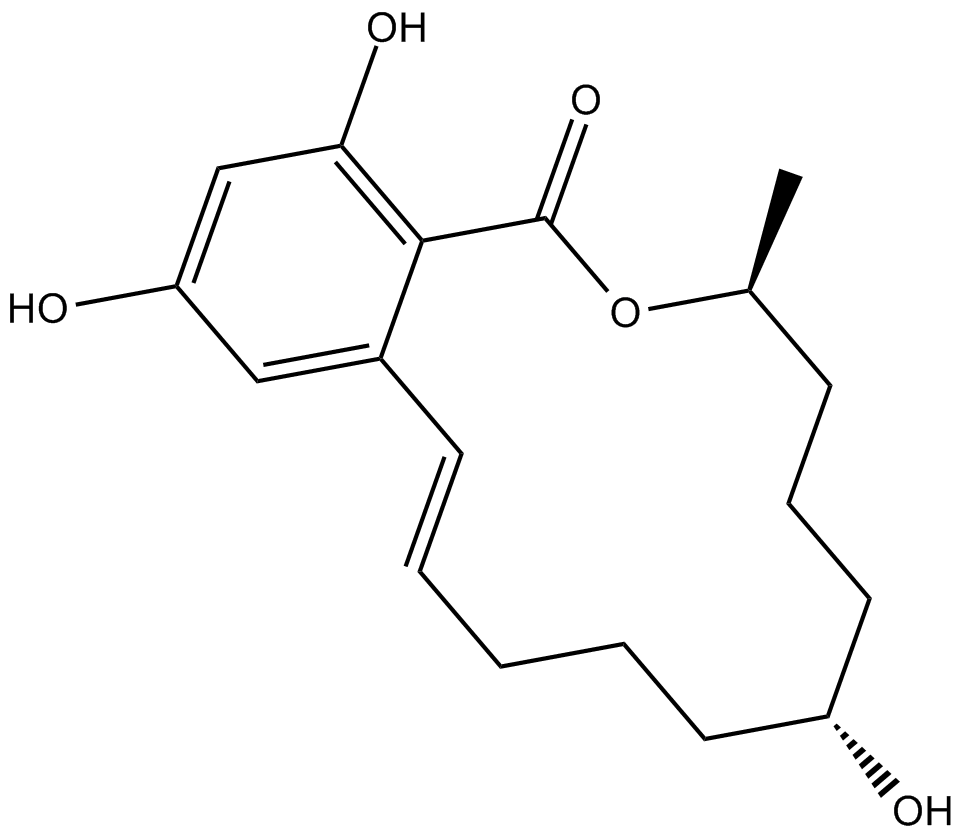 C3405 α-ZearalenolSummary: estrogen receptor agonist
C3405 α-ZearalenolSummary: estrogen receptor agonist -
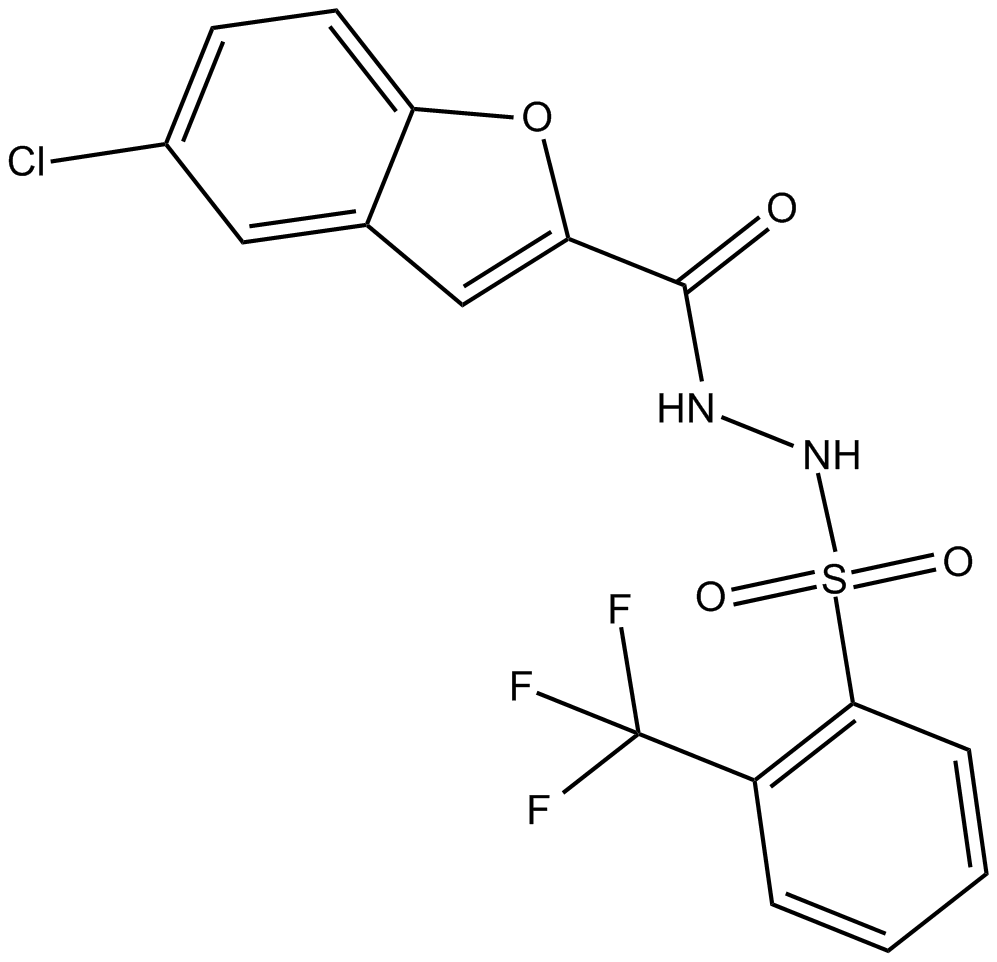 C3463 BCATc Inhibitor 2Summary: cytosolic BCAT (BCATc) inhibitor
C3463 BCATc Inhibitor 2Summary: cytosolic BCAT (BCATc) inhibitor


