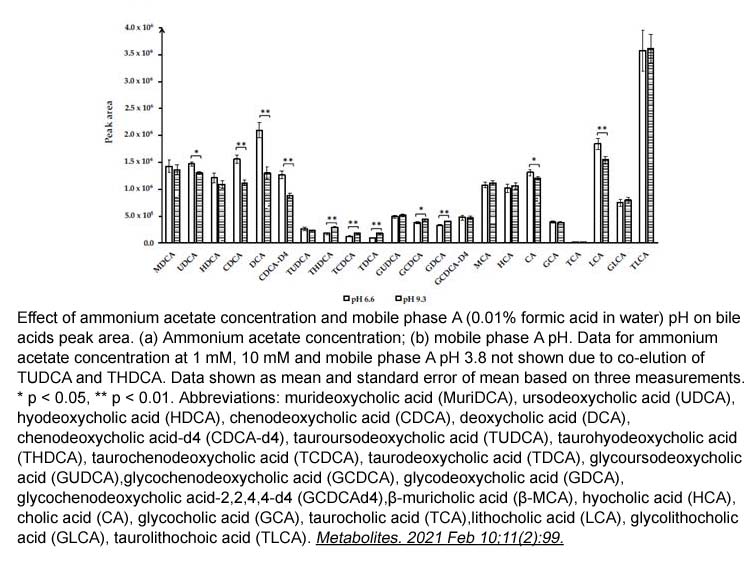
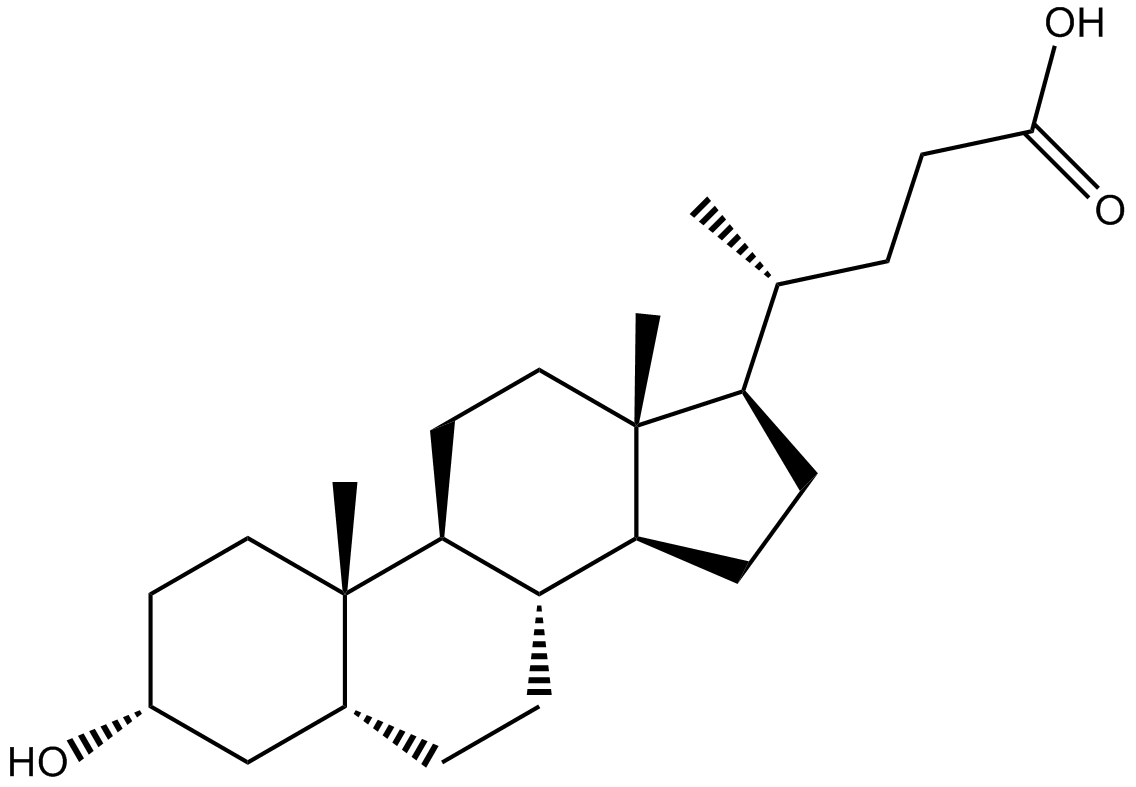
Lithocholic Acid
Lithocholic Acid (CAS 434-13-9) is a secondary bile acid compound, functioning as an inhibitor or modulator in hepatic tissue and exhibiting antagonist or agonist activity in various cellular pathways. Additionally, it interferes with bile secretion processes and may influence toxin-induced hepatic effects.
In experimental models, Lithocholic Acid induces intrahepatic cholestasis with significant hepatotoxicity, as measured by [key metric] in [cell lines/animal models]. It can also promote tumorigenesis in certain contexts and modulate cellular proliferation or apoptosis, as observed in [experimental systems]. Lithocholic Acid is recognized for its ability to activate or antagonize multiple nuclear receptors, including [target receptors], impacting downstream gene expression pathways.
In application, Lithocholic Acid is widely used for investigating mechanisms of bile acid toxicity and cholestatic liver injury. It serves as a research tool for studying the pathogenesis of liver diseases, tumor promotion, and the physiological roles of bile acids in cellular signaling. Lithocholic Acid is also utilized in assays evaluating bile acid receptor modulation, providing insights into drug interactions and metabolic regulation. Its distinctive biochemical properties make it an important compound in liver biology and toxicology research, particularly in the context of secondary bile acid effects and their association with disease states.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 376.57 |
| Cas No. | 434-13-9 |
| Formula | C24H40O3 |
| Synonyms | Lithocholic acid; LCA |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥12.95 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥26.6 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | (4R)-4-[(3R,5R,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C[C@H](CCC(O)=O)[C@@H](CC1)[C@@](C)(CC2)[C@@H]1[C@H](CC1)[C@H]2[C@@](C)(CC2)[C@H]1C[C@@H]2O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
HL-1 cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is > 13 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20 °C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
50 or 100 μM |
|
Applications |
In HL-1 cells, Lithocholic Acid reduced and prevented cardiomyocyte apoptosis at the concentrations of 50 and 100 μM, respectively. In the presences of the pro-apoptotic stimulus, Doxazosin, Lithocholic Acid inhibited hyperphosphorylation of EphA2. In addition, Lithocholic Acid increased the expression of total EphA2. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Mice |
|
Dosage form |
0.125 mg/g; i.p.; b.i.d., for 4 days. |
|
Applications |
In PXR-/- mice, Lithocholic Acid resulted in sticky residues. Analysis of the urine revealed that PXR-/- mice showed substantially increased levels of Lithocholic Acid compared with wild-type animals. In addition, wild-type mice treated with Lithocholic Acid in a shorter term showed significant increases in hepatic Cyp3a11 and Oatp2 expression, whereas Lithocholic Acid treatment exhibited no effect on the expression of those genes in PXR-/- mice. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Jehle J, Staudacher I, Wiedmann F, Schweizer P, Becker R, Katus H, Thomas D. Regulation of apoptosis in HL-1 cardiomyocytes by phosphorylation of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 and protection by lithocholic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;167(7):1563-72. [2]. Staudinger JL, Goodwin B, Jones SA, Hawkins-Brown D, MacKenzie KI, LaTour A, Liu Y, Klaassen CD, Brown KK, Reinhard J, Willson TM, Koller BH, Kliewer SA. The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3369-74. |
|
| Description | Lithocholic Acid, a bile acid, is an activator of the vitamin D receptor, PXR and FXR. | |||||
| Targets | VDR | PXR | FXR | |||
| IC50 | 29μM(Ki) | |||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
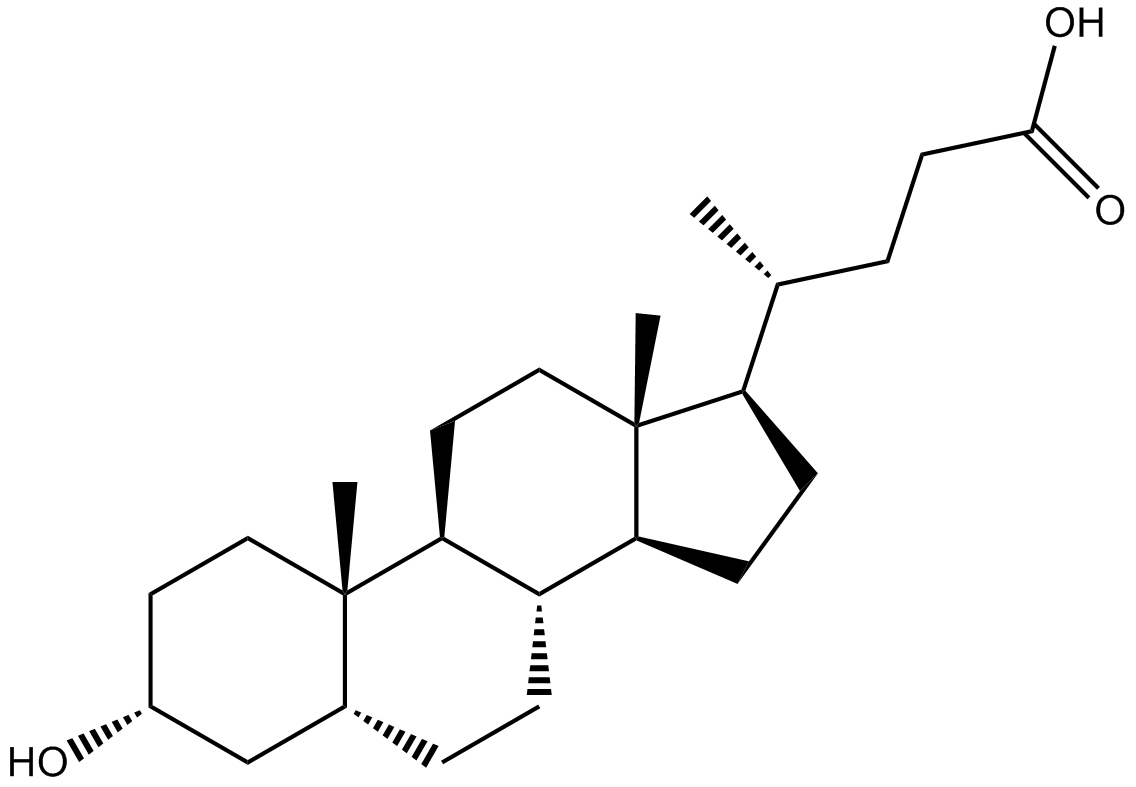
Related Biological Data