[D-Lys3]-GHRP-6
IC50: 0.9 μM
[D-Lys3]-GHRP-6 is an antagonist at the ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1a) and weakly binds to melanocortin receptors (Ki = 26-120 μM).
In vitro: [D-Lysa]GHRP-6 used similar affinities to bind to all the four MC receptors, to which the structurally related Met-enkephalin and the functionally related GHuRH, together with LHRH and somatostatin-14 did not bind. This (the low affinity of the GH-releasing/enkephalin peptides) may indicate that they do not interact with the MC receptors at pharmacological concentrations. [DLys3] GHRP-6 only used slightly higher affinity than GHRP-6 to bind to the MC1 receptor. [1].
Compared with GHRP-6, [D-Lys3]GHRP-6 has higher affinity for all the MC receptors, especially for the MC3 and MC4 receptors. Interestingly, [D-Lys 3] GHRP-6 binds to the MC1 receptor with only slightly higher affinity compared with GHRP-6, which may indicate that the basic hydrophilic residue in position 8 is not important for the MC 1 receptor (as the same as he other MC receptor subtypes) [1,2]. The peptidic GHS-receptor antagonist (D-Lys3)-GHRP-6 (10-4 M) antagonized ghrelin (10-7 M) weakly, showing a much weaker affinity (IC50, 0.9×10-6 M) to the GHS-receptor than ghrelin (IC50, 0.3×10-9 M). Ghrelin increased the electrical activity in 76% of all cells inhibited by leptin (n=17). These data reveal that ghrelin interacts with the leptin hypothalamic network in the arcuate nucleus. Leptin and ghrelin oppositely effect on neurons in the arcuate nucleus, which may serve as a neurophysiological correlate of the orexigenic and anorectic effects of them [2].
In vivo: The administration of D-Lys3-GHRP-6 (an antagonist of GHS receptors) alone had no significantly influence on GH secretion. Oppositely, pretreatment with this antagonist efficiently inhibited the stimulatory effect of AMPA and NMDA on GH secretion. To confirm this contention, further experiments to evaluate different protocols (doses, times, additional GHS receptor antagonists) of administration of D-Lys3-GHRP-6 are carried out. Nevertheless, it is possible that ghrelin may only intervene in situations of hypo- or hypersecretion of GH but not involved in the control of basal GH secretion [2].
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
References:
[1]. Schith HB, Muceniece R, Wikberg JE. Characterization of the binding of MSH-B, HB-228, GHRP-6 and 153N-6 to the human melanocortin receptor subtypes. Neuropeptides. 1997 Dec;31(6):565-71.
[2]. Traebert M, Riediger T, Whitebread S, Scharrer E, Schmid HA. Ghrelin acts on leptin-responsive neurones in the rat arcuate nucleus. J Neuroendocrinol. 2002 Jul;14(7):580-6.
[3]. Pinilla L, Barreiro ML, Tena-Sempere M, Aguilar E.Role of ghrelin in the control of growth hormone secretion in prepubertal rats: interactions with excitatory amino acids. Neuroendocrinology. 2003 Feb;77(2):83-90.
- 1. Caishun Zhang, Junhua Yuan, et al. "Ghrelin in the lateral parabrachial nucleus influences the excitability of glucosensing neurons, increases food intake and body weight." Endocr Connect. 2020 Oct 1;EC-20-0285.R1. PMID:33112816
- 2. Fan XT, Tian Z, et al. "Ghrelin Receptor Is Required for the Effect of Nesfatin-1 on Glucose Metabolism." Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Oct 24;9:633. PMID:30405536
| Physical Appearance | White lyophilised solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 930.12 |
| Cas No. | 136054-22-3 |
| Formula | C49H63N13O6 |
| Solubility | ≥51.1 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥51.8 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥50.7 mg/mL in H2O |
| SDF | Download SDF |
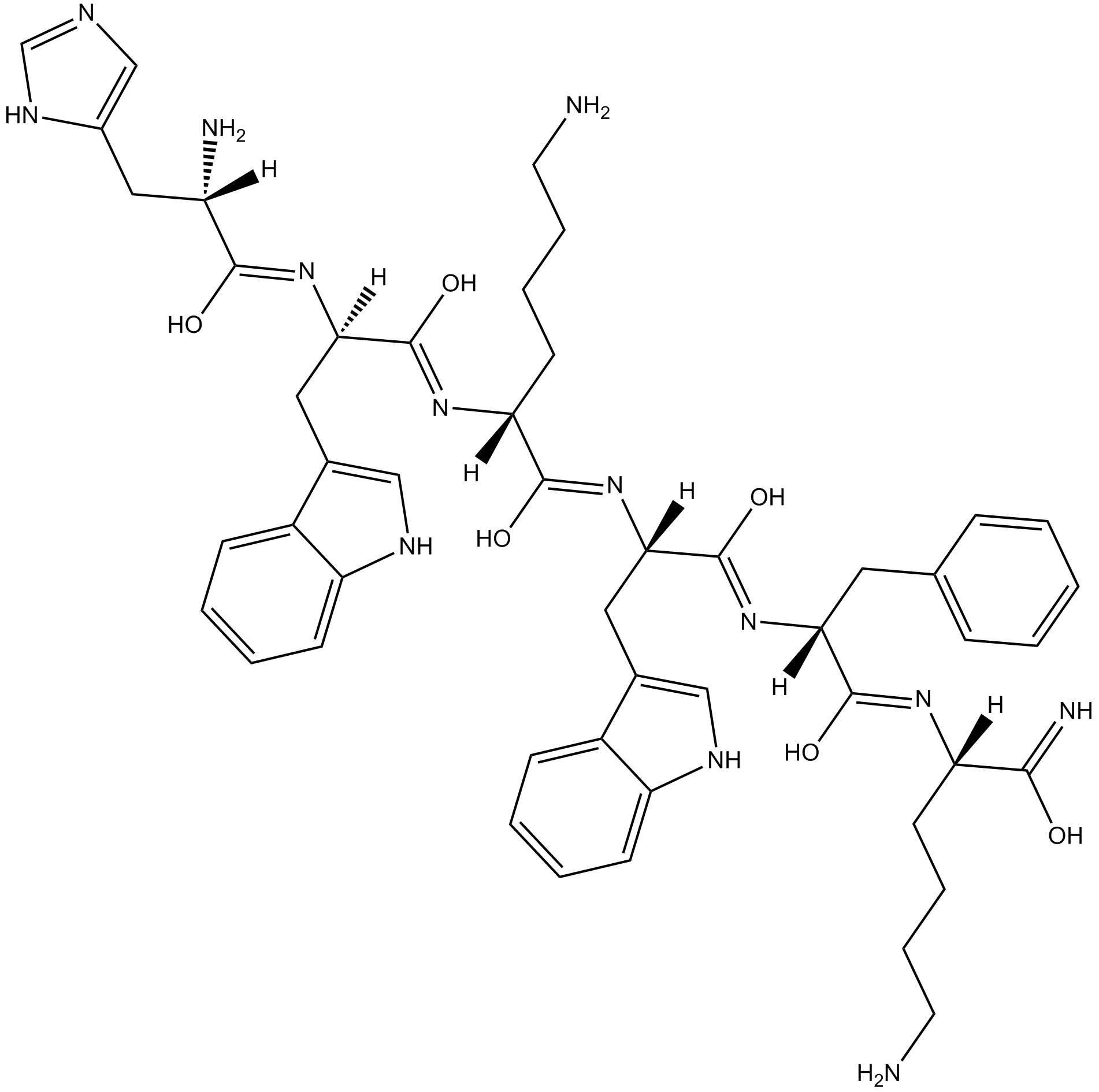
| Canonical SMILES | NCCCC[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@](N)([H])CC1=CN=CN1)([H])CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C23)([H])CCCCN)([H])CC4=CNC5=CC=CC=C45)([H])CC6=CC=CC=C6)([H])C(O)=N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
![[D-Lys3]-GHRP-6](/media/diy/images/struct/B5234.png)
Related Biological Data
![[D-Lys3]-GHRP-6 [D-Lys3]-GHRP-6](/media/diy/images/wb/B5234_1.jpg)
Related Biological Data
![[D-Lys3]-GHRP-6 [D-Lys3]-GHRP-6](/media/diy/images/wb/B5234_2.jpg)