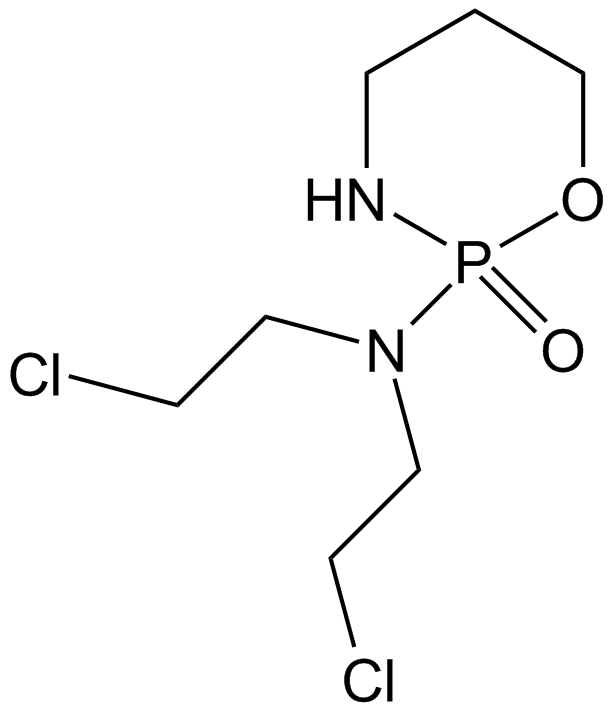
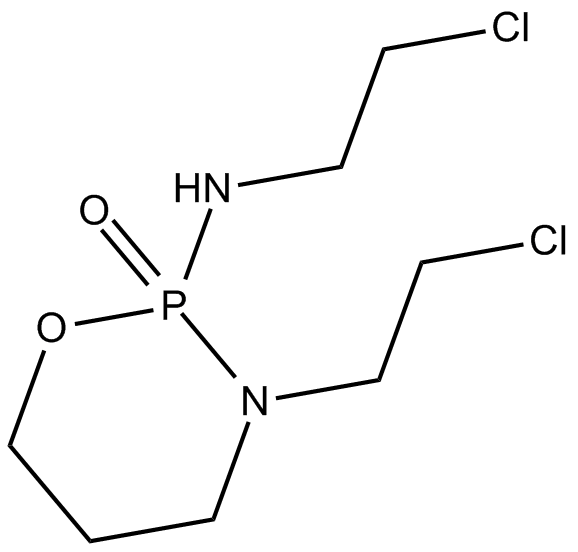
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CAS 50-18-0) is a synthetic alkylating agent, structurally related to nitrogen mustards, functioning as a DNA cross-linking cytotoxic compound in proliferating cells and exhibiting immunosuppressive activity in various immune cell populations. Additionally, it undergoes hepatic bioactivation to generate active metabolites that promote its antineoplastic effects.
In preclinical and clinical studies, Cyclophosphamide induces apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation with significant cytotoxic effects, tested against a range of human cancer cell lines and animal models. It can also suppress both humoral and cellular immune responses by interfering with lymphocyte function and survival.
In research and clinical contexts, Cyclophosphamide is widely used for the treatment of malignant neoplasms, including lymphomas, leukemias, multiple myeloma, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer, as well as for conditioning regimens in bone marrow transplantation. It is also a recognized agent in the management of certain autoimmune diseases due to its potent immunomodulatory properties. Cyclophosphamide’s broad application highlights its importance as a cornerstone in both oncology and immunology research and therapy.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 261.09 |
| Cas No. | 50-18-0 |
| Formula | C7H15Cl2N2O2P |
| Synonyms | NSC 26271; Endoxan; Cytoxan; Neosar; Procytox; Revimmune; Cytophosphane |
| Solubility | ≥11.85 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥13.05 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥50.8 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)-2-oxo-1,3,2λ5-oxazaphosphinan-2-amine |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=P1(N(CCCl)CCCl)OCCCN1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
9L gliosarcoma cells retrovirally transduced with CYP2B6 |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1 mM cyclophosphamide for 48 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Cyclophosphamide was shown to cause tumor cell death by stimulating apoptosis, as evidenced by the induction of plasma membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, and cleavage of the caspase 3 and caspase 7 substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in drug-treated cells. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Female C57BL/6 mice, 8 weeks of age |
|
Dosage form |
2 mg Injected intraperitoneally |
|
Applications |
Low-dose cyclophosphamide not only decreased the number of regulatory T cells (TREGs), but also led to decreased functionality of TREGs. Cyclophosphamide treatment enhanced apoptosis and decreased homeostatic proliferation of these cells. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Schwartz PS, Waxman DJ. Cyclophosphamide induces caspase 9-dependent apoptosis in 9L tumor cells. Molecular Pharmacology, 2001, 60(6): 1268-1279. 2. Lutsiak ME, Semnani RT, De Pascalis R, et al. Inhibition of CD4(+)25+ T regulatory cell function implicated in enhanced immune response by low-dose cyclophosphamide. Blood, 2005, 105(7): 2862-2868. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure