Metabolism
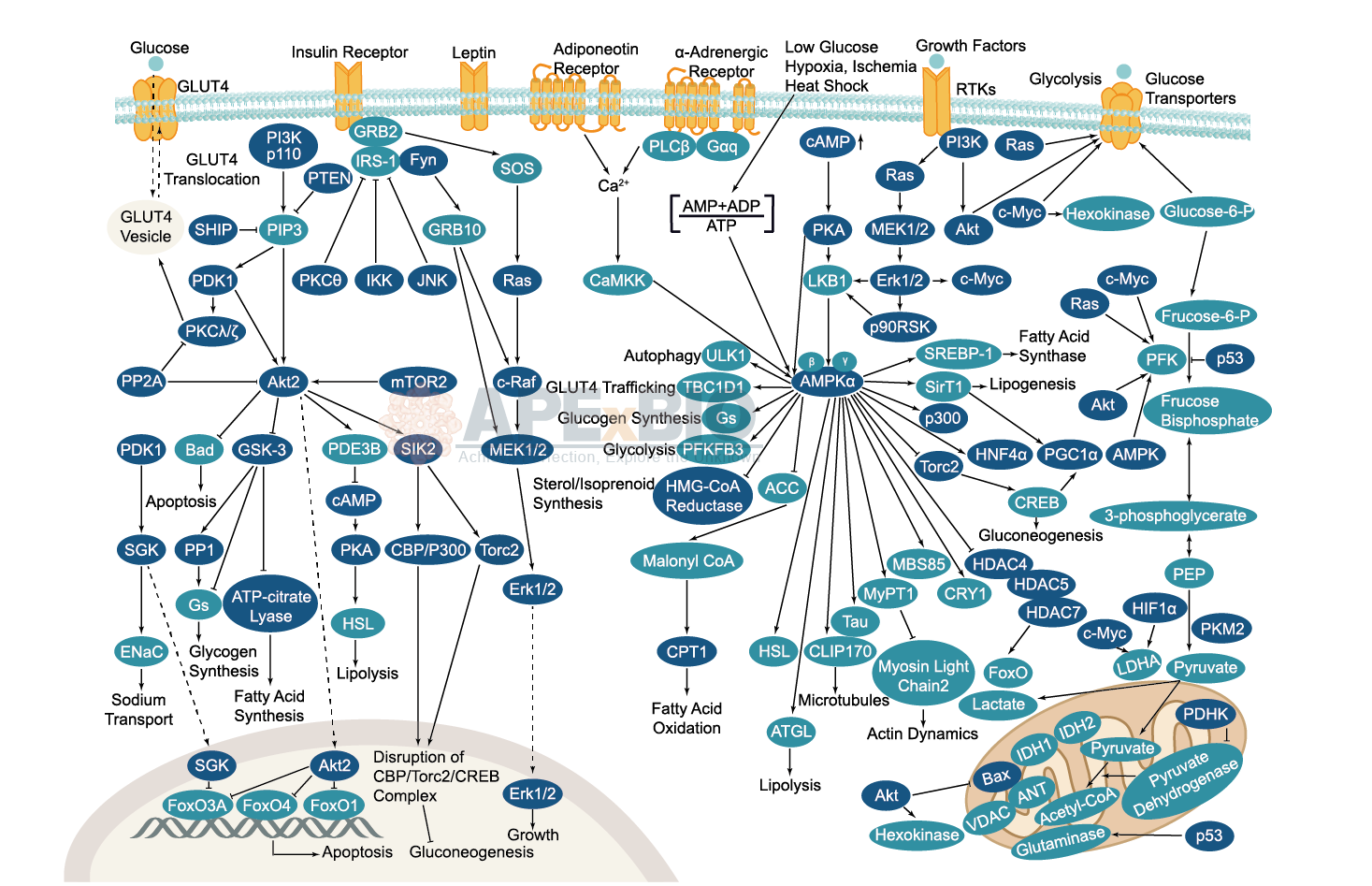

Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
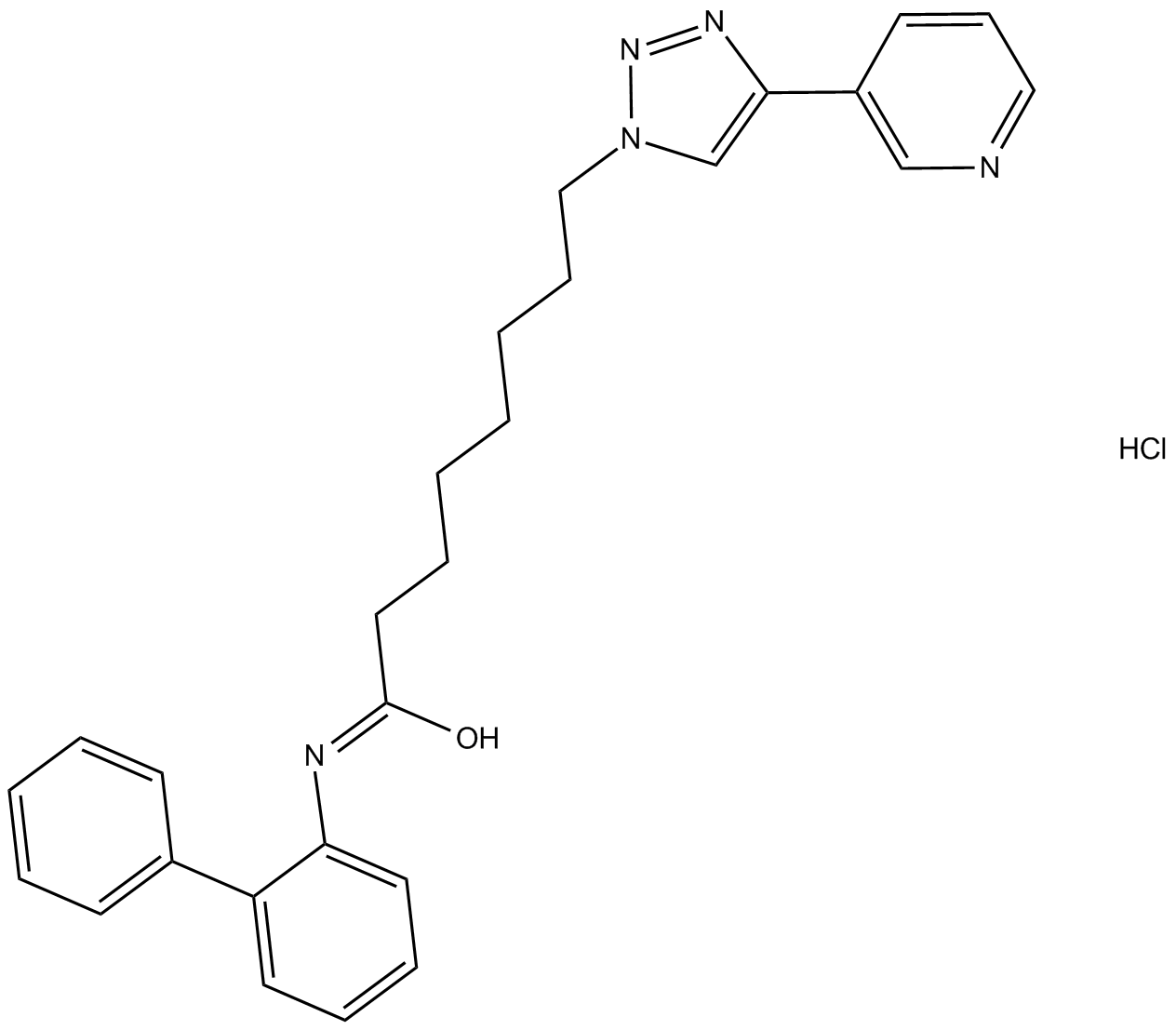 B5729 GPP 78 hydrochlorideSummary: NAMPT inhibitor
B5729 GPP 78 hydrochlorideSummary: NAMPT inhibitor -
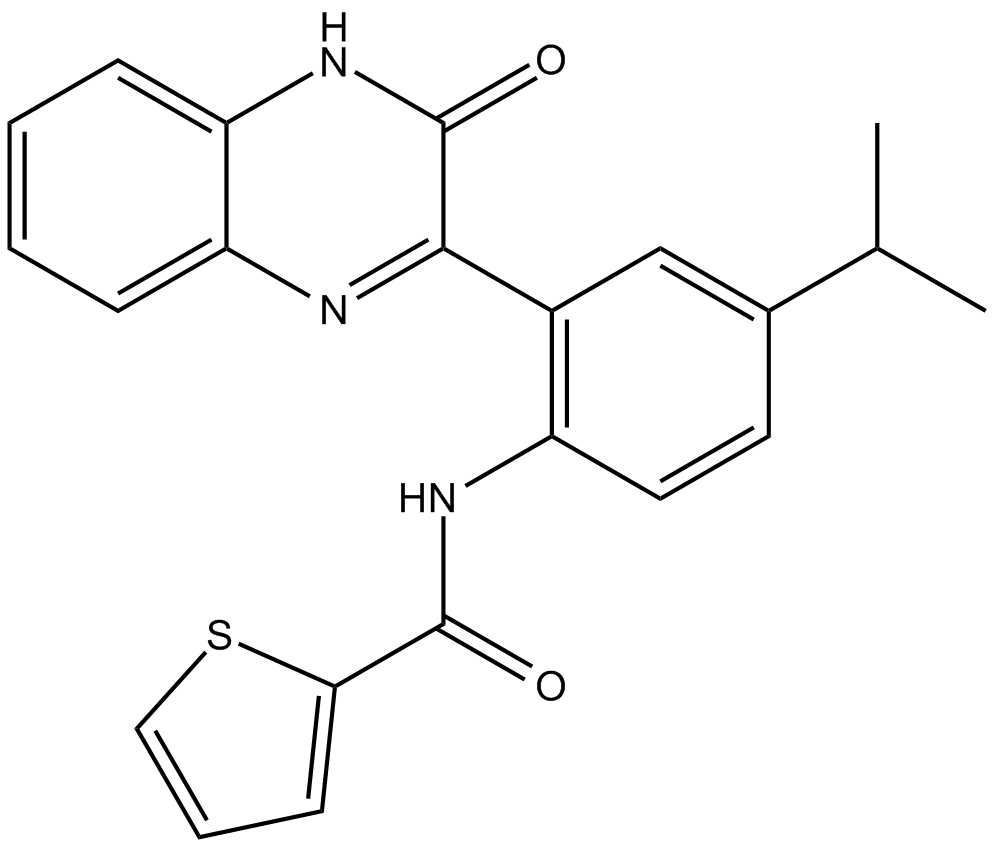 B5750 ML 281Target: STKSummary: serine/threonine kinase STK33 inhibitor
B5750 ML 281Target: STKSummary: serine/threonine kinase STK33 inhibitor -
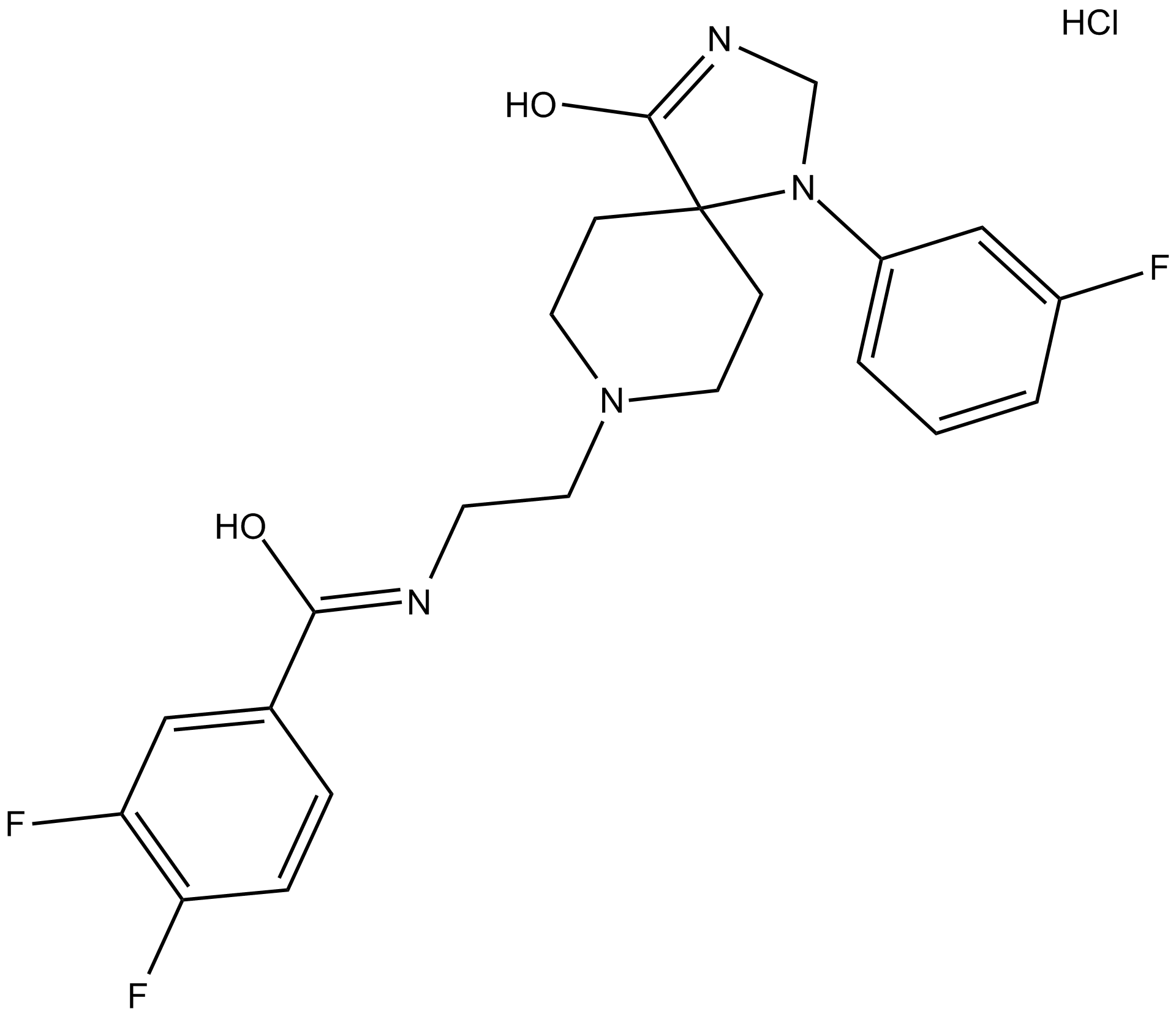 B5754 ML 298 hydrochlorideSummary: phospholipase D2 (PLD2) inhibitor
B5754 ML 298 hydrochlorideSummary: phospholipase D2 (PLD2) inhibitor -
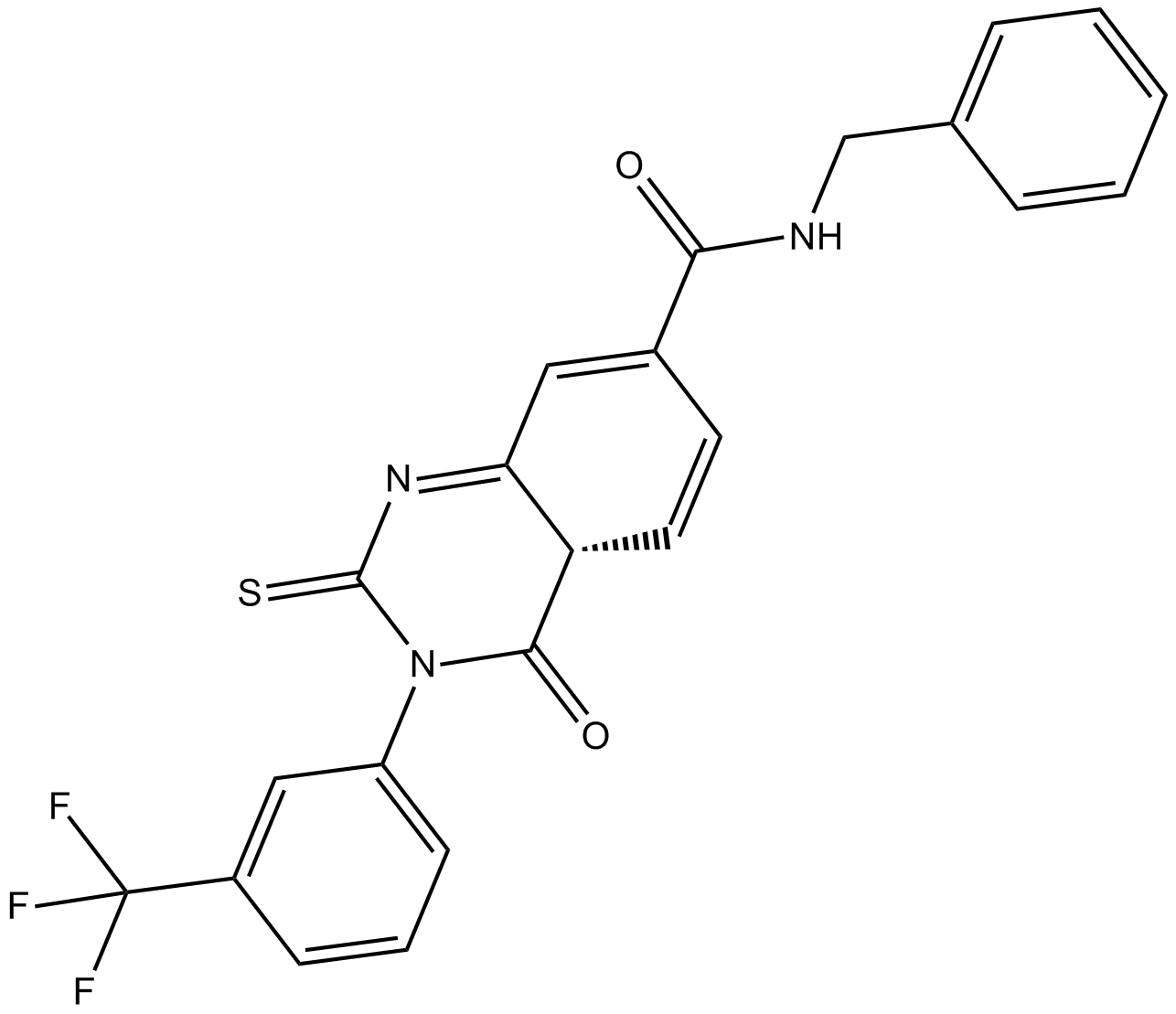 B5799 Qc 1Summary: threonine dehydrogenase (TDH) inhibitor
B5799 Qc 1Summary: threonine dehydrogenase (TDH) inhibitor -
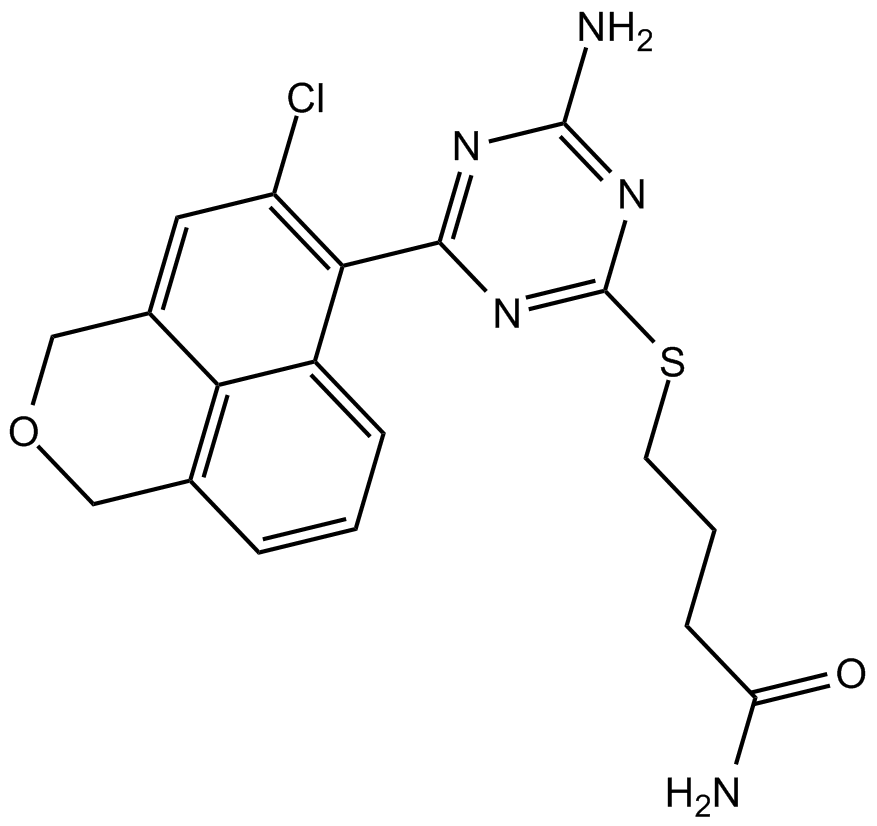 B4571 CH5138303Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, orally available
B4571 CH5138303Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, orally available -
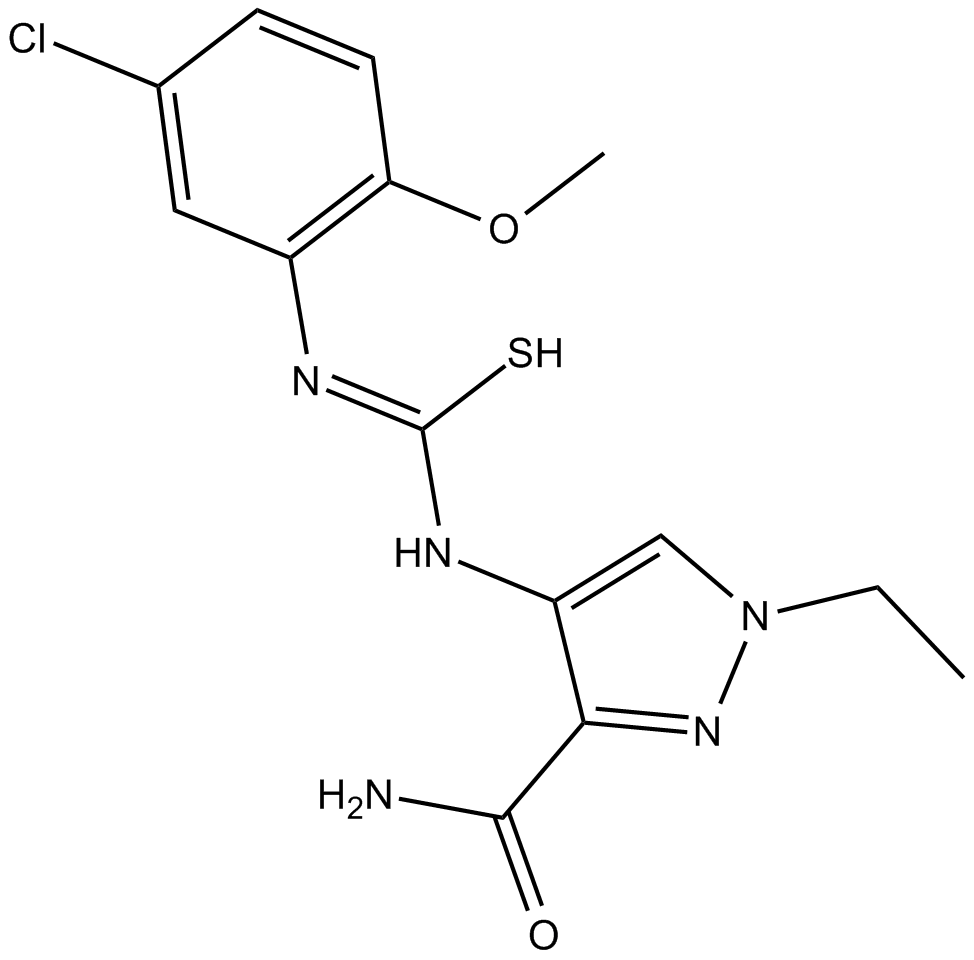 B4753 FPH2 (BRD-9424)1 CitationSummary: inducer of proliferation of primary human hepatocytes
B4753 FPH2 (BRD-9424)1 CitationSummary: inducer of proliferation of primary human hepatocytes -
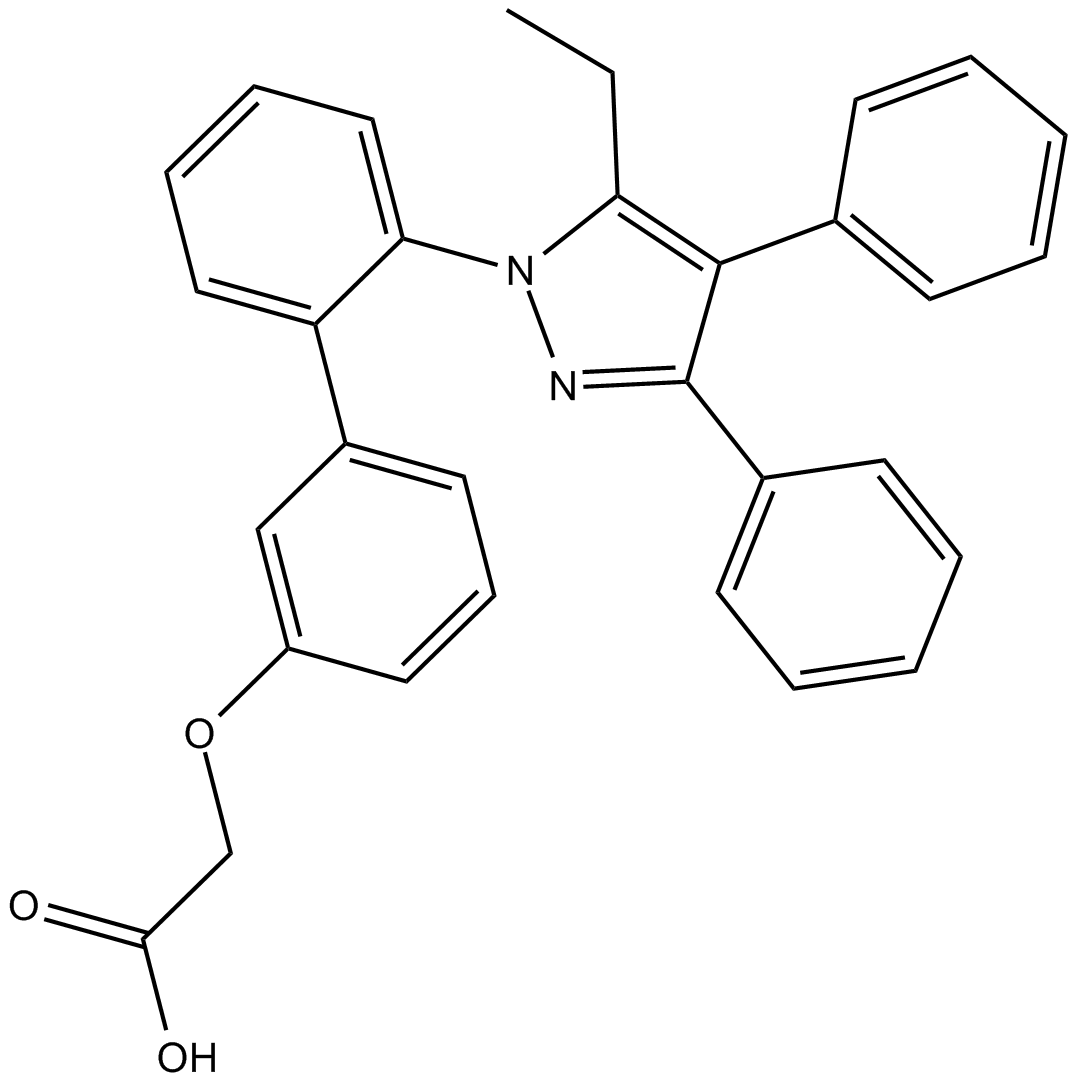 B7794 BMS 3094035 CitationTarget: Fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs)Summary: FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective
B7794 BMS 3094035 CitationTarget: Fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs)Summary: FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective -
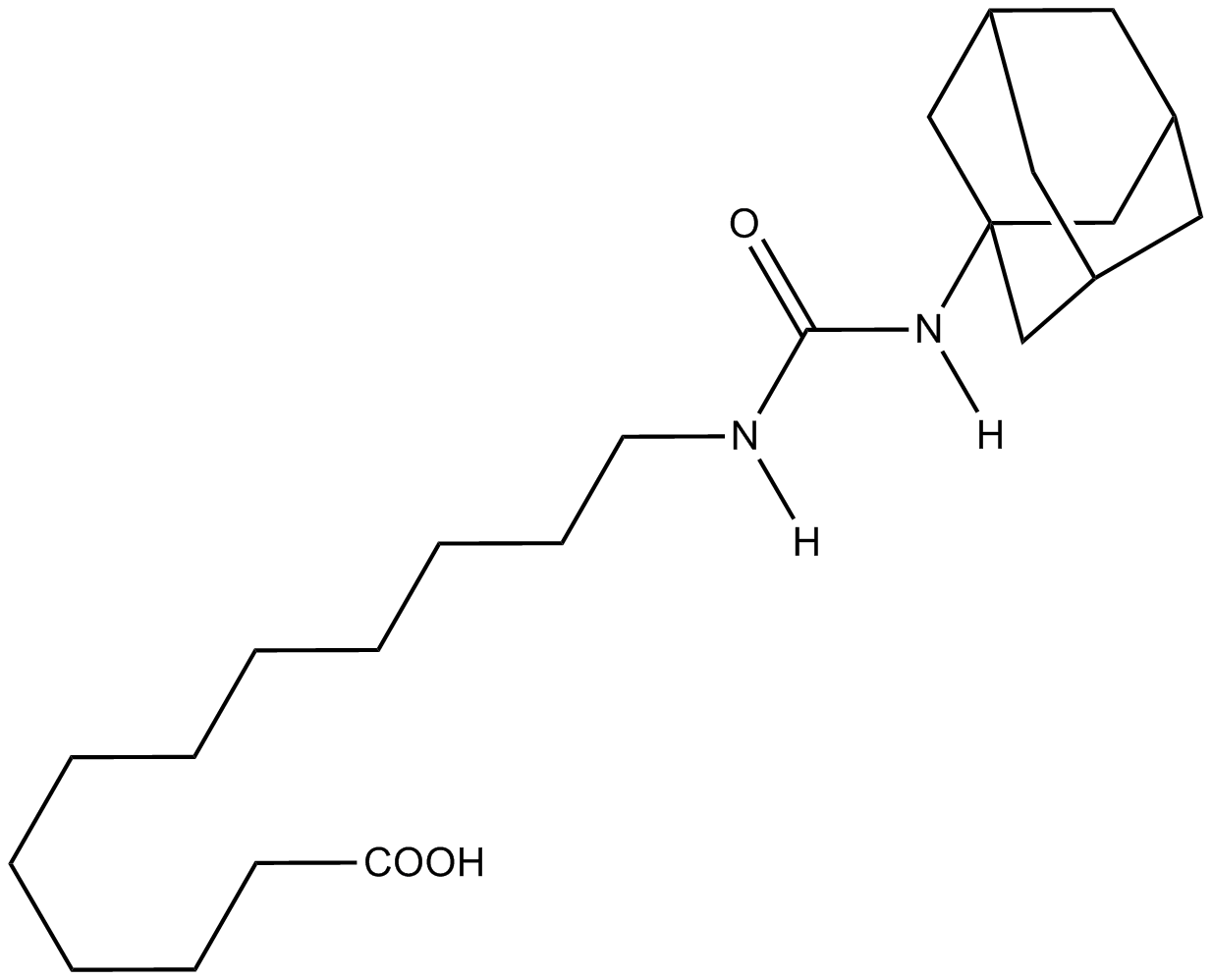 A8957 AUDASummary: Potent epoxide hydrolase inhibitor/PPARα activator
A8957 AUDASummary: Potent epoxide hydrolase inhibitor/PPARα activator -
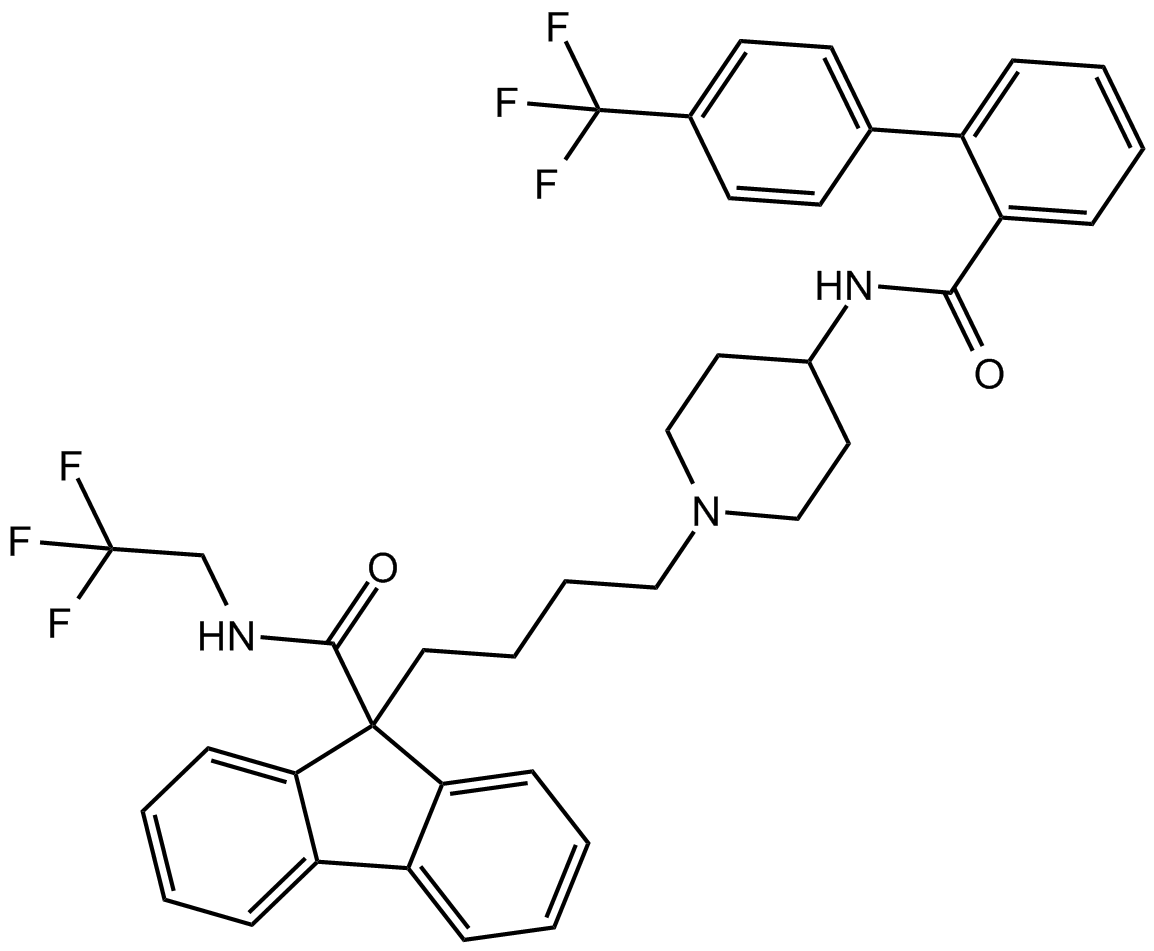 B4885 LomitapideSummary: MTP inhibitor, orally active
B4885 LomitapideSummary: MTP inhibitor, orally active -
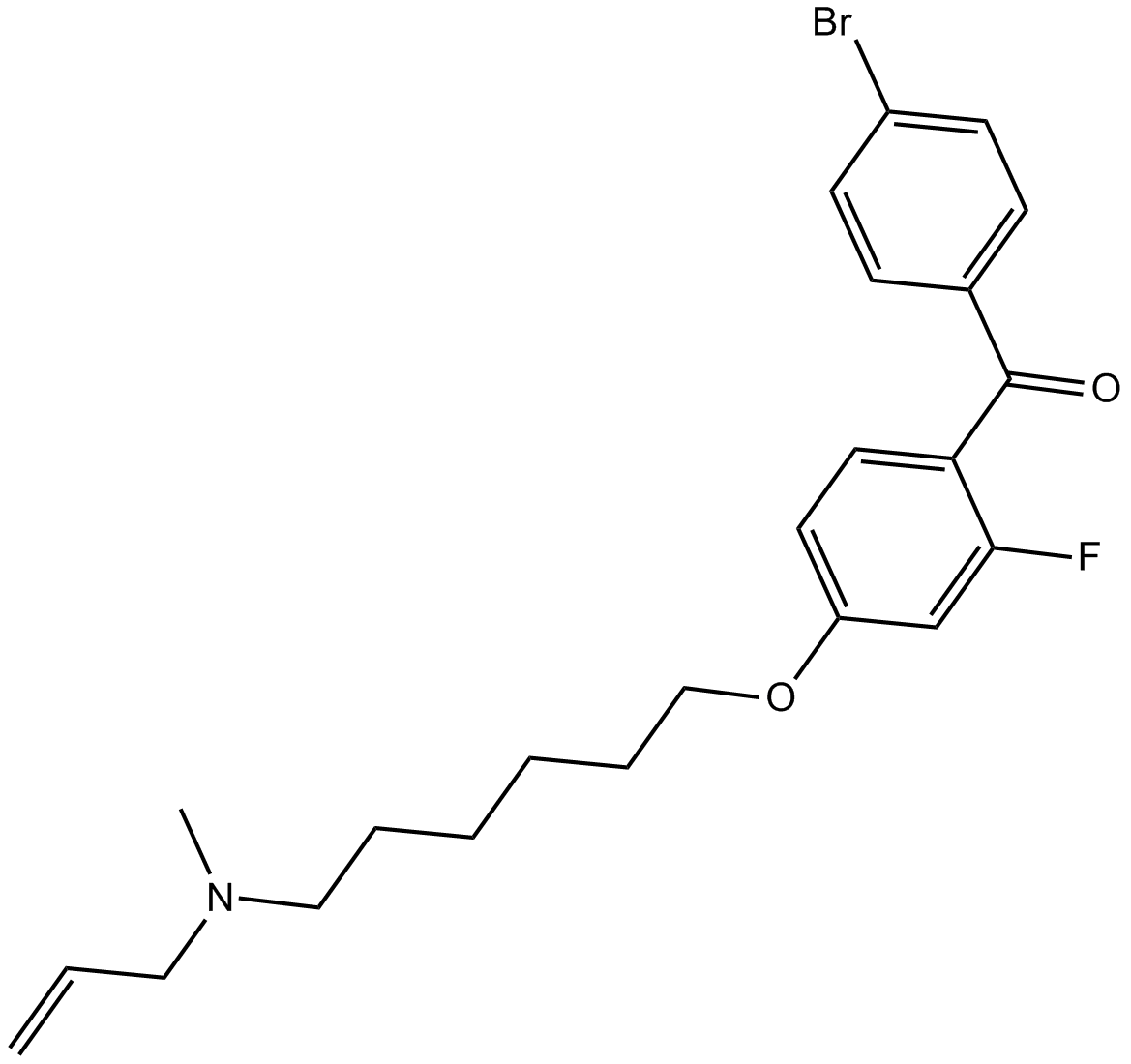 B4859 Ro 48-8071Summary: Oxidosqualene cyclase inhibitor
B4859 Ro 48-8071Summary: Oxidosqualene cyclase inhibitor


