Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel


Membrane Transporters mediate the movement of ions and molecules via binding and moving the substance across the membrane. There are two main actions of transporter: facilitated diffusion (passive transport) and active transport. Membrane transporters which bind the hydrolysis of ATP to the transport of target molecules are referred to as ATPases. For instance, Na+,K+-ATPases or Na+,K+-pumps are responsible for the transport of Na+ out of and K+ into cells.
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
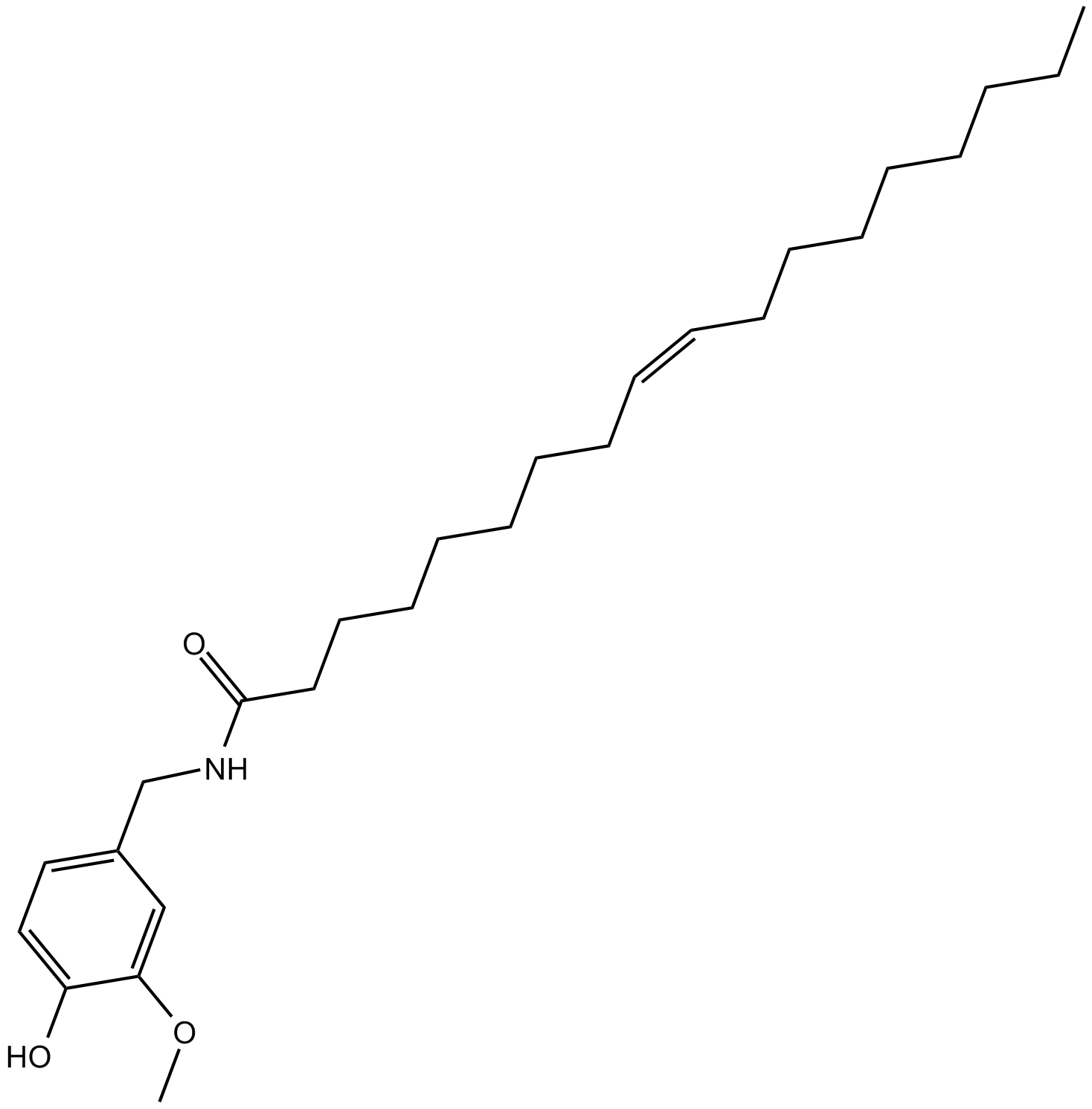 B6512 OlvanilSummary: vanilloid receptor agonist
B6512 OlvanilSummary: vanilloid receptor agonist -
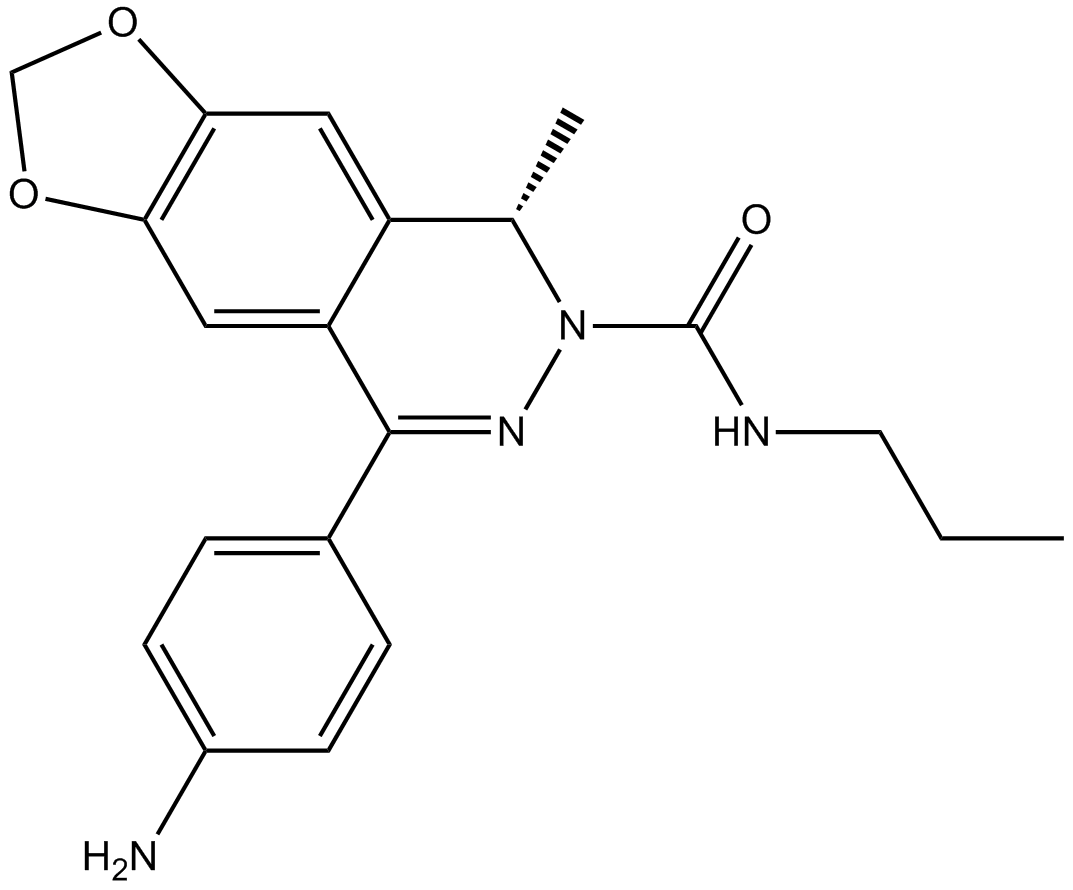 B6524 SYM 2206Summary: AMPA receptor antagonist
B6524 SYM 2206Summary: AMPA receptor antagonist -
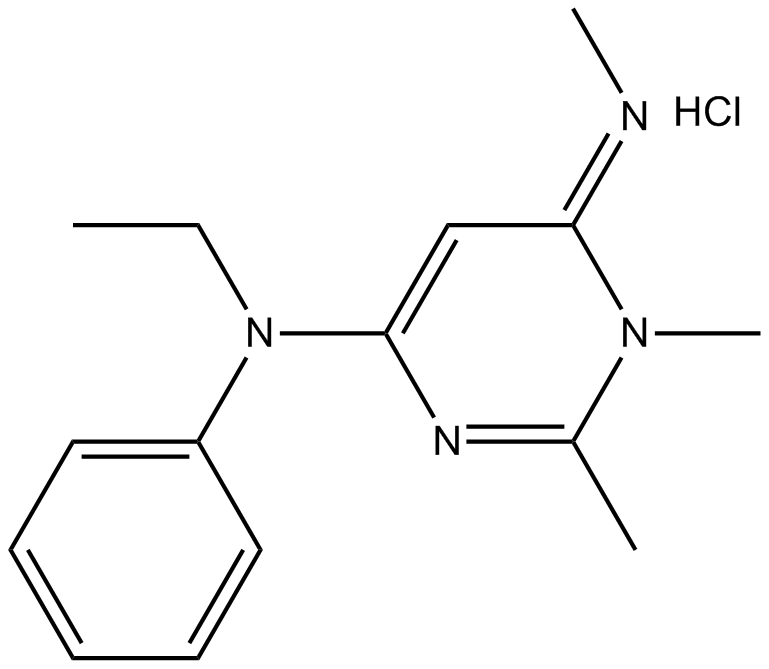 B6542 ZD 7288Summary: HCN channel inhibitor
B6542 ZD 7288Summary: HCN channel inhibitor -
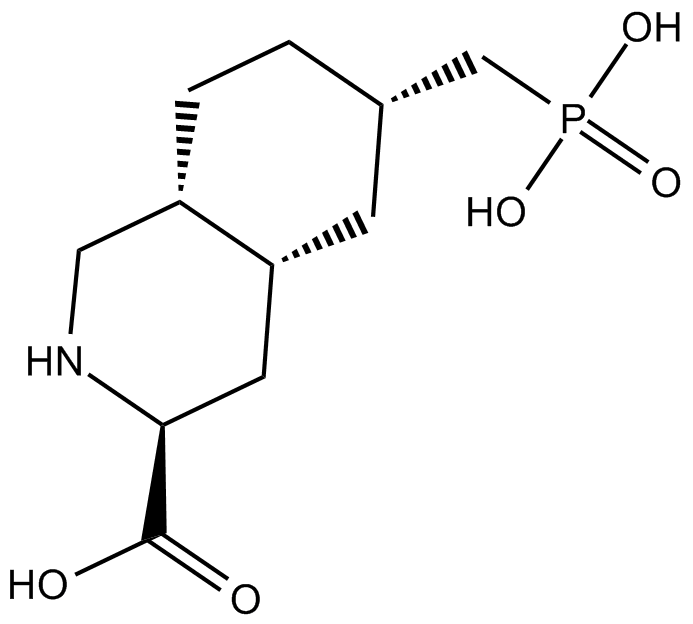 B6551 LY 235959Summary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B6551 LY 235959Summary: NMDA receptor antagonist -
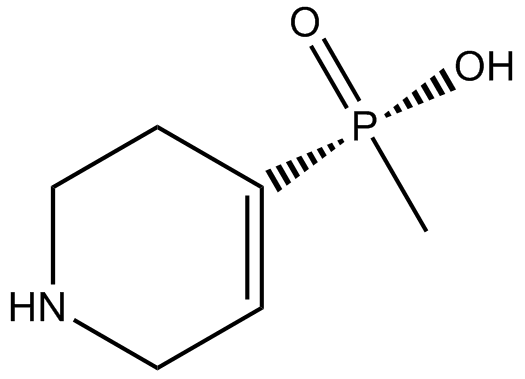 B6562 TPMPASummary: GABAA-ρ antagonist
B6562 TPMPASummary: GABAA-ρ antagonist -
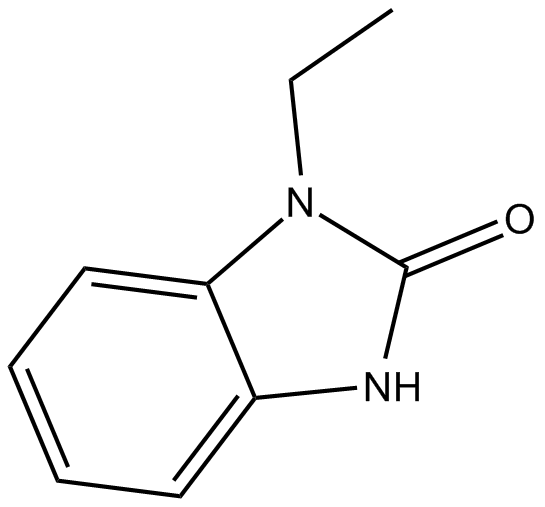 B6563 1-EBIOSummary: Activator of epithelial KCa channels
B6563 1-EBIOSummary: Activator of epithelial KCa channels -
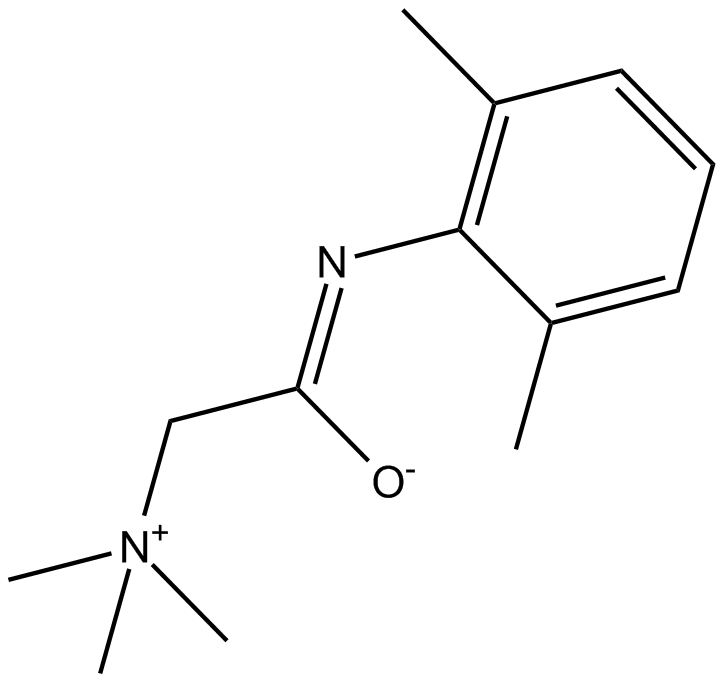 B6565 QX 222Summary: Sodium channel blocker
B6565 QX 222Summary: Sodium channel blocker -
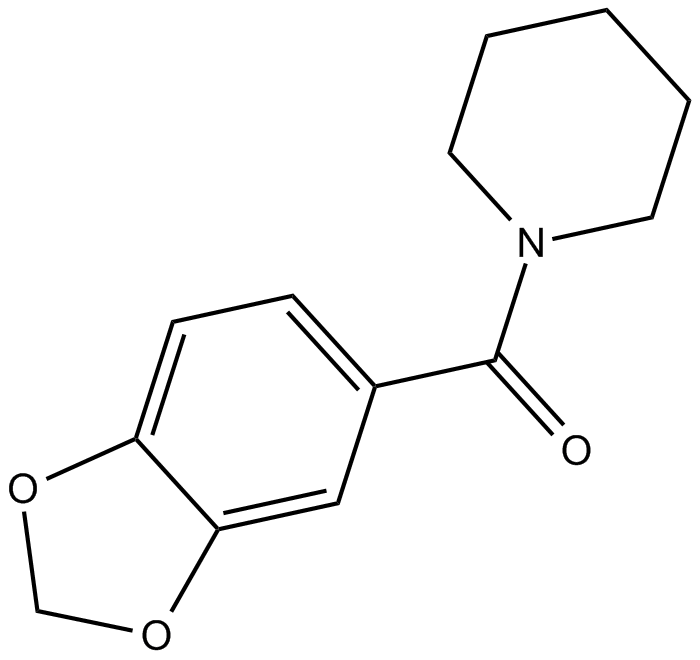 B6568 1-BCPSummary: potentiator of AMPA-mediated responses
B6568 1-BCPSummary: potentiator of AMPA-mediated responses -
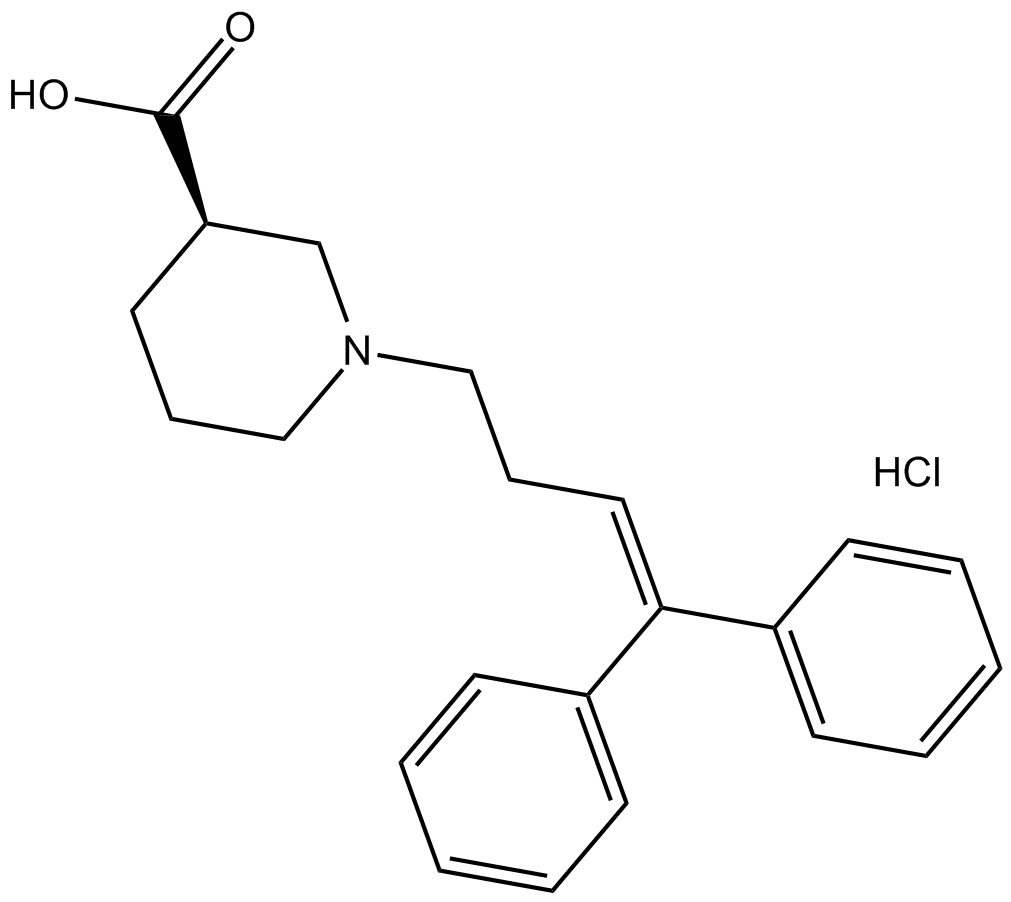 B6589 SKF 89976A hydrochlorideSummary: GABA uptake inhibitor
B6589 SKF 89976A hydrochlorideSummary: GABA uptake inhibitor -
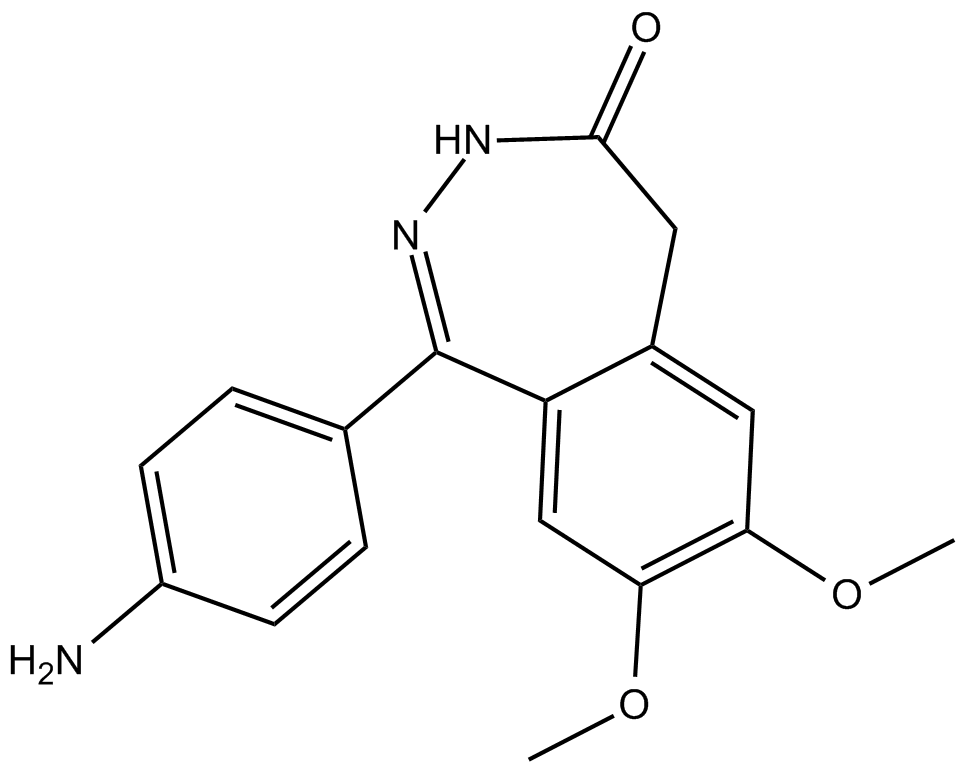 B6590 CFM-2Summary: AMPA antagonist
B6590 CFM-2Summary: AMPA antagonist


