MAPK/ERK


The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a highly conserved family of serine/threonine kinases that mediate a board range of cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, motility, migration, stress response, apoptosis and survival. The activation of MAPK involves signaling pathways consisting of MAPK kinase (i.e. MAPKKK or MEKK) that activates MAPK/ERK (i.e. MAPKK or MEK). A variety of extracellular signals such as mitogens, cytokines, growth factors, and environmental stressors stimulate a phosphorylation-dependent increase in the activity of MAPK.
Activated MAPKs transduce the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs), e.g. RSK, MSK, or MNK family, and MK2/3/5. There are three main MAPK families, signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (Erk1/2 or p44/42), the c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1-3 (JNK1-3)/ stress activated protein kinases (SAPK1A, 1B, 1C), the p38 isoforms (p38α, β, γ, and δ). ERK signaling is involved in cell division, migration and survival. p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK pathways are activated by cellular stress. The p38 MAPK pathway regulates cell motility, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. JNK/SAPK signaling affects apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MAPK pathway results in tumorgenesis and other pathological conditions.
-
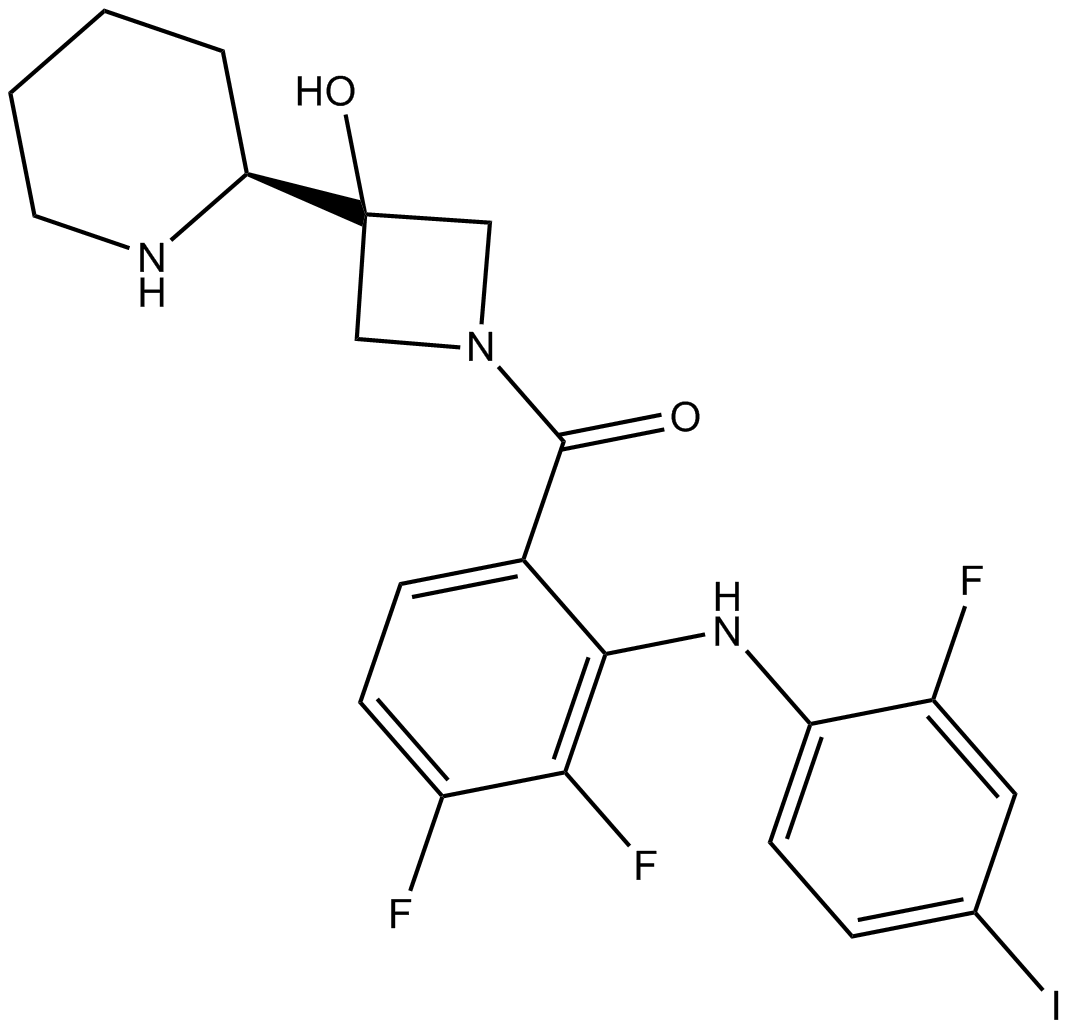 A3321 Cobimetinib3 CitationSummary: Selective MEK inhibitor
A3321 Cobimetinib3 CitationSummary: Selective MEK inhibitor -
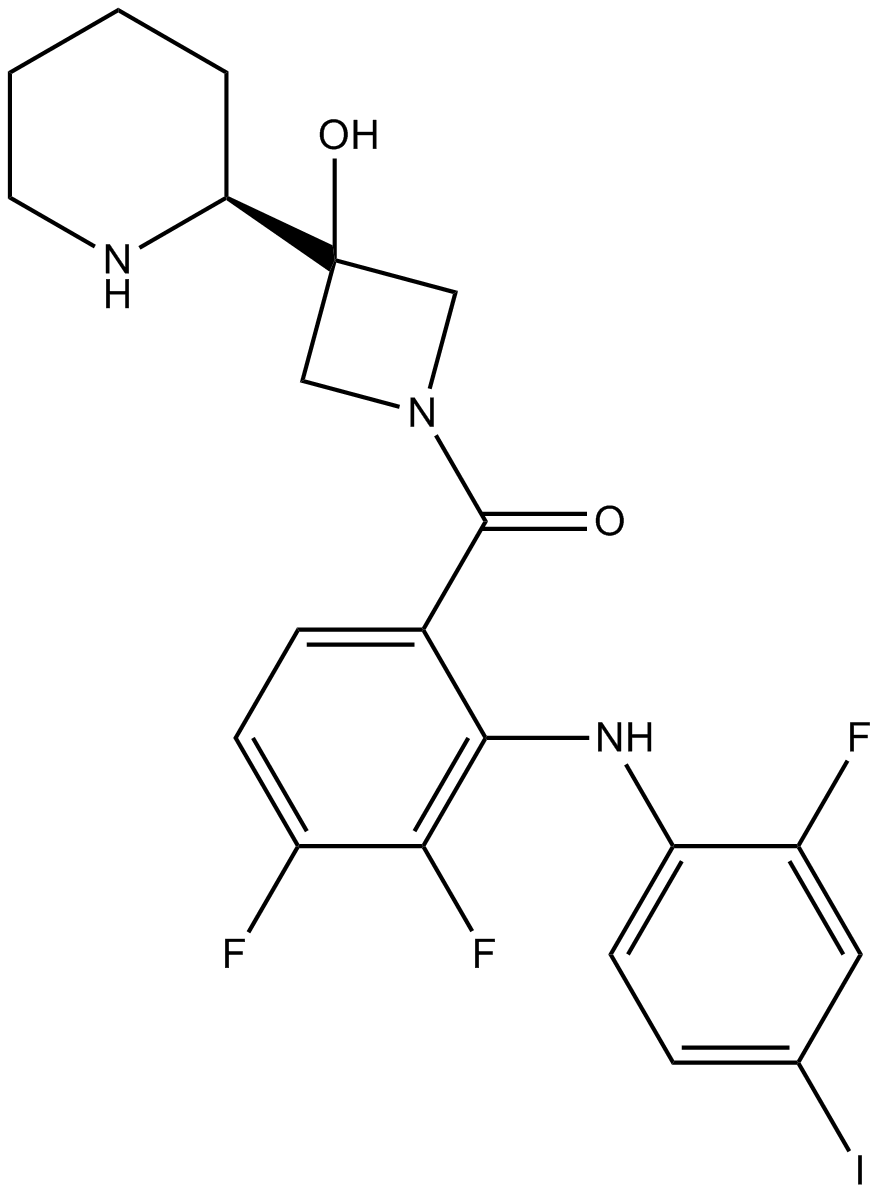 A3322 Cobimetinib (racemate)Summary: Selective MEK inhibitor
A3322 Cobimetinib (racemate)Summary: Selective MEK inhibitor -
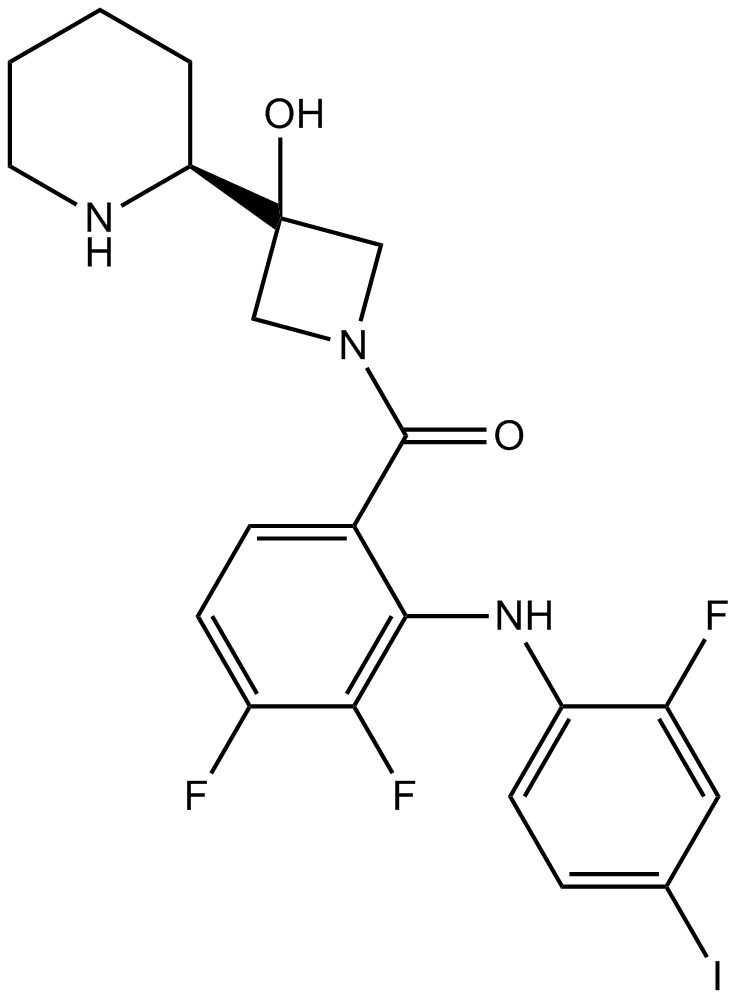 A3323 Cobimetinib (R-enantiomer)Summary: Selective MEK inhibitor
A3323 Cobimetinib (R-enantiomer)Summary: Selective MEK inhibitor -
 A3347 Dabrafenib Mesylate (GSK-2118436)Target: RafSummary: Inhibitor of BRAF(V600) mutants
A3347 Dabrafenib Mesylate (GSK-2118436)Target: RafSummary: Inhibitor of BRAF(V600) mutants -
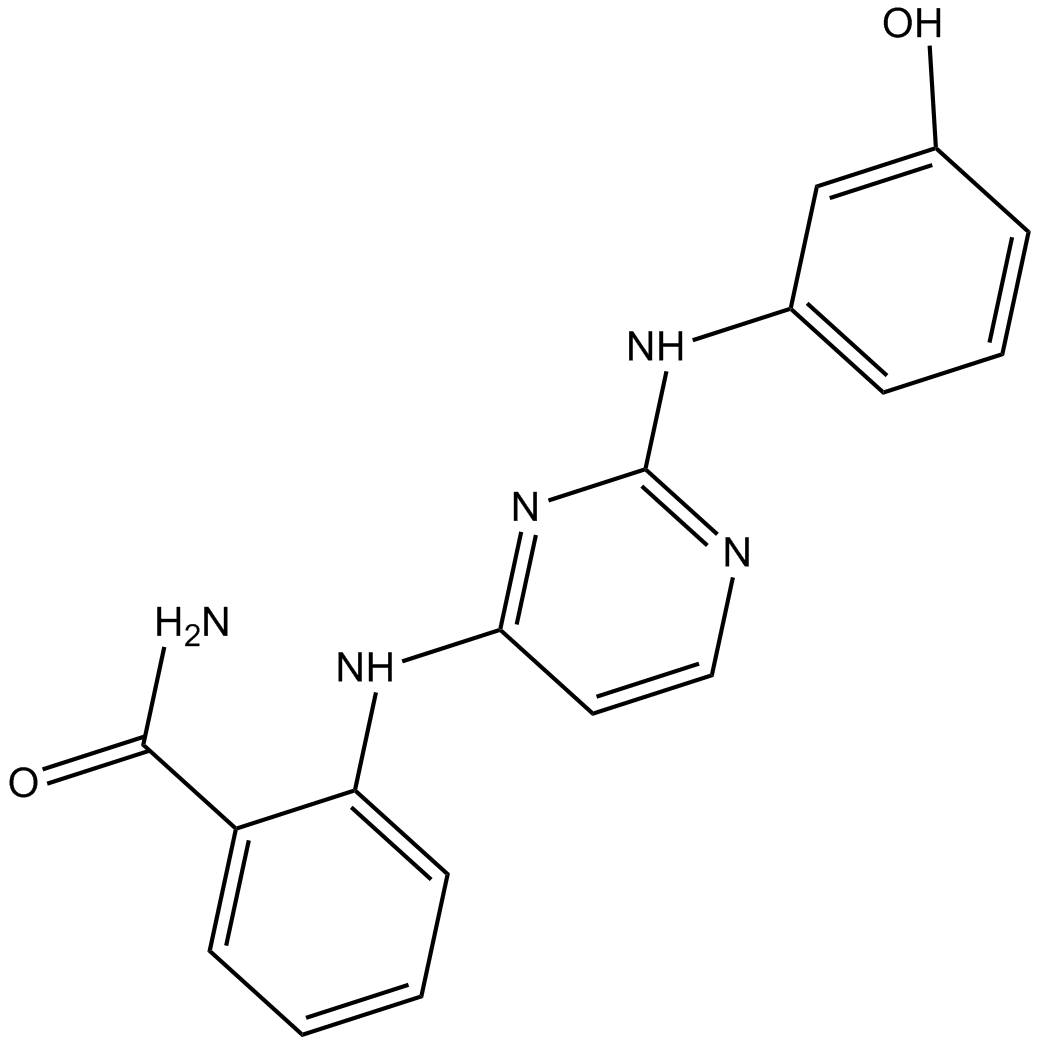 A3353 DB07268Summary: JNK1 inhibitor
A3353 DB07268Summary: JNK1 inhibitor -
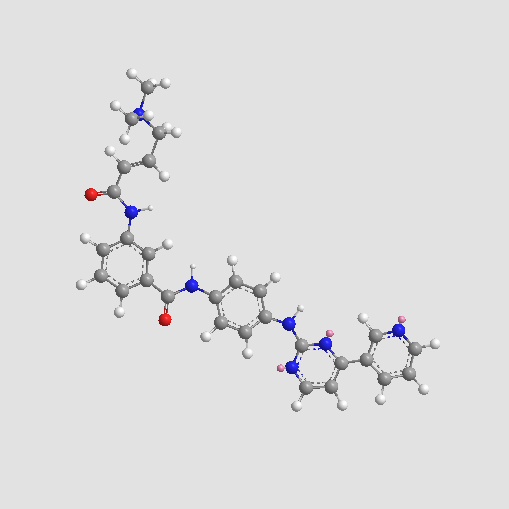 A3519 JNK-IN-7Target: JNKSummary: Selective JNK inhibitor
A3519 JNK-IN-7Target: JNKSummary: Selective JNK inhibitor -
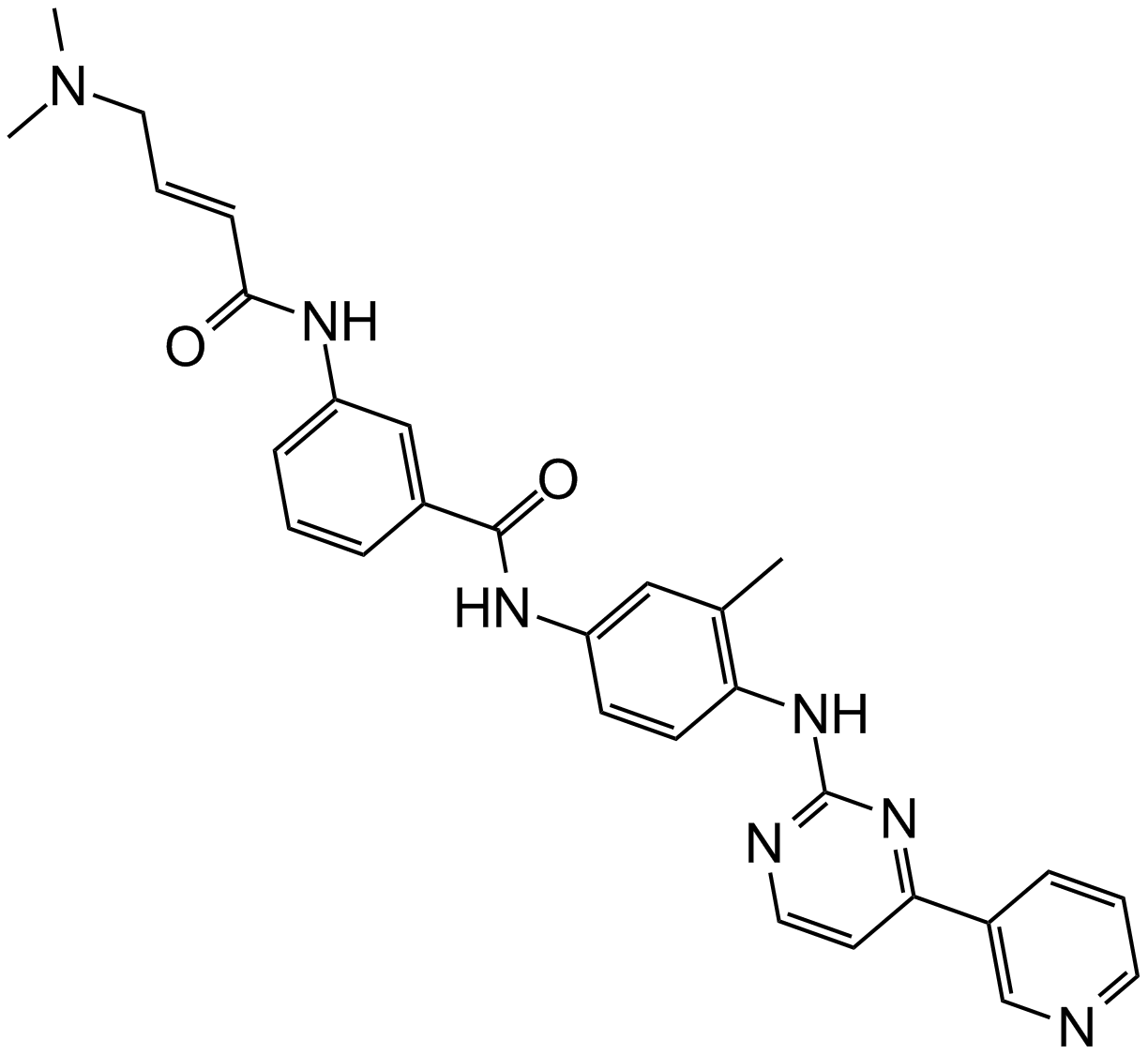 A3520 JNK-IN-8Summary: JNK inhibitor, selective and irreversible
A3520 JNK-IN-8Summary: JNK inhibitor, selective and irreversible -
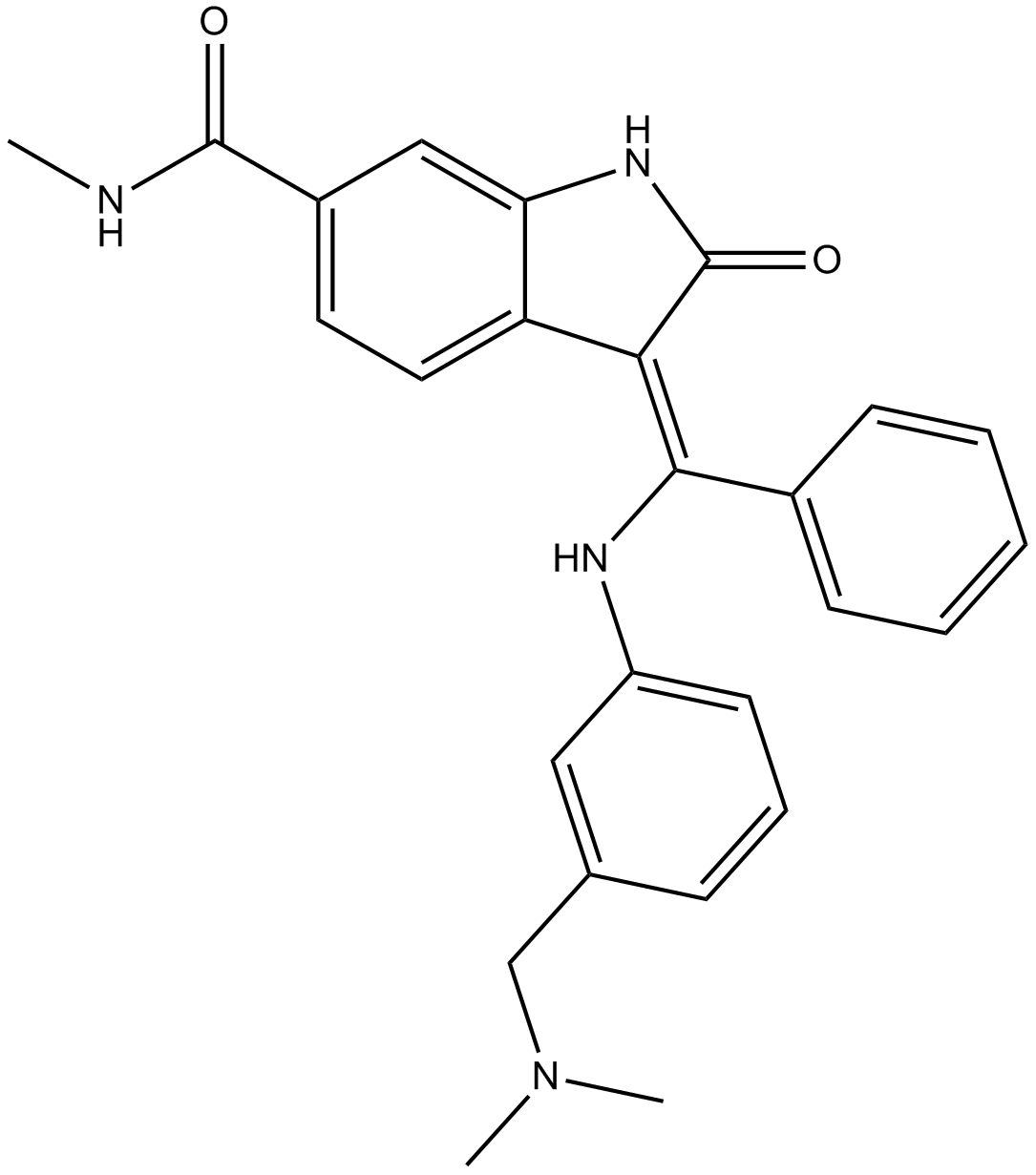 A3594 MEK inhibitorSummary: Potent MEK inhibitor, Antitumor agent
A3594 MEK inhibitorSummary: Potent MEK inhibitor, Antitumor agent -
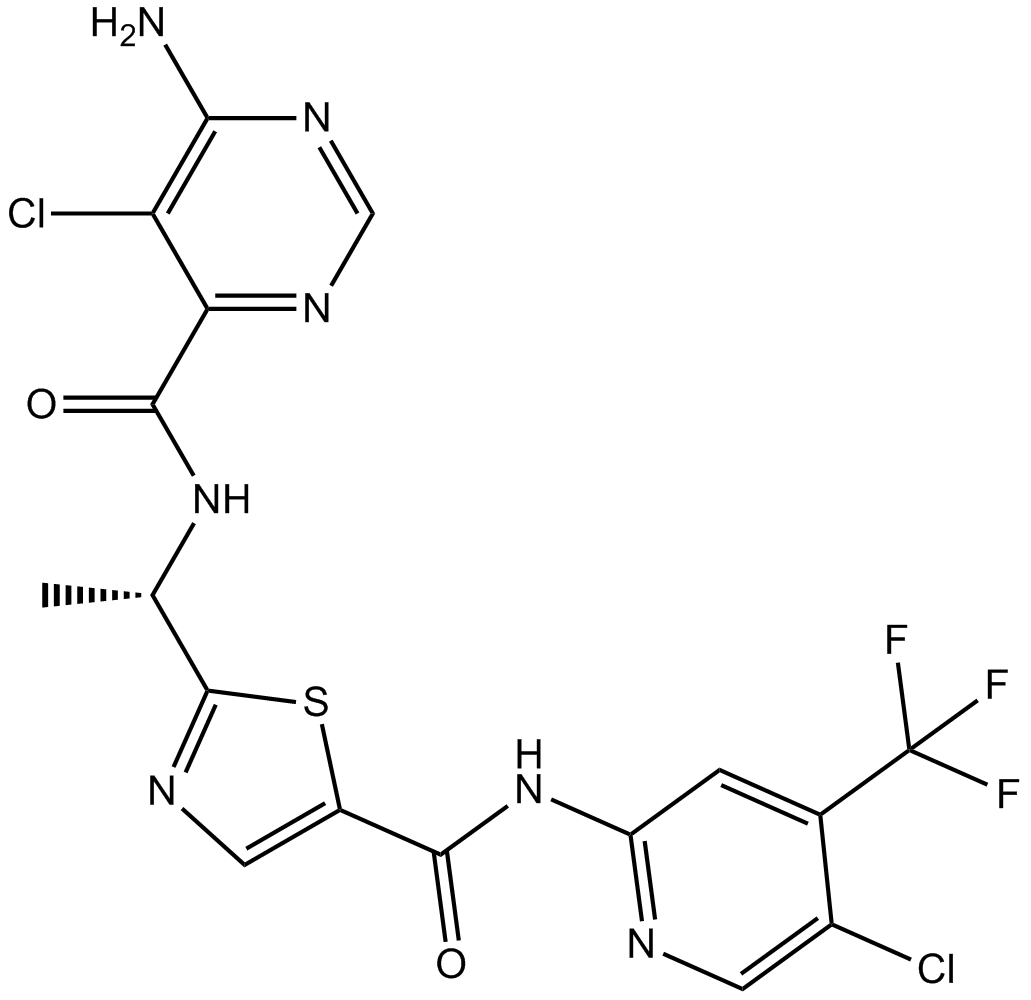 A3627 MLN 2480Summary: Pan-Raf kinase inhibitor,investigational
A3627 MLN 2480Summary: Pan-Raf kinase inhibitor,investigational -
 A3787 Salirasib2 CitationSummary: Inhibitor of active Ras protein
A3787 Salirasib2 CitationSummary: Inhibitor of active Ras protein


