Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
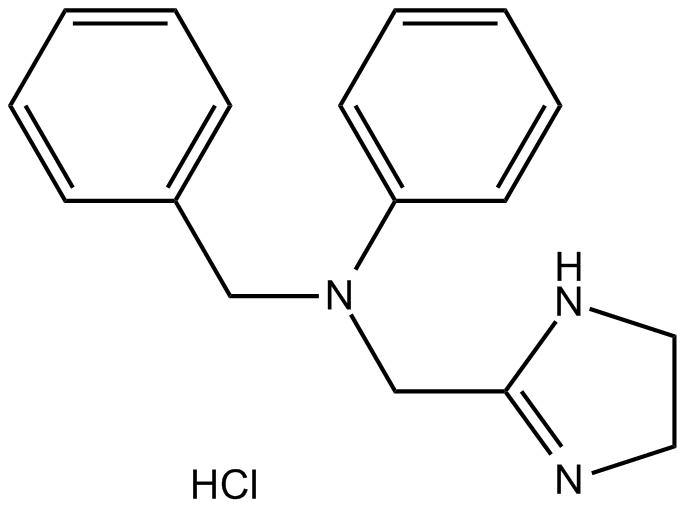 B1664 Antazoline HClSummary: Histamine receptor inhibitor
B1664 Antazoline HClSummary: Histamine receptor inhibitor -
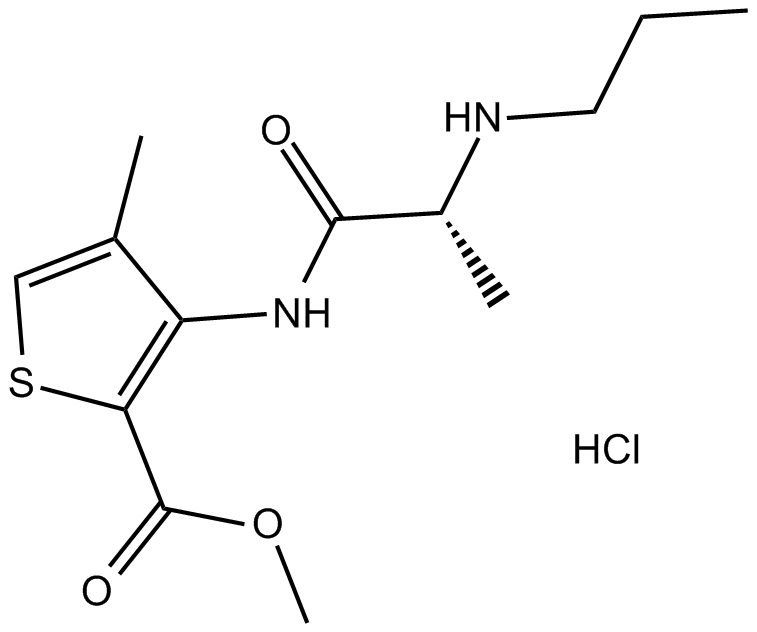 B1887 Articaine HClSummary: dental local anesthetic
B1887 Articaine HClSummary: dental local anesthetic -
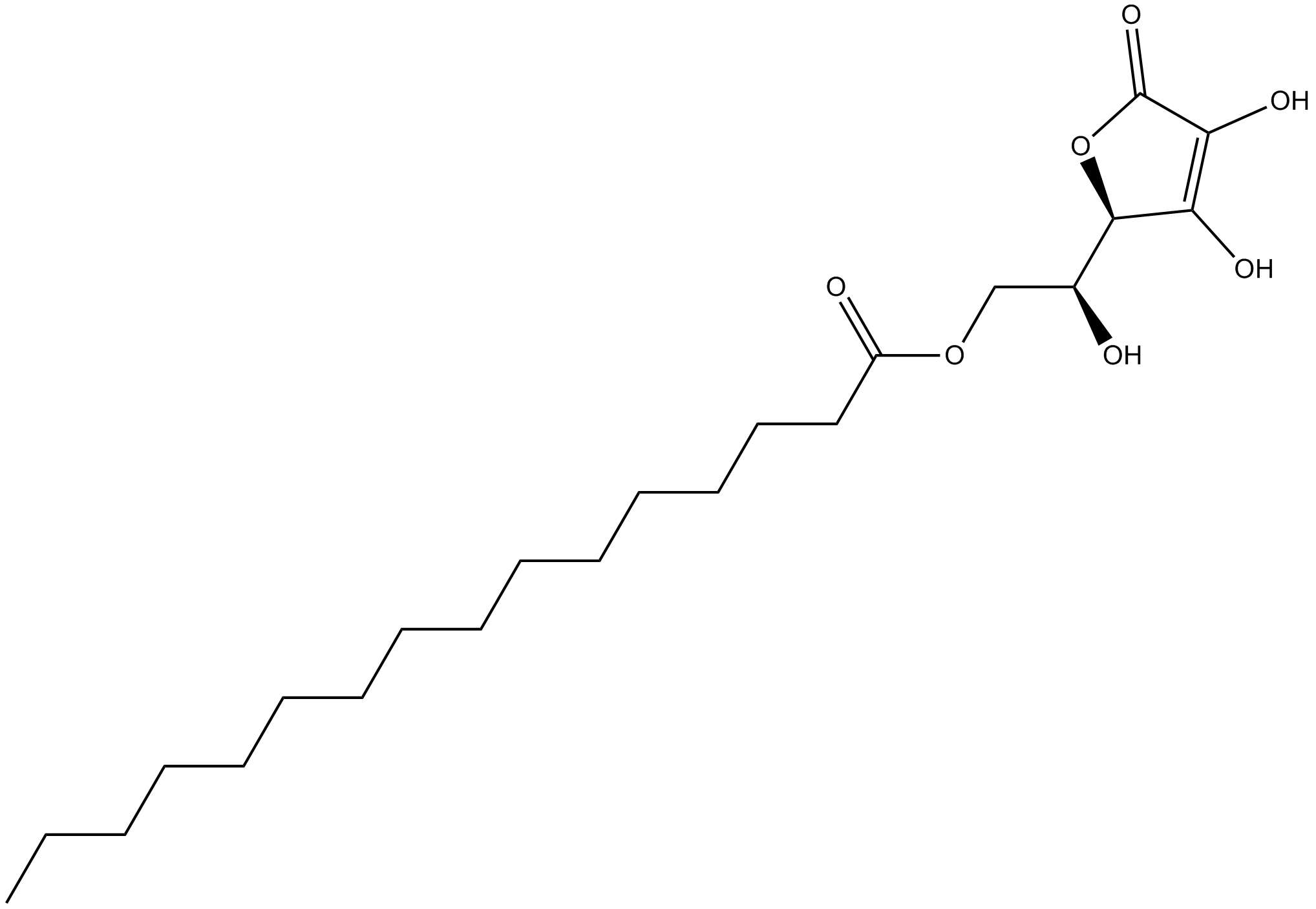 B2105 L-Ascorbyl 6-palmitateSummary: synthetic lipophilic ascorbic acid derivative
B2105 L-Ascorbyl 6-palmitateSummary: synthetic lipophilic ascorbic acid derivative -
 B1891 AzacyclonolSummary: tranquilizer,antipsychotic
B1891 AzacyclonolSummary: tranquilizer,antipsychotic -
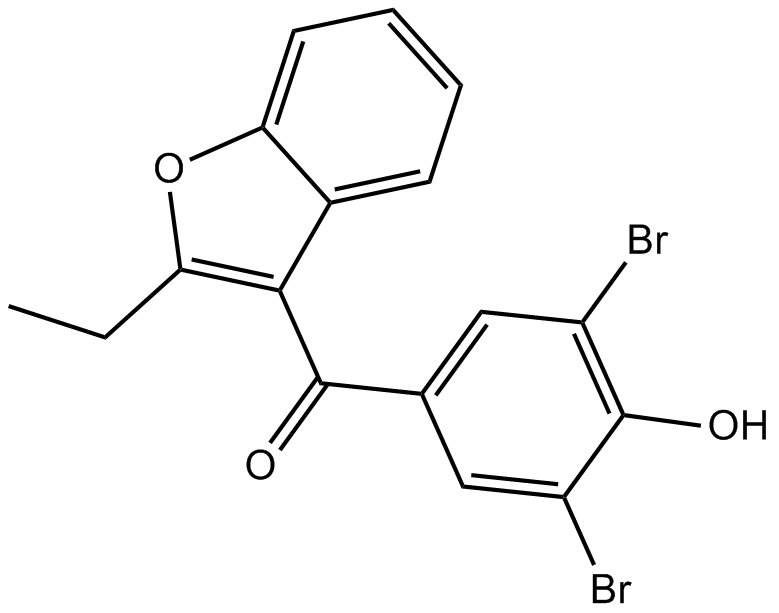 B1673 BenzbromaroneSummary: TMEM16A/B calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) blocker
B1673 BenzbromaroneSummary: TMEM16A/B calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) blocker -
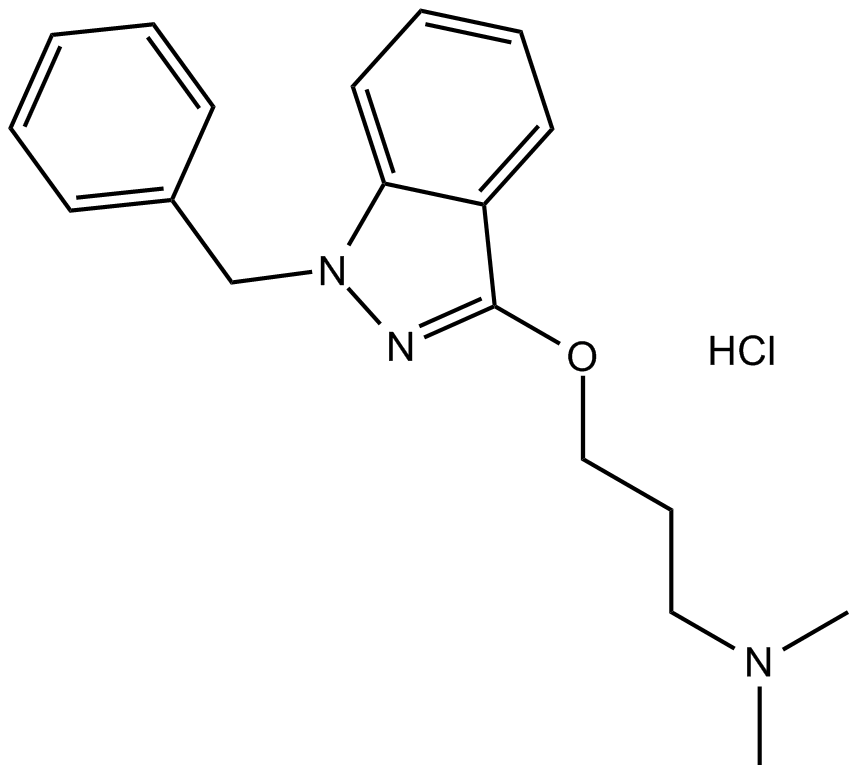 B1677 Benzydamine HClSummary: Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
B1677 Benzydamine HClSummary: Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) -
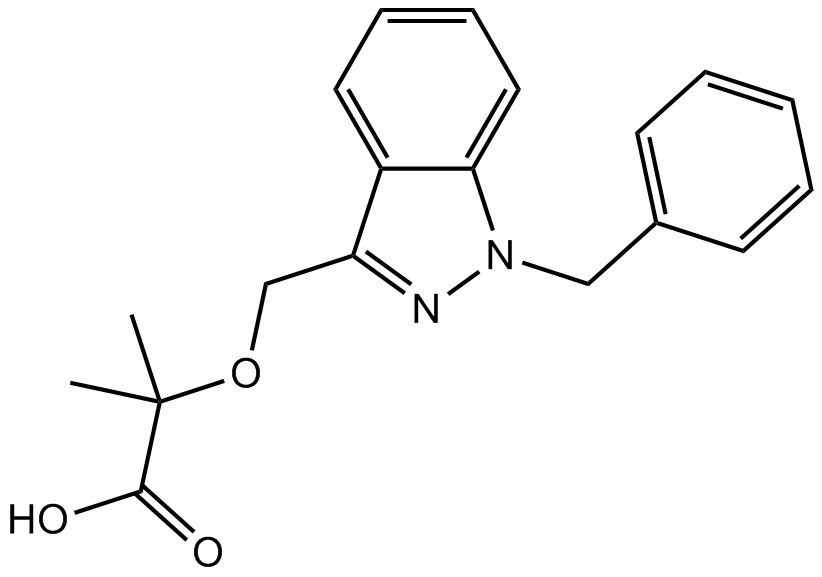 B2156 BindaritTarget: Monocyte chemotactic proteinsSummary: CCL2, CCL7 and CCL8 inhibitor
B2156 BindaritTarget: Monocyte chemotactic proteinsSummary: CCL2, CCL7 and CCL8 inhibitor -
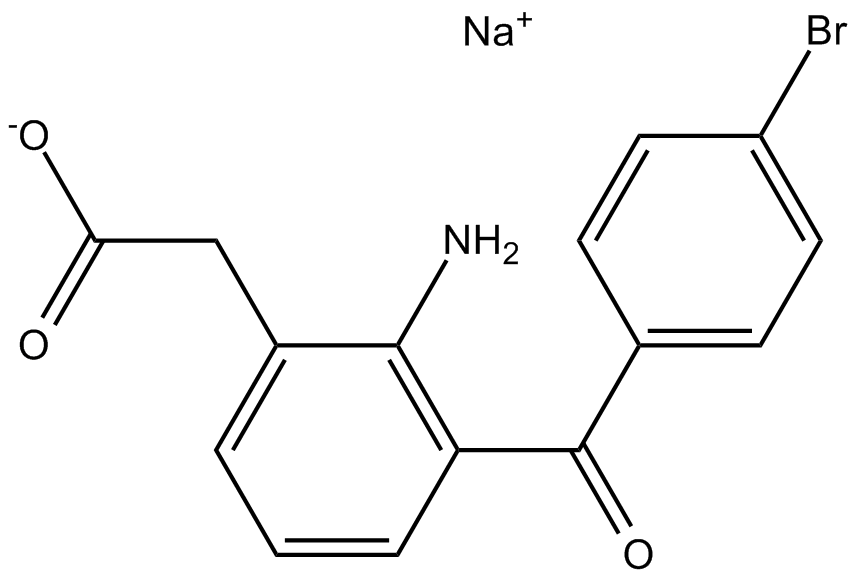 B1684 Bromfenac SodiumTarget: COXSummary: COX inhibitor
B1684 Bromfenac SodiumTarget: COXSummary: COX inhibitor -
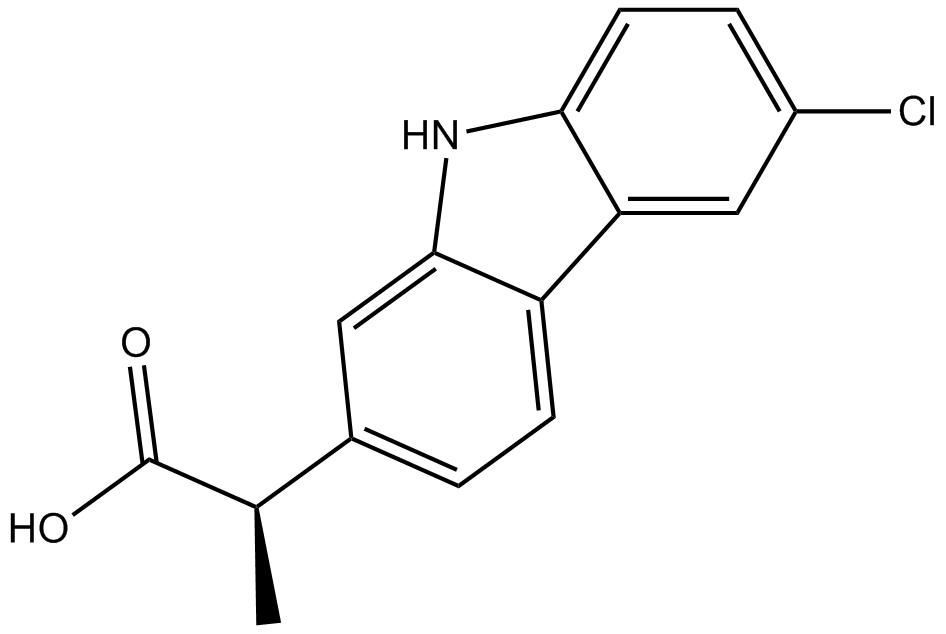 B1690 CarprofenSummary: COX inhibitor
B1690 CarprofenSummary: COX inhibitor -
 B1710 ClofazimineSummary: Tuberculosis drug
B1710 ClofazimineSummary: Tuberculosis drug


